Korean J Gastroenterol.
2017 Dec;70(6):278-282. 10.4166/kjg.2017.70.6.278.
Rumination
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. mipark@ns.kosinmed.or.kr
- KMID: 2398877
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2017.70.6.278
Abstract
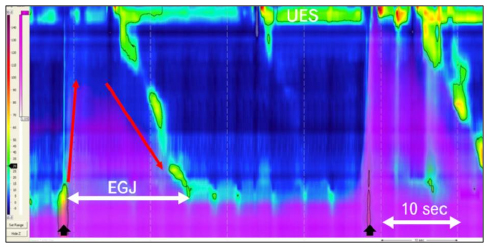
- Rumination syndrome is one of the functional gastroduodenal disorders. Effortless and repetitive regurgitation of recently ingested food from the stomach to the oral cavity followed by rechewing and reswallowing or spitting are the characteristic clinical features. This disorder is believed to be uncommon, but many patients with this disorder are overlooked by their physicians. Rumination might be caused by a reversal of the gastric contents through the esophagogastric junction, which is initiated by an increase in intragastric pressure. The characteristic symptoms are sufficient for the diagnosis of rumination syndrome. Postprandial high resolution esophageal impedance manometry can detect gastric pressurization exceeding 30 mmHg associated with the return of ingested material into the proximal esophagus, which is a pathognomonic finding of rumination syndrome. An extensive explanation of the condition and the underlying mechanism is the first step of the treatment of rumination syndrome. Behavioral therapy through diaphragmatic breathing is the mainstay of treatment. Further studies on the long term effects of biofeedback therapy as well as a proper strategy for refractory rumination syndrome are needed.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. O'Brien MD, Bruce BK, Camilleri M. The rumination syndrome: clinical features rather than manometric diagnosis. Gastroenterology. 1995; 108:1024–1029.2. Fleisher DR. Infant rumination syndrome: report of a case and review of the literature. Am J Dis Child. 1979; 133:266–269.3. Rogers B, Stratton P, Victor J, Kennedy B, Andres M. Chronic regurgitation among persons with mental retardation: a need for combined medical and interdisciplinary strategies. Am J Ment Retard. 1992; 96:522–527.4. Soykan I, Chen J, Kendall BJ, McCallum RW. The rumination syndrome: clinical and manometric profile, therapy, and long-term outcome. Dig Dis Sci. 1997; 42:1866–1872.5. Stanghellini V, Chan FK, Hasler WL, et al. Gastroduodenal disorders. Gastroenterology. 2016; 150:1380–1392.6. Parkman HP, Yates K, Hasler WL, et al. Clinical features of idiopathic gastroparesis vary with sex, body mass, symptom onset, delay in gastric emptying, and gastroparesis severity. Gastroenterology. 2011; 140:101–115.7. Rajindrajith S, Devanarayana NM, Crispus Perera BJ. Rumination syndrome in children and adolescents: a school survey assessing prevalence and symptomatology. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012; 12:163.8. Ryu KH, Lee JS, Lim HH, et al. A case of rumination syndrome with simultaneous repeatetive contractions in ambulatory 24 hour antroduodenal manometry. Korean J Gastrointest Motil. 2001; 7:239–244.9. Lee TH. A case of rumination documented by using high-resolution impedance manometry. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2013; 19:259–260.10. Smout AJ, Breumelhof R. Voluntary induction of transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxations in an adult patient with the rumination syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 1990; 85:1621–1625.11. Gourcerol G, Dechelotte P, Ducrotte P, Leroi AM. Rumination syndrome: when the lower oesophageal sphincter rises. Dig Liver Dis. 2011; 43:571–574.12. Barba E, Burri E, Accarino A, et al. Biofeedback-guided control of abdominothoracic muscular activity reduces regurgitation episodes in patients with rumination. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015; 13:100–106.e1.13. Amarnath RP, Abell TL, Malagelada JR. The rumination syndrome in adults. A characteristic manometric pattern. Ann Intern Med. 1986; 105:513–518.14. Halland M, Parthasarathy G, Bharucha AE, Katzka DA. Diaphragmatic breathing for rumination syndrome: efficacy and mechanisms of action. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2005; 28:384–391.15. Kessing BF, Govaert F, Masclee AA, Conchillo JM. Impedance measurements and high-resolution manometry help to better define rumination episodes. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2011; 46:1310–1315.16. Kessing BE, Bredenoord AJ, Smout AJ. Objective manometric criteria for the rumination syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014; 109:52–59.17. Thumshirn M, Camilleri M, Hanson RB, Williams DE, Schei AJ, Kammer PP. Gastric mechanosensory and lower esophageal sphincter function in rumination syndrome. Am J Physiol. 1998; 275(2 Pt 1):G314–G321.18. Bredenoord AJ, Chial HJ, Camilleri M, Mullan BP, Murray JA. Gastric accommodation and emptying in evaluation of patients with upper gastrointestinal symptoms. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003; 1:264–272.19. Malcolm A, Thumshirn MB, Camilleri M, Williams DE. Rumination syndrome. Mayo Clin Proc. 1997; 72:646–652.20. Khan S, Hyman PE, Cocjin J, Di Lorenzo C. Rumination syndrome in adolescents. J Pediatr. 2000; 136:528–531.21. Mousa HM, Montgomery M, Alioto A. Adolescent rumination syndrome. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2014; 16:398.22. Absah I, Rishi A, Talley NJ, Katzka D, Halland M. Rumination syndrome: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2017; 29:e12954.23. Tack J, Blondeau K, Boecxstaens V, Rommel N. Review article: the pathophysiology, differential diagnosis and management of rumination syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011; 33:782–788.24. Mittal RK, Shaffer HA, Parollisi S, Baggett L. Influence of breathing pattern on the esophagogastric junction pressure and esophageal transit. Am J Physiol. 1995; 269(4 Pt 1):G577–G583.25. Whitehead WE. Biofeedback in the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders. Biofeedback Self Regul. 1978; 3:375–384.26. Levine DF, Wingate DL, Pfeffer JM, Butcher P. Habitual rumination: a benign disorder. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed. 1983; 287:255–256.27. Tucker E, Knowles K, Wright J, Fox MR. Rumination variations: aetiology and classification of abnormal behavioural responses to digestive symptoms based on high-resolution manometry studies. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013; 37:263–274.28. Vijayvargiya P, Iturrino J, Camilleri M, et al. Novel association of rectal evacuation disorder and rumination syndrome: diagnosis, co-morbidities, and treatment. United European Gastroenterol J. 2014; 2:38–46.29. Barba E, Accarino A, Soldevilla A, Malagelada JR, Azpiroz F. Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of biofeedback for the treatment of rumination. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016; 111:1007–1013.30. Lee H, Rhee PL, Park EH, et al. Clinical outcome of rumination syndrome in adults without psychiatric illness: a prospective study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007; 22:1741–1747.31. Blondeau K, Boecxstaens V, Rommel N, et al. Baclofen improves symptoms and reduces postprandial flow events in patients with rumination and supragastric belching. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 10:379–384.32. Oelschlager BK, Chan MM, Eubanks TR, Pope CE 2nd, Pellegrini CA. Effective treatment of rumination with Nissen fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg. 2002; 6:638–644.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Relationship Among Rumination, Coping Strategies, and Subjective Well-being in Chinese Patients With Breast Cancer: A Cross-sectional study
- Childhood Trauma and Non-Suicidal Self-Injury Among Chinese Adolescents: The Chain-Mediated Role of Alexithymia and Rumination
- A Neurofeedback Protocol for Executive Function to Reduce Depression and Rumination: A Controlled Study
- Attachment Style, Complicated Grief and Post-Traumatic Growth in Traumatic Loss: The Role of Intrusive and Deliberate Rumination
- Exposure Frequency of Job Related Trauma Types and PTSD Symptoms of Firefighters: The Moderating Effect of Anger Rumination