Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2017 Nov;21(4):247-251. 10.14701/ahbps.2017.21.4.247.
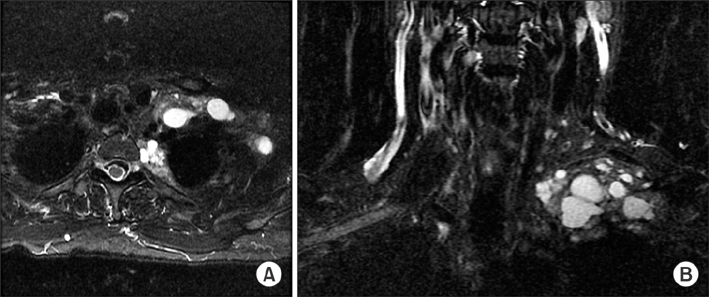
Metastatic adenocarcinoma of the pancreas presents as metastases to the axillary/supraclavicular region as the first sign of the disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of General Surgery, Geisinger Wyoming Valley Medical Center, Wilkes-Barre, PA, USA.
- 2Department of Hematology/Oncology, Geisinger Wyoming Valley Medical Center, Wilkes-Barre, PA, USA.
- 3Department of Pathology, Geisinger Wyoming Valley Medical Center, Wilkes-Barre, PA, USA.
- 4Department of Surgical Oncology, Geisinger Wyoming Valley Medical Center, Wilkes-Barre, PA, USA. jcoxenberg@geisinger.edu
- KMID: 2397808
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2017.21.4.247
Abstract
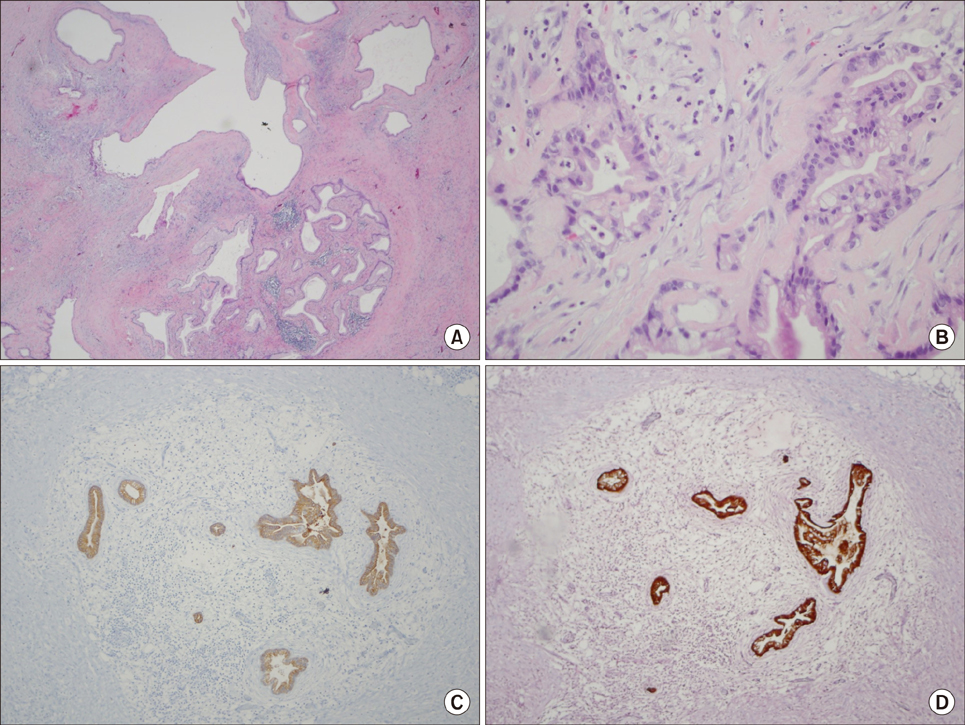
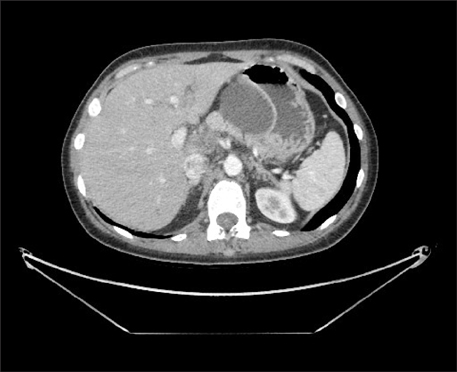
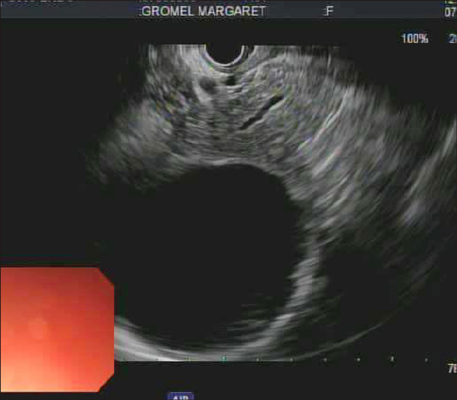
- Mucinous tumors of the pancreas are rare and the diagnosis of invasive carcinoma can be a dilemma. While metastatic disease from mucinous cystadenocarcinoma (MCAC) and invasive intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMN) have been reported, no extraperitoneal mucinous cystic metastatic disease has been described. When metastatic, the overall survival rates for invasive adenocarcinoma, mucinous cystadenocarcinoma (MCAC) and invasive intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMN) are similar. The best improvement in the overall and progression free survival has been demonstrated with FOLFIRINOX (folinic acid - fluorouracil - irinotecan - oxaliplatin) for metastatic adenocarcinoma and Gemcitabine based regimens for MCAC. However, the variable responses of metastatic mucinous lesions have been observed and the overall prognosis remains poor. We describe a case of a patient who presented with metastatic adenocarcinoma of the pancreas as cystic masses in the supraclavicular and axillary regions. Additionally, this patient was initially treated with FOLFIRINOX and continues to have stable primary and metastatic disease after 18 months from the diagnosis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Crippa S, Salvia R, Warshaw AL, Domínguez I, Bassi C, Falconi M, et al. Mucinous cystic neoplasm of the pancreas is not an aggressive entity: lessons from 163 resected patients. Ann Surg. 2008; 247:571–579.2. Di Marco M, Vecchiarelli S, Macchini M, Pezzilli R, Santini D, Casadei R, et al. Preoperative gemcitabine and oxaliplatin in a patient with ovarian metastasis from pancreatic cystadenocarcinoma. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2012; 6:530–537.3. Limmathurotsakul D, Rerknimitr P, Korkij W, Noppakun N, Kullavanijaya P, Rerknimitr R. Metastatic mucinous cystic adenocarcinoma of the pancreas presenting as Sister Mary Joseph's nodule. JOP. 2007; 8:344–349.4. Obayashi K, Ohwada S, Sunose Y, Yamamoto K, Igarashi R, Hamada K, et al. Remarkable effect of gemcitabine-oxaliplatin (GEMOX) therapy in a patient with advanced metastatic mucinous cystic neoplasm of the pancreas. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2008; 35:1915–1917.5. Shamsi K, Deckers F, De Schepper A, Hauben E, Van Marck E. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the pancreas with liver metastases. An unusual presentation of a rare tumor. Ann Radiol (Paris). 1993; 36:328–331.6. Woo SM, Ryu JK, Lee SH, Yoo JW, Park JK, Kim YT, et al. Survival and prognosis of invasive intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: comparison with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreas. 2008; 36:50–55.7. Björk Werner J, Sturesson C, Dawiskiba S, Andersson R. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the pancreas - outcome following different modes of treatment. Ann Gastroenterol. 2011; 24:213–217.8. Conroy T, Desseigne F, Ychou M, Bouché O, Guimbaud R, Bécouarn Y, et al. FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:1817–1825.9. Tanaka M, Chari S, Adsay V, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Falconi M, Shimizu M, et al. International consensus guidelines for management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms and mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Pancreatology. 2006; 6:17–32.10. Lin F, Chen ZE, Wang HL. Utility of immunohistochemistry in the pancreatobiliary tract. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2015; 139:24–38.11. Goh BK, Tan YM, Chung YF, Chow PK, Cheow PC, Wong WK, et al. A review of mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas defined by ovarian-type stroma: clinicopathological features of 344 patients. World J Surg. 2006; 30:2236–2245.12. Le Borgne J, de Calan L, Partensky C. French Surgical Association. Cystadenomas and cystadenocarcinomas of the pancreas: a multiinstitutional retrospective study of 398 cases. Ann Surg. 1999; 230:152–161.13. Wood D, Silberman AW, Heifetz L, Memsic L, Shabot MM. Cystadenocarcinoma of the pancreas: neo-adjuvant therapy and CEA monitoring. J Surg Oncol. 1990; 43:56–60.14. Doberstein C, Kirchner R, Gordon L, Silberman AW, Morgenstern L, Shapiro S. Cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Mt Sinai J Med. 1990; 57:102–105.15. Delcore R, Thomas JH, Forster J, Hermreck AS. Characteristics of cystic neoplasms of the pancreas and results of aggressive surgical treatment. Am J Surg. 1992; 164:437–442.16. Yip D, Karapetis C, Strickland A, Steer CB, Goldstein D. Chemotherapy and radiotherapy for inoperable advanced pancreatic cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006; (3):CD002093.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Metastatic tumors in supraclavicular lymph node: pathological analysis of 125 cases
- A Case of Umbilical Metastasis as the Presenting Sign of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
- A Case of Cutaneous Metastases to the Face and Scalp from Colon Adenocarcinoma
- A Case of Skin Metastasis Manifested as a Presenting Sign of Pancreatic Tail Cancer
- Multiple Cutaneous Edema and Infiltration of Signet-ring Cells in the Lymphatics as an Initial Manifestation of Metastatic Gastric Adenocarcinoma