Int J Thyroidol.
2017 Nov;10(2):82-88. 10.11106/ijt.2017.10.2.82.
Secular Trends for Diagnostic Motives and Environmental Risk Factors in Thyroid Cancer Using Questionnaire Survey
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Center for Thyroid Cancer, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea. waterfol@ncc.re.kr
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Metropolitan Government Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Korea National Institute of Health, Cheongju, Korea.
- KMID: 2396811
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11106/ijt.2017.10.2.82
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
We analyzed the clinicopathologic differences of thyroid cancer by diagnosis periods, diagnostic motives, residence history and clinical risk factors in thyroid cancer patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Total 1599 thyroid cancer patients who answered the questionnaires about family history of thyroid cancer, residence history including duration of residence and location were enrolled from two hospitals, Seoul National University Hospital and National Cancer Center in Korea. Demographics and environmental information were collected via questionnaires and clinical data were reviewed via electronic medical records.
RESULTS
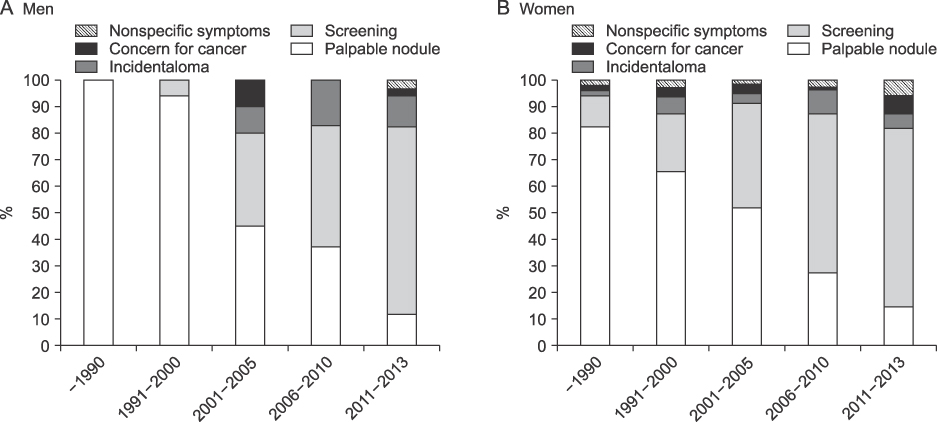
More thyroid cancer has been diagnosed in 2011 to 2013 by screening test without specific symptom than before 1990. The size of cancer at diagnosis was significantly smaller and multifocal tumor was more frequently found in 2011 to 2013 than before 1990 as well. The tumors of obese or overweight patients tended to harbor extrathyroidal extension and lymph node metastasis than normal weight subjects with statistical significance. However, there were no differences in clinicopathologic characteristics according to residence and smoking history.
CONCLUSION
In this study, there were some different clinicopathologic characteristics according to the diagnosis era, diagnostic motives, family history of thyroid cancer and body mass index.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Survival Comparison of Incidentally Found versus Clinically Detected Thyroid Cancers: An Analysis of a Nationwide Cohort Study
Shinje Moon, Eun Kyung Lee, Hoonsung Choi, Sue K. Park, Young Joo Park
Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(1):81-92. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2023.1668.
Reference
-
1. Jung KW, Won YJ, Oh CM, Kong HJ, Lee DH, Lee KH. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2014. Cancer Res Treat. 2017; 49(2):292–305.
Article2. Pellegriti G, Frasca F, Regalbuto C, Squatrito S, Vigneri R. Worldwide increasing incidence of thyroid cancer: update on epidemiology and risk factors. J Cancer Epidemiol. 2013; 2013:965212.
Article3. Kilfoy BA, Zheng T, Holford TR, Han X, Ward MH, Sjodin A, et al. International patterns and trends in thyroid cancer incidence, 1973-2002. Cancer Causes Control. 2009; 20(5):525–531.
Article4. Davies L, Welch HG. Increasing incidence of thyroid cancer in the United States, 1973-2002. JAMA. 2006; 295(18):2164–2167.
Article5. Liu S, Semenciw R, Ugnat AM, Mao Y. Increasing thyroid cancer incidence in Canada, 1970-1996: time trends and age-period-cohort effects. Br J Cancer. 2001; 85(9):1335–1339.
Article6. Nikiforov YE, Fagin JA. Risk factors for thyroid cancer. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 1997; 8(1):20–25.
Article7. Ahn HY, Park YJ. Incidence and clinical characteristics of thyroid cancer in Korea. Korean J Med. 2009; 77(5):537–542.8. Feldt-Rasmussen U. Iodine and cancer. Thyroid. 2001; 11(5):483–486.
Article9. Nagataki S, Nystrom E. Epidemiology and primary prevention of thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 2002; 12(10):889–896.
Article10. Lind P, Langsteger W, Molnar M, Gallowitsch HJ, Mikosch P, Gomez I. Epidemiology of thyroid diseases in iodine sufficiency. Thyroid. 1998; 8(12):1179–1183.
Article11. Franceschi S. Iodine intake and thyroid carcinoma--a potential risk factor. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 1998; 106:Suppl 3. S38–S44.12. Cao LZ, Peng XD, Xie JP, Yang FH, Wen HL, Li S. The relationship between iodine intake and the risk of thyroid cancer: A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017; 96(20):e6734.13. Lee JH, Hwang Y, Song RY, Yi JW, Yu HW, Kim SJ, et al. Relationship between iodine levels and papillary thyroid carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Head Neck. 2017; 39(8):1711–1718.
Article14. Lee HS, Min H. Iodine intake and tolerable upper intake level of iodine for Koreans. Korean J Nutr. 2011; 44(1):82–91.
Article15. Park YJ, Ahn HY, Choi HS, Kim KW, Park DJ, Cho BY. The long-term outcomes of the second generation of familial nonmedullary thyroid carcinoma are more aggressive than sporadic cases. Thyroid. 2012; 22(4):356–362.
Article16. Mazeh H, Benavidez J, Poehls JL, Youngwirth L, Chen H, Sippel RS. In patients with thyroid cancer of follicular cell origin, a family history of nonmedullary thyroid cancer in one first-degree relative is associated with more aggressive disease. Thyroid. 2012; 22(1):3–8.
Article17. D'Avanzo B, La Vecchia C, Franceschi S, Negri E, Talamini R. History of thyroid diseases and subsequent thyroid cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1995; 4(3):193–199.18. Cho YA, Kim J. Thyroid cancer risk and smoking status: a meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control. 2014; 25(9):1187–1195.
Article19. Iribarren C, Haselkorn T, Tekawa IS, Friedman GD. Cohort study of thyroid cancer in a San Francisco Bay area population. Int J Cancer. 2001; 93(5):745–750.
Article20. Engeland A, Tretli S, Akslen LA, Bjorge T. Body size and thyroid cancer in two million Norwegian men and women. Br J Cancer. 2006; 95(3):366–370.
Article21. Dal Maso L, La Vecchia C, Franceschi S, Preston-Martin S, Ron E, Levi F, et al. A pooled analysis of thyroid cancer studies. V. Anthropometric factors. Cancer Causes Control. 2000; 11(2):137–144.22. Gallagher EJ, LeRoith D. Obesity and diabetes: the increased risk of cancer and cancer-related mortality. Physiol Rev. 2015; 95(3):727–748.
Article23. Braun S, Bitton-Worms K, LeRoith D. The link between the metabolic syndrome and cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 2011; 7(7):1003–1015.
Article24. Tsugane S, Inoue M. Insulin resistance and cancer: epidemiological evidence. Cancer Sci. 2010; 101(5):1073–1079.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Epidemiological characteristics of breast cancer in Koreans
- Dietary Factors and the Risk of Thyroid Cancer: A Review
- Secular trends of body sizes in Korean children and adolescents: from 1965 to 2010
- Diagnostic Approaches to Patients with Thyroid Nodules
- Impact of dietary risk factors on cardiometabolic and cancer mortality burden among Korean adults: results from nationally representative repeated cross-sectional surveys 1998–2016