Korean J Ophthalmol.
2017 Dec;31(6):524-532. 10.3341/kjo.2015.0143.
Retinopathy of Prematurity-assist: Novel Software for Detecting Plus Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Vitreoretinal Surgery, Farabi Eye Hospital, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. riazifahimi@yahoo.com
- 2Department of Computer Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Mashhad, Iran.
- 3Department of Pediatric Opthalmology, Farabi Eye Hospital, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
- KMID: 2396703
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2015.0143
Abstract
- PURPOSE
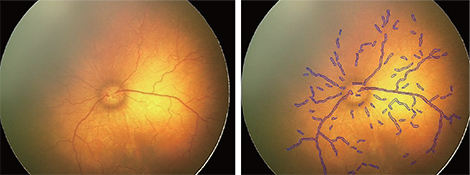
To design software with a novel algorithm, which analyzes the tortuosity and vascular dilatation in fundal images of retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) patients with an acceptable accuracy for detecting plus disease.
METHODS
Eighty-seven well-focused fundal images taken with RetCam were classified to three groups of plus, non-plus, and pre-plus by agreement between three ROP experts. Automated algorithms in this study were designed based on two methods: the curvature measure and distance transform for assessment of tortuosity and vascular dilatation, respectively as two major parameters of plus disease detection.
RESULTS
Thirty-eight plus, 12 pre-plus, and 37 non-plus images, which were classified by three experts, were tested by an automated algorithm and software evaluated the correct grouping of images in comparison to expert voting with three different classifiers, k-nearest neighbor, support vector machine and multilayer perceptron network. The plus, pre-plus, and non-plus images were analyzed with 72.3%, 83.7%, and 84.4% accuracy, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
The new automated algorithm used in this pilot scheme for diagnosis and screening of patients with plus ROP has acceptable accuracy. With more improvements, it may become particularly useful, especially in centers without a skilled person in the ROP field.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Blencowe H, Cousens S, Oestergaard MZ, et al. National, regional, and worldwide estimates of preterm birth rates in the year 2010 with time trends since 1990 for selected countries: a systematic analysis and implications. Lancet. 2012; 379:2162–2172.2. Gilbert C, Foster A. Childhood blindness in the context of VISION 2020: the right to sight. Bull World Health Organ. 2001; 79:227–232.3. Gilbert C, Fielder A, Gordillo L, et al. Characteristics of infants with severe retinopathy of prematurity in countries with low, moderate, and high levels of development: implications for screening programs. Pediatrics. 2005; 115:e518–e525.4. Early Treatment for Retinopathy of Prematurity Cooperative Group. Revised indications for the treatment of retinopathy of prematurity: results of the early treatment for retinopathy of prematurity randomized trial. Arch Ophthalmol. 2003; 121:1684–1694.5. Davitt BV, Wallace DK. Plus disease. Surv Ophthalmol. 2009; 54:663–670.6. Freedman SF, Kylstra JA, Capowski JJ, et al. Observer sensitivity to retinal vessel diameter and tortuosity in retinopathy of prematurity: a model system. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1996; 33:248–254.7. Chiang MF, Jiang L, Gelman R, et al. Interexpert agreement of plus disease diagnosis in retinopathy of prematurity. Arch Ophthalmol. 2007; 125:875–880.8. Wallace DK, Quinn GE, Freedman SF, Chiang MF. Agreement among pediatric ophthalmologists in diagnosing plus and pre-plus disease in retinopathy of prematurity. J AAPOS. 2008; 12:352–356.9. Wilson CM, Wong K, Ng J, et al. Digital image analysis in retinopathy of prematurity: a comparison of vessel selection methods. J AAPOS. 2012; 16:223–228.10. Pourreza R, Banaee T, Pourreza H, Kakhki RD. A radon transform based approach for extraction of blood vessels in conjunctival images. In : Gelbukh A, Morales EF, editors. MICAI 2008: advances in artificial intelligence. Berlin: Springer Berlin Heidelberg;2008. p. 948–956.11. Guo Z, Hall RW. Parallel thinning with two-subiteration algorithms. Commun ACM. 1989; 32:359–373.12. Frette OI, Virnovsky G, Silin D. Estimation of the curvature of an interface from a digital 2D image. Comput Mater Sci. 2009; 44:867–875.13. Maurer CR, Qi R, Raghavan V. A linear time algorithm for computing exact Euclidean distance transforms of binary images in arbitrary dimensions. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2003; 25:265–270.14. Shah DN, Wilson CM, Ying GS, et al. Comparison of expert graders to computer-assisted image analysis of the retina in retinopathy of prematurity. Br J Ophthalmol. 2011; 95:1442–1445.15. Chiang MF, Gelman R, Martinez-Perez ME, et al. Image analysis for retinopathy of prematurity diagnosis. J AAPOS. 2009; 13:438–445.16. Chiang MF, Gelman R, Jiang L, et al. Plus disease in retinopathy of prematurity: an analysis of diagnostic performance. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 105:73–84.17. Martinez-Perez ME, Hughes AD, Stanton AV, et al. Retinal vascular tree morphology: a semi-automatic quantification. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2002; 49:912–917.18. Swanson C, Cocker KD, Parker KH, et al. Semiautomated computer analysis of vessel growth in preterm infants without and with ROP. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003; 87:1474–1477.19. Gelman R, Martinez-Perez ME, Vanderveen DK, et al. Diagnosis of plus disease in retinopathy of prematurity using retinal image multiscale analysis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005; 46:4734–4738.20. Thyparampil PJ, Park Y, Martinez-Perez ME, et al. Plus disease in retinopathy of prematurity: quantitative analysis of vascular change. Am J Ophthalmol. 2010; 150:468–475.e2.21. Wallace DK. Computer-assisted quantification of vascular tortuosity in retinopathy of prematurity (an American Ophthalmological Society thesis). Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 105:594–615.22. Cabrera MT, Freedman SF, Kiely AE, et al. Combining ROPtool measurements of vascular tortuosity and width to quantify plus disease in retinopathy of prematurity. J AAPOS. 2011; 15:40–44.23. Bullitt E, Gerig G, Pizer SM, et al. Measuring tortuosity of the intracerebral vasculature from MRA images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2003; 22:1163–1171.24. Aylward S, Bullitt E, Pizer S, Eberly D. Intensity ridge and widths for tubular object segmentation and description. Proceedings of the Workshop on Mathematical Methods in Biomedical Image Analysis. 1996; San Francisco, USA. Los Alamitos: IEEE Computer Society Press;1996.25. Kiely AE, Wallace DK, Freedman SF, Zhao Z. Computer-assisted measurement of retinal vascular width and tortuosity in retinopathy of prematurity. Arch Ophthalmol. 2010; 128:847–852.26. Wilson CM, Cocker KD, Moseley MJ, et al. Computerized analysis of retinal vessel width and tortuosity in premature infants. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008; 49:3577–3585.27. Shah DN, Wilson CM, Ying GS, et al. Semiautomated digital image analysis of posterior pole vessels in retinopathy of prematurity. J AAPOS. 2009; 13:504–506.28. Ghodasra DH, Karp KA, Ying GS, et al. Risk stratification of preplus retinopathy of prematurity by semiautomated analysis of digital images. Arch Ophthalmol. 2010; 128:719–723.29. Wittenberg LA, Jonsson NJ, Chan RV, Chiang MF. Computer-based image analysis for plus disease diagnosis in retinopathy of prematurity. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2012; 49:11–19.30. Wallace DK, Zhao Z, Freedman SF. A pilot study using “ROPtool” to quantify plus disease in retinopathy of prematurity. J AAPOS. 2007; 11:381–387.31. Grisan E, Foracchia M, Ruggeri A. A novel method for the automatic grading of retinal vessel tortuosity. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2008; 27:310–319.32. Wilson CM, Ells AL, Fielder AR. The challenge of screening for retinopathy of prematurity. Clin Perinatol. 2013; 40:241–259.33. Keck KM, Kalpathy-Cramer J, Ataer-Cansizoglu E, et al. Plus disease diagnosis in retinopathy of prematurity: vascular tortuosity as a function of distance from optic disk. Retina. 2013; 33:1700–1707.34. Cheung CS, Butty Z, Tehrani NN, Lam WC. Computer-assisted image analysis of temporal retinal vessel width and tortuosity in retinopathy of prematurity for the assessment of disease severity and treatment outcome. J AAPOS. 2011; 15:374–380.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Cryotherapy for Retinopathy of Prematurity
- Letter to the Editor: Effect of Intravitreal Bevacizumab Injection on Retinopathy of Prematurity
- The Effect of Cryotherapy and Laser Photocoagulation for the Retinopathy of Prematurity
- The Effect of Cryotherapy on Stage 3 Retinopathy of Prematurity
- Treatment of Acute Retinopathy of Prematurity with Argon Indirect Laser Ophthalmoscope 2nd Report