Brain Tumor Res Treat.
2017 Oct;5(2):70-76. 10.14791/btrt.2017.5.2.70.
Ependymomas: Prognostic Factors and Outcome Analysis in a Retrospective Series of 33 Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Chonnam National University Research Institute of Medical Sciences, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital & Medical School, Hwasun, Korea. jung-ty@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Chonnam National University Research Institute of Medical Sciences, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital & Medical School, Hwasun, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Chonnam National University Research Institute of Medical Sciences, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital & Medical School, Hwasun, Korea.
- KMID: 2396450
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2017.5.2.70
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the prognostic factors and outcomes in patients with ependymoma to management plans.
METHODS
Between 1997 and 2013, 33 patients with 25 ependymomas (WHO grade II) and eight anaplastic ependymomas (WHO grade III) were pathologically diagnosed. Six were pediatric patients (mean age, 6.15 years; range, 1.3-11 years), while 27 were adults (mean age, 47.5 years; range, 19-70 years). Of those, there were 12 adult patients with totally resected ependymomas without anaplastic pathology and adjuvant treatment. Prognostic factors were assessed in ependymoma patients. Prognostic factors were studied using Kaplan-Meier estimates in subgroups.
RESULTS
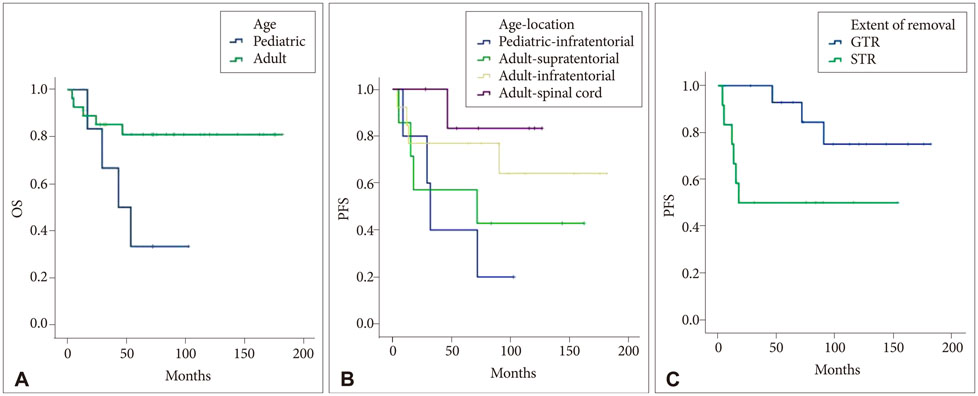
For six pediatric patients, the progression-free survival (PFS) was 43.7±13.5 months, and the overall survival (OS) was 58.1±13.7 months. For 27 adult patients, the PFS was 125.6±14.3 months, and the OS was 151.2±12.5 months. Age demonstrated a statistically significant effect on PFS (p=0.03) and OS (p=0.03). In adult ependymomas, the extent of tumor removal significantly affected PFS (p=0.03) and trended towards an effect on OS (p=0.06). Out of 12 patients with totally resected ependymomas without anaplastic pathology and adjuvant treatment, one patient showed tumor recurrence during follow-up (mean, 93.5 months; range, 27.9-162.7 months).
CONCLUSION
Adult patients with ependymomas were found to have better survival rates compared to pediatric patients. We suggest that totally resected adult ependymomas without anaplastic pathology could be observed without any adjuvant treatment, regardless of the tumor location.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Treatment Decisions of World Health Organization Grade II and III Ependymomas in Molecular Era
Tae-Young Jung, Shin Jung, Hoon Kook, Hee-Jo Baek
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2018;61(3):312-318. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2018.0003.
Reference
-
1. Oya N, Shibamoto Y, Nagata Y, Negoro Y, Hiraoka M. Postoperative radiotherapy for intracranial ependymoma: analysis of prognostic factors and patterns of failure. J Neurooncol. 2002; 56:87–94.2. Metellus P, Barrie M, Figarella-Branger D, et al. Multicentric French study on adult intracranial ependymomas: prognostic factors analysis and therapeutic considerations from a cohort of 152 patients. Brain. 2007; 130(Pt 5):1338–1349.
Article3. Paulino AC, Wen BC, Buatti JM, et al. Intracranial ependymomas: an analysis of prognostic factors and patterns of failure. Am J Clin Oncol. 2002; 25:117–122.4. Mansur DB, Perry A, Rajaram V, et al. Postoperative radiation therapy for grade II and III intracranial ependymoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005; 61:387–391.
Article5. Tamburrini G, D'Ercole M, Pettorini BL, Caldarelli M, Massimi L, Di Rocco C. Survival following treatment for intracranial ependymoma: a review. Childs Nerv Syst. 2009; 25:1303–1312.
Article6. Shu HK, Sall WF, Maity A, et al. Childhood intracranial ependymoma: twenty-year experience from a single institution. Cancer. 2007; 110:432–441.7. van Veelen-Vincent ML, Pierre-Kahn A, Kalifa C, et al. Ependymoma in childhood: prognostic factors, extent of surgery, and adjuvant therapy. J Neurosurg. 2002; 97:827–835.
Article8. Metellus P, Figarella-Branger D, Guyotat J, et al. Supratentorial ependymomas: prognostic factors and outcome analysis in a retrospective series of 46 adult patients. Cancer. 2008; 113:175–185.
Article9. Merchant TE, Li C, Xiong X, Kun LE, Boop FA, Sanford RA. Conformal radiotherapy after surgery for paediatric ependymoma: a prospective study. Lancet Oncol. 2009; 10:258–266.
Article10. Gatta G, Botta L, Rossi S, et al. Childhood cancer survival in Europe 1999-2007: results of EUROCARE-5--a population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2014; 15:35–47.
Article11. McGuire CS, Sainani KL, Fisher PG. Both location and age predict survival in ependymoma: a SEER study. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2009; 52:65–69.
Article12. Ward S, Harding B, Wilkins P, et al. Gain of 1q and loss of 22 are the most common changes detected by comparative genomic hybridisation in paediatric ependymoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2001; 32:59–66.
Article13. Kurt E, Zheng PP, Hop WC, et al. Identification of relevant prognostic histopathologic features in 69 intracranial ependymomas, excluding myxopapillary ependymomas and subependymomas. Cancer. 2006; 106:388–395.
Article14. Pajtler KW, Witt H, Sill M, et al. Molecular classification of ependymal tumors across all CNS compartments, histopathological grades, and age groups. Cancer Cell. 2015; 27:728–743.
Article15. Korshunov A, Neben K, Wrobel G, et al. Gene expression patterns in ependymomas correlate with tumor location, grade, and patient age. Am J Pathol. 2003; 163:1721–1727.
Article16. Gajjar A, Packer RJ, Foreman NK, et al. Children's Oncology Group's 2013 blueprint for research: central nervous system tumors. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2013; 60:1022–1026.
Article17. Paulino AC. Radiotherapeutic management of intracranial ependymoma. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2002; 19:295–308.
Article18. Timmermann B, Kortmann RD, Kühl J, et al. Combined postoperative irradiation and chemotherapy for anaplastic ependymomas in childhood: results of the German prospective trials HIT 88/89 and HIT 91. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000; 46:287–295.
Article19. Metellus P, Guyotat J, Chinot O, et al. Adult intracranial WHO grade II ependymomas: long-term outcome and prognostic factor analysis in a series of 114 patients. Neuro Oncol. 2010; 12:976–984.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy of Two-Stage Surgery for Spinal Cord Ependymomas
- Prognostic Factors and Treatment Outcome for Thymoma
- Analysis of Prognostic Factors for Chronic Subdural Hematoma
- Clinicoradiologic Characteristics of Intradural Extramedullary Conventional Spinal Ependymoma
- Prognostic Factors of Chronic Subdural Hematoma