Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab.
2017 Sep;22(3):170-175. 10.6065/apem.2017.22.3.170.
Impact of targeted education on managing warning and error signals by children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes using the Accu-Chek Combo Insulin Pump System
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Paediatric Endocrinology, Mafraq Hospital, AbuDhabi, United Arab Emirates. adeeb@mafraqhospital.ae
- KMID: 2396136
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6065/apem.2017.22.3.170
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Insulin pumps are widely used in diabetes. They are equipped with safety alarms to alert users. Pump manuals contain alarm codes and how to troubleshoot them. However, these manuals are lengthy and difficult to use, particularly in emergencies. We aim to assess the impact of targeted education on warnings and errors in improving competency to troubleshoot the alarms.
METHODS
Twenty-one patients, with a median age of 13, were recruited over a 5-month period. Each patient had 2 study visits. The frequencies and types of alarms were recorded, and patients were given a summary sheet that outlined common alarms encountered and troubleshooting tips. In visit 2, the frequencies and types of alarms were compared to those of visit 1. The patients were asked to fill a questionnaire and to rate the education session given in visit 1, their level of competency in decrypting alarm codes, and their promptness in responding to alarms.
RESULTS
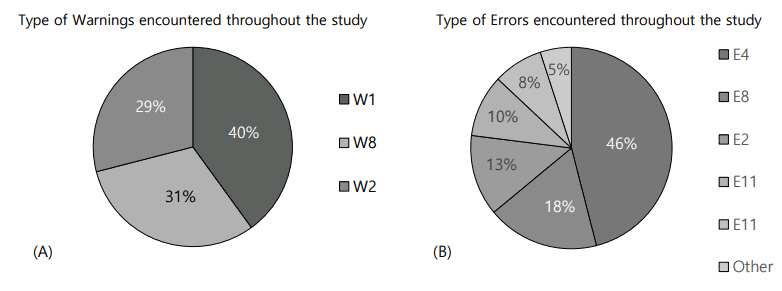
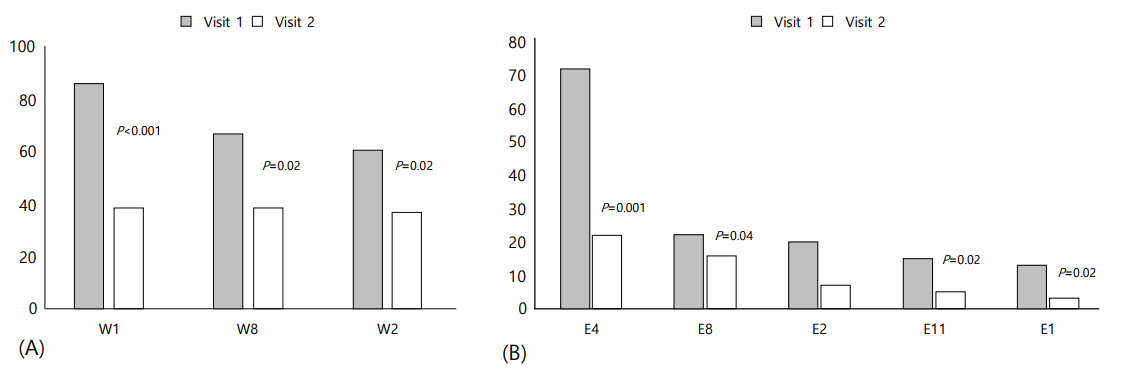
Low cartridge (W1), low battery (W2), and bolus cancelled (W8) were the commonest warnings. The most noted errors were occlusion (E4), power interruption (E8), empty battery (E2), set not primed (E11), and cartridge empty (E1). The numbers of warning and error signals markedly decreased after targeted education (P < 0.05). The ability in decrypting warning signals significantly improved (P=0.02), and the frequency of response to pump alarms significantly increased (P=0.001).
CONCLUSION
Certain warnings and errors are more common than others in insulin pumps. Targeted education is useful in improving competency and response of patients in managing pump alarms.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Bangstad HJ, Danne T, Deeb LC, Jarosz-Chobot P, Urakami T, Hanas R, et al. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2006-2007. Insulin treatment. Pediatr Diabetes. 2007; 8:88–102.2. Danne T, von Schütz W, Lange K, Nestoris C, Datz N, Kordonouri O. Current practice of insulin pump therapy in children and adolescents: the Hannover recipe. Pediatr Diabetes. 2006; 7 Suppl 4:25–31.3. McMahon SK, Airey FL, Marangou DA, McElwee KJ, Carne CL, Clarey AJ, et al. Insulin pump therapy in children and adolescents: improvements in key parameters of diabetes management including quality of life. Diabet Med. 2005; 22:92–6.
Article4. Liberman A, Buckingham B, Phillip M. Diabetes technology and the human factor. Int J Clin Pract Suppl. 2011; (170):83–90.
Article5. O'Connell MA, Donath S, Cameron FJ. Poor adherence to integral daily tasks limits the efficacy of CSII in youth. Pediatr Diabetes. 2011; 12:556–9.6. Grunberger G, Abelseth JM, Bailey TS, Bode BW, Handelsman Y, Hellman R, et al. Consensus Statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists/American College of Endocrinology insulin pump management task force. Endocr Pract. 2014; 20:463–89.
Article7. Asma D, Salima A, Hana Y, Layla A, Shaker S, Mary T. Improving glycemic control in children with diabetes through implementation of multidisciplinary team approach. J Endocrinol Diab. 2016; 3:1–4.
Article8. Schmid V, Hohberg C, Borchert M, Forst T, Pfützner A. Pilot study for assessment of optimal frequency for changing catheters in insulin pump therapy-trouble starts on day 3. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2010; 4:976–82.
Article9. Kerr D, Morton J, Whately-Smith C, Everett J, Begley JP. Laboratory-based non-clinical comparison of occlusion rates using three rapid-acting insulin analogs in continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion catheters using low flow rates. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2008; 2:450–5.
Article10. Deeb A, Abu-Awad S, Abood S, El-Abiary M, Al-Jubeh J, Yousef H, et al. Important determinants of diabetes control in insulin pump therapy in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2015; 17:166–70.
Article11. Weissberg-Benchell J, Antisdel-Lomaglio J, Seshadri R. Insulin pump therapy: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26:1079–87.
Article12. van Bon AC, Bode BW, Sert-Langeron C, DeVries JH, Charpentier G. Insulin glulisine compared to insulin aspart and to insulin lispro administered by continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in patients with type 1 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2011; 13:607–14.
Article13. Zisser H. Quantifying the impact of a short-interval interruption of insulin-pump infusion sets on glycemic excursions. Diabetes Care. 2008; 31:238–9.
Article14. Gibney M, Xue Z, Swinney M, Bialonczyk D, Hirsch L. Reduced silent occlusions with a novel catheter infusion set (BD FlowSmart): results from two open-label comparative studies. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2016; 18:136–43.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effective Use of Insulin Pump in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
- Evaluation of ACCU-CHEK(R) Inform II Blood Glucose Meter and ACCU-CHEK(R) Performa Strip
- Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Adolescents and Young Adults
- Pharmacothearpy of Adolescents with Diabetes
- 2024 Policy Revision for Support of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Patients