Yonsei Med J.
2008 Feb;49(1):155-158.
Rituximab-CHOP Induced Interstitial Pneumonitis in Patients with Disseminated Extranodal Marginal Zone B Cell Lymphoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea. brightree@lycos.co.kr
- 2Department of Diagnostic Radiology, College of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- 3Gyeongsang Institute of Health Science, Jinju, Korea.
- 4Gyeongnam Regional Cancer Center, Jinju, Korea.
Abstract
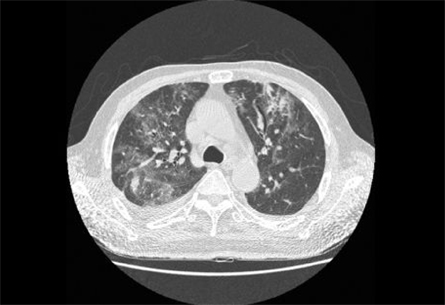
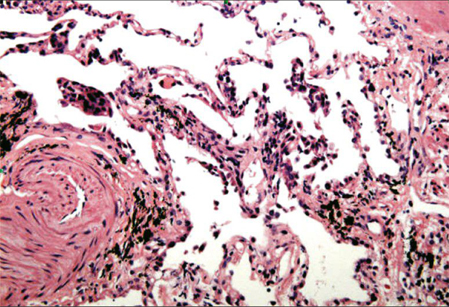
- A 69-year-old male was diagnosed in February 2004 with stage IV extranodal marginal zone B cell lymphoma involving the mediastinal nodes, lung parenchyma and bone marrow with high LDH. Shortness of breath developed following the 5th course of Rituximab-CHOP chemotherapy (cyclophosphamide, Vincristine, Doxorubicin, Prednisolone). Bronchoscopy guided transbronchial lung biopsy revealed interstitial thickening and type II pneumocyte activation, compatible with interstitial pneumonitis. After treatment with prednisolone a complete resolution of the dyspnea was observed. The patient was well on routine follow-up at the outpatient clinic, with no progression of lymphoma or interstitial pneumonitis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Antibodies, Monoclonal/*adverse effects/*therapeutic use
Antineoplastic Combined Chemotherapy Protocols/*adverse effects/*therapeutic use
Biopsy
Cyclophosphamide/adverse effects/therapeutic use
Doxorubicin/adverse effects/therapeutic use
Humans
Lung Diseases, Interstitial/*chemically induced/*pathology/radiography/surgery
Lymphoma, B-Cell, Marginal Zone/*drug therapy
Male
Prednisone/adverse effects/therapeutic use
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Vincristine/adverse effects/therapeutic use
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hiddemann W, Kneba M, Dreyling M, Schmitz N, Lengfelder E, Schmits R, et al. Frontline therapy with rituximab added to the combination of cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP) significantly improves the outcome for patients with advanced-stage follicular lymphoma compared with therapy with CHOP alone: results of a prospective randomized study of the German Low-Grade Lymphoma Study Group. Blood. 2005. 106:3725–3732.
Article2. Ahmed S, Kussick SJ, Siddiqui AK, Bhuiya TA, Khan A, Sarewitz S, et al. Bronchial-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma: a clinical study of a rare disease. Eur J Cancer. 2004. 40:1320–1326.
Article3. Conconi A, Martinelli G, Thieblemont C, Ferreri AJ, Devizzi L, Peccatori F, et al. Clinical activity of rituximab in extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of MALT type. Blood. 2003. 102:2741–2745.
Article4. Coiffier B. State-of-the-art therapeutics: diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2005. 23:6387–6393.
Article5. Braendstrup P, Bjerrum OW, Nielsen OJ, Jensen BA, Clausen NT, Hansen PB, et al. Rituximab chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody treatment for adult refractory idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Am J Hematol. 2005. 78:275–280.
Article6. Higashida J, Wun T, Schmidt S, Naguwa SM, Tuscano JM. Safety and efficacy of rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis refractory to disease modifying antirheumatic drugs and anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha treatment. J Rheumatol. 2005. 32:2109–2115.7. Maloney DG, Smith B, Rose A. Rituximab: mechanism of action and resistance. Semin Oncol. 2002. 29(1 Suppl 2):2–9.
Article8. Kanelli S, Ansell SM, Habermann TM, Inwards DJ, Tuinstra N, Witzig TE. Rituximab toxicity in patients with peripheral blood malignant B-cell Lymphocytosis. Leuk Lymphoma. 2001. 42:1329–1337.
Article9. Burton C, Kaczmarski R, Jan-Mohamed R. Interstitial pneumonitis related to rituximab therapy. N Engl J Med. 2003. 348:2690–2691.
Article10. Byrd JC, Peterson BL, Morrison VA, Park K, Jacobson R, Hoke E, et al. Randomized phase 2 study of fludarabine with concurrent versus sequential treatment with rituximab in symptomatic, untreated patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: results from Cancer and Leukemia Group B 9712 (CALGB 9712). Blood. 2003. 101:6–14.
Article11. Tsang R, Gospodarowicz MK, Pintilie M, Bezjak A, Wells W, Hodgson DC, et al. Stage I and II MALT lymphoma: results of treatment with radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001. 50:1258–1264.
Article12. Schechter NR, Portlock CS, Yahalom J. Treatment of mucosa-asociated lymphoid tissue lymphoma of the stomach with radiation alone. J Clin Oncol. 1998. 16:1916–1921.
Article13. Thieblemont C. Clinical presentation and management of marginal zone lymphomas. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2005. 307–313.
Article14. Soda R, Costanzo A, Cantonetti M, Orlandi A, Bianchi L, Chimenti S. Systemic therapy of primary cutaneous B-cell lymphoma, marginal zone type, with rituximab, a chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody. Acta Derm Venereol. 2001. 81:207–208.
Article15. Lee Y, Kyung SY, Choi SJ, Bang SM, Jeong SH, Shin DB, et al. Two cases of interstitial pneumonitis caused by rituximab therapy. Korean J Intern Med. 2006. 21:183–186.
Article16. Hainsworth JD, Litchy S, Lamb MR, Rodriguez GI, Scroggin C Jr, Greco FA. First-line treatment with brief-duration chemotherapy plus rituximab in elderly patients with intermediate-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: phase II trial. Clin Lymphoma. 2003. 4:36–42.
Article17. Alexandrescu DT, Dutcher JP, O'Boyle K, Albulak M, Oiseth S, Wiernik PH. Fatal intra-alveolar hemorrhage after rituximab in a patient with non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2004. 45:2321–2325.
Article18. Herishanu Y, Polliack A, Leider-Trejo L, Grieff Y, Metser U, Naparstek E. Fatal interstitial pneumonitis related to rituximab-containing regimen. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma. 2006. 6:407–409.
Article19. Selenko N, Maidic O, Draxier S, Berer A, Jäger U, Knapp W, et al. CD20 antibody (C2B8)-induced apoptosis of lymphoma cells promotes phagocytosis by dendritic cells and cross-priming of CD8+ cytotoxic T cells. Leukemia. 2001. 5:1619–1626.
Article20. Hultin LE, Hausner MA, Hultin PM, Giorgi JV. CD20 (pan-B cell) antigen is expressed at a low level on a subpopulation of human T lymphocytes. Cytometry. 1993. 14:196–204.
Article21. Algino KM, Thomason RW, King DE, Montiel MM, Craig FE. CD20 (pan-B cell antigen) expression on bone marrow-derived T cells. Am J Clin Pathol. 1996. 106:78–81.
Article22. Warzynski MJ, Graham DM, Axtell RA, Zakem MH, Rotman RK. Low level CD20 expression on T cell malignancies. Cytometry. 1994. 18:88–92.
Article23. Jensen M, Winkler U, Manzke O, Diehl V, Engert A. Rapid tumor lysis in a patient with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia and lymphocytosis treated with an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (IDEC-C2B8, rituximab). Ann Hematol. 1998. 77:89–91.
Article24. Byrd JC, Waselenko JK, Maneatis TJ, Murphy T, Ward FT, Monahan BP, et al. Rituximab therapy in hematologic malignancy patients with circulating blood tumor cells: association with increased infusion-related side effects and rapid blood tumor clearance. J Clin Oncol. 1999. 17:791–795.
Article25. Merad M, Le Cesne A, Baldeyrou P, Mesurolle B, Le Chevalier T. Docetaxel and interstitial pulmonary injury. Ann Oncol. 1997. 8:191–194.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Regression of Extensive Colonic Extranodal Marginal Zone B Cell Lymphoma after Treatment with Rituximab
- Rituximab-induced Interstitial Pneumonitis in a Young Patient: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- A Case of Primary Pulmonary Extranodal Marginal Zone B-Cell Lymphoma of the MALT Type
- Two Cases of Interstitial Pneumonitis Caused by Rituximab Therapy
- Clinical Study of Ocular Adnexal Extranodal Marginal Zone B-cell Lymphoma: From the Perspective of Dermatology