Nutr Res Pract.
2017 Feb;11(1):70-75. 10.4162/nrp.2017.11.1.70.
Filipino women's diet and health study (FiLWHEL): design and methods
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food and Nutrition, Sookmyung Women's University, Seoul 04310, Korea.
- 2Division of Endocrinology, Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, Gyeonggi 18450, Korea.
- 3Department of Food and Nutrition, College of Human Ecology, Seoul National University, 1 Gwanak-ro, Gwanak-gu, Seoul 08826, Korea. jungelee@snu.ac.kr
- 4Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Hanyang University School of Medicine, 153, Gyeongchun-ro, Guri City, Gyeonggi 11923, Korea. lekang@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 2395296
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2017.11.1.70
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
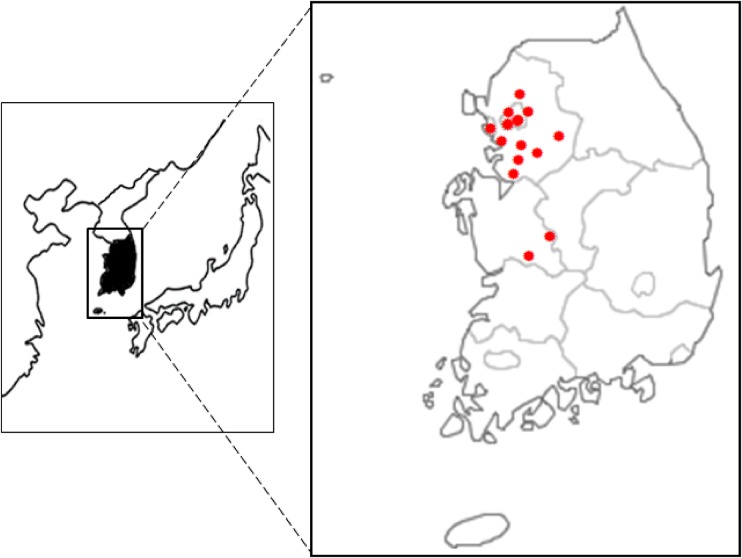
Immigration to South Korea from neighboring Asian countries has risen dramatically, primarily due to marriage between Korean men and foreign women. Although Filipino women rank fourth among married immigrant women, little is known about the health condition of this population. This manuscript focuses on the design and methods of Filipino women's diet and health study (FiLWHEL).
SUBJECTS/METHODS
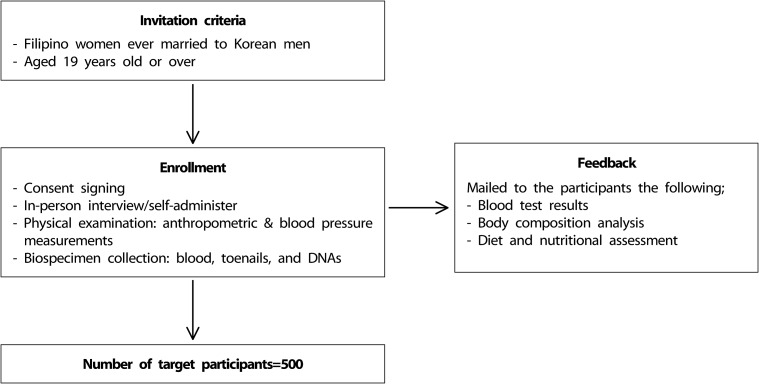
FiLWHEL is a cohort of Filipino women married to Korean men, aged 19 years old or over. The data collection comprised three parts: questionnaire, physical examination, and biospecimen collection. Questionnaires focused on demographic factors, diet, other health-related behaviors, acculturation and immigration-related factors, medical history, quality of life, and children's health information. Participants visited the recruitment site and answered the structured questionnaires through a face-to-face interview. We also measured their anthropometric features and collected fasting blood samples, toenails, and DNA samples. Recruitment started in 2014.
RESULTS
/CONCLUSIONS: Collection of data is ongoing, and we plan to prospectively follow our cohort participants. We expect that our study, which is focused on married Filipino women immigrants, can elucidate nutritional/health status and the effects of transitional experiences from several lifestyle factors.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Consumption of Han-sik and its Association with Socioeconomic Status among Filipino Immigrant Women: the Filipino Women's Diet and Health Study (FiLWHEL)
Nayeon Kim, Minji Kang, Grace Abris, Sherlyn Mae P. Provido, Hyojee Joung, Sangmo Hong, Sung Hoon Yu, Chang Beom Lee, Jung Eun Lee
Korean J Community Nutr. 2018;23(6):475-487. doi: 10.5720/kjcn.2018.23.6.475.Association of fried food intake with prehypertension and hypertension: the Filipino women's diet and health study
Sherlyn Mae P. Provido, Grace P. Abris, Sangmo Hong, Sung Hoon Yu, Chang Beom Lee, Jung Eun Lee
Nutr Res Pract. 2020;14(1):76-84. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2020.14.1.76.
Reference
-
1. Ministry of Justice, Korea Immigration Service. Korea immigration service statistics annual report: 2009 [Internet]. Seoul: Ministry of Justice;2010. cited 2014 October 12. Available from: http://www.immigration.go.kr/HP/COM/bbs_003/ListShowData.do?strNbodCd=noti0096&strWrtNo=120&strAnsNo=A&strOrgGbnCd=104000&strRtnURL=IMM_6050&strAllOrgYn=N&strThisPage=1&strFilePath=imm/.2. Hi Korea: e-Government for Foreigner. The requirements for a marriage migrant visa(F-6) [Internet]. Seoul: Hi Korea;2014. cited 2016 March 17. Available from: http://www.hikorea.go.kr/pt/NtcCotnDetailR_en.pt?bbsGbCd=BS10&bbsSeq=2&langCd=EN&ntccttSeq=48.3. Seoul Special City, Multicultural Affairs Division (KR). The hanultari living guide for multicultural families living in Seoul [Internet]. Seoul: Seoul Special City;2014. cited 2016 March 17. Available from: http://english.seoul.go.kr/wp-content/uploads/2014/05/The-Hanultari-Living-Guide_English.pdf.4. Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs (KR). Let's live a happy life in Korea: guide book for married immigrants in Korea [Internet]. Seoul: Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs;cited 2016 March 17. Available from: http://www.129.go.kr/upload/english/hapeng.pdf.5. Ministry of Justice, Korea Immigration Service. Vibrant Korea growing with immigrants [Internet]. Seoul: Ministry of Justice;2015. cited 2016 March 17. Available from: http://www.moj.go.kr/HP/TIMM/imm_07/image/bro_eng.pdf.6. Statistics Korea. Vital statistics of immigrants in 2014 [Internet]. Daejeon: Statistics Korea;2015. cited 2016 March 17. Available from: http://kostat.go.kr/portal/eng/pressReleases/8/3/index.board?bmode=read&aSeq=350648&pageNo=&rowNum=10&amSeq=&sTarget=&sTxt=.7. Ministry of Justice, Korea Immigration Service. Korea immigration service statistics annual report: 2014 [Internet]. Seoul: Ministry of Justice;2015. cited 2016 February 2. Available from: http://www.immigration.go.kr/HP/COM/bbs_003/ListShowData.do?strNbodCd=noti0096&strWrtNo=128&strAnsNo=A&strOrgGbnCd=104000&strRtnURL=IMM_6050&strAllOrgYn=N&strThisPage=1&strFilePath=imm.8. Yang SJ, Choi HY, Chee YK, Kim JA. Prevalence and correlates of obesity and overweight among asian immigrant women in Korea. Asia Pac J Public Health. 2012; 24:620–630. PMID: 21807629.
Article9. McCracken M, Olsen M, Chen MS Jr, Jemal A, Thun M, Cokkinides V, Deapen D, Ward E. Cancer incidence, mortality, and associated risk factors among Asian Americans of Chinese, Filipino, Vietnamese, Korean, and Japanese ethnicities. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007; 57:190–205. PMID: 17626117.
Article10. Ryan C, Shaw R, Pliam M, Zapolanski AJ, Murphy M, Valle HV, Myler R. Coronary heart disease in Filipino and Filipino-American patients: prevalence of risk factors and outcomes of treatment. J Invasive Cardiol. 2000; 12:134–139. PMID: 10731280.11. Choi SE, Chow VH, Chung SJ, Wong ND. Do risk factors explain the increased prevalence of type 2 diabetes among California Asian adults? J Immigr Minor Health. 2011; 13:803–808. PMID: 20936431.
Article12. Araneta MR, Barrett-Connor E. Ethnic differences in visceral adipose tissue and type 2 diabetes: Filipino, African-American, and white women. Obes Res. 2005; 13:1458–1465. PMID: 16129729.
Article13. Food and Nutrition Research Institute (PH). The 8th national nutrition survey: 2013 [Internet]. Metro Manila: Food and Nutrition Research Institute;2014. cited 2016 March 18. Available from: http://www.fnri.dost.gov.ph/index.php/nutrition-statistic/19-nutrition-statistic/118-8th-national-nutrition-survey.14. Kim S, Moon S, Popkin BM. The nutrition transition in South Korea. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000; 71:44–53. PMID: 10617945.
Article15. Popkin BM. Nutritional patterns and transitions. Popul Dev Rev. 1993; 19:138–157.
Article16. Rosenmöller DL, Gasevic D, Seidell J, Lear SA. Determinants of changes in dietary patterns among Chinese immigrants: a cross-sectional analysis. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2011; 8:42. PMID: 21592378.
Article17. Wandel M, Råberg M, Kumar B, Holmboe-Ottesen G. Changes in food habits after migration among South Asians settled in Oslo: the effect of demographic, socio-economic and integration factors. Appetite. 2008; 50:376–385. PMID: 17949850.
Article18. Batis C, Hernandez-Barrera L, Barquera S, Rivera JA, Popkin BM. Food acculturation drives dietary differences among Mexicans, Mexican Americans, and non-Hispanic Whites. J Nutr. 2011; 141:1898–1906. PMID: 21880951.
Article19. Serafica RC, Lane SH, Ceria-Ulep CD. Dietary acculturation and predictors of anthropometric indicators among Filipino Americans. Sage Open. 2013; 3:2158244013495543.
Article20. O'Brien PS, Wheeler T, Barker D. Fetal Programming: Influences on Development and Disease in Later Life. London: RCOG Press;1999.21. Barker DJ. The fetal and infant origins of adult disease. BMJ. 1990; 301:1111. PMID: 2252919.
Article22. Hales CN, Barker DJ. Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus: the thrifty phenotype hypothesis. Diabetologia. 1992; 35:595–601. PMID: 1644236.
Article23. Food and Nutrition Research Institute (PH). The 7th national nutrition survey: Philippines, 2008 anthropometric survey component [Internet]. Metro Manila: Food and Nutrition Research Institute;2008. cited 2015 January 1. Available from: http://www.fnri.dost.gov.ph/images/stories/7thNNS/anthrop/anthrop_preschool_adoles.pdf.24. Haddad L, Alderman H, Appleton S, Song L, Yohannes Y. Reducing child malnutrition: How far does income growth take us? World Bank Econ Rev. 2003; 17:107–131.
Article25. Yang YM, Wang HH. Acculturation and health-related quality of life among Vietnamese immigrant women in transnational marriages in Taiwan. J Transcult Nurs. 2011; 22:405–413. PMID: 21807958.
Article26. Howes OD, McDonald C, Cannon M, Arseneault L, Boydell J, Murray RM. Pathways to schizophrenia: the impact of environmental factors. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2004; 7(Suppl 1):S7–S13. PMID: 14972079.
Article27. Cantor-Graae E, Selten JP. Schizophrenia and migration: a meta-analysis and review. Am J Psychiatry. 2005; 162:12–24. PMID: 15625195.
Article28. Black PH, Garbutt LD. Stress, inflammation and cardiovascular disease. J Psychosom Res. 2002; 52:1–23. PMID: 11801260.
Article29. Cohen S, Janicki-Deverts D, Miller GE. Psychological stress and disease. JAMA. 2007; 298:1685–1687. PMID: 17925521.
Article30. Uitewaal PJ, Manna DR, Bruijnzeels MA, Hoes AW, Thomas S. Prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus, other cardiovascular risk factors, and cardiovascular disease in Turkish and Moroccan immigrants in North West Europe: a systematic review. Prev Med. 2004; 39:1068–1076. PMID: 15539038.
Article31. Macfarlane DJ, Lee CC, Ho EY, Chan KL, Chan DT. Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of IPAQ (short, last 7 days). J Sci Med Sport. 2007; 10:45–51. PMID: 16807105.
Article32. Nedjat S, Montazeri A, Holakouie K, Mohammad K, Majdzadeh R. Psychometric properties of the Iranian interview-administered version of the World Health Organization's Quality of Life Questionnaire (WHOQOL-BREF): a population-based study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2008; 8:61. PMID: 18366715.
Article33. Kim SH, Jo MW, Lee JW, Lee HJ, Kim JK. Validity and reliability of EQ-5D-3L for breast cancer patients in Korea. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2015; 13:203. PMID: 26694964.
Article34. Narrow WE, Clarke DE, Kuramoto SJ, Kraemer HC, Kupfer DJ, Greiner L, Regier DA. DSM-5 field trials in the United States and Canada, Part III: development and reliability testing of a cross-cutting symptom assessment for DSM-5. Am J Psychiatry. 2013; 170:71–82. PMID: 23111499.
Article35. Rosner B. Fundamentals of Biostatistics. 7th ed. Boston (MA): Brooks/Cole, Cengage Learning;2011. p. 352–426.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Consumption of Han-sik and its Association with Socioeconomic Status among Filipino Immigrant Women: the Filipino Women's Diet and Health Study (FiLWHEL)
- Association between Sleep Duration and Metabolic Disorders among Filipino Immigrant Women: The Filipino Women’s Diet and Health Study (FiLWHEL)
- Association of fried food intake with prehypertension and hypertension: the Filipino women's diet and health study
- Comparing Non-Communicable Disease Risk Factors in Asian Migrants and Native Koreans among the Asian Population
- Associations between Health Behaviors and Health-Related Quality of Life among Breast Cancer Survivors