Ann Dermatol.
2017 Apr;29(2):243-246. 10.5021/ad.2017.29.2.243.
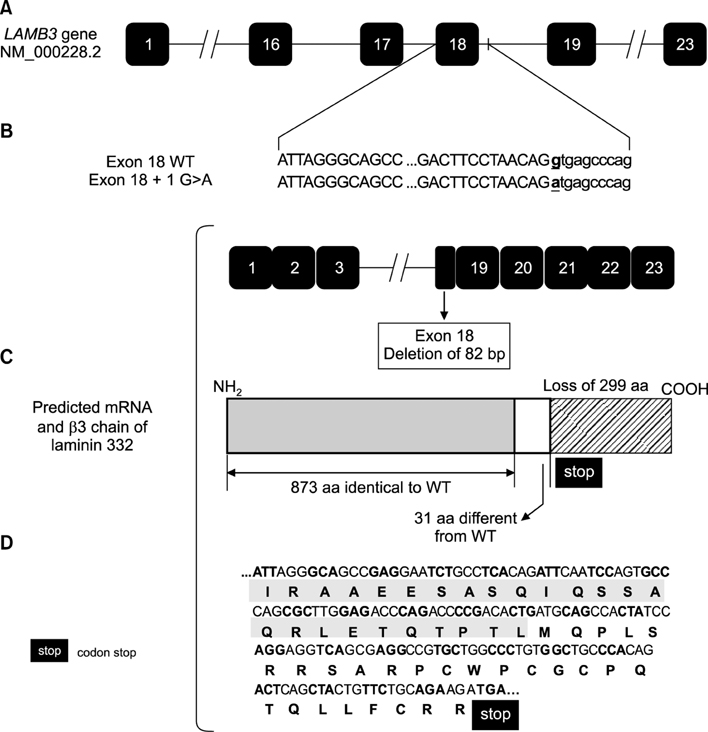
Identification of a Novel Mutation of LAMB3 Gene in a Lybian Patient with Hereditary Epidermolysis Bullosa by Whole Exome Sequencing
- Affiliations
-
- 1Biomedical Genomics and Oncogenetics Laboratory LR11IPT05, Pasteur Institute of Tunis, University of Tunis El Manar, Tunis, Tunisia. laroussi.nadia@yahoo.fr
- 2Department of Human and Experimental Pathology, Pasteur Institute of Tunis, University of Tunis El Manar, Tunis, Tunisia.
- 3Department of Dermatology, El Thawra Hospital, Al Bayda, Libya.
- 4Department of Dermatology and Research Unit on Keratinization Disorders, La Rabta Hospital, Tunis, Tunisia.
- 5Unit of Genetics of Human Development, Institut Pasteur, Paris, France.
- KMID: 2394857
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2017.29.2.243
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Masunaga T. Epidermal basement membrane: its molecular organization and blistering disorders. Connect Tissue Res. 2006; 47:55–66.
Article2. Kiezun A, Garimella K, Do R, Stitziel NO, Neale BM, McLaren PJ, et al. Exome sequencing and the genetic basis of complex traits. Nat Genet. 2012; 44:623–630.
Article3. Cheng JB, Cho RJ. Genetics and epigenetics of the skin meet deep sequence. J Invest Dermatol. 2012; 132:923–932.
Article4. Ben Brick AS, Laroussi N, Mesrati H, Kefi R, Bchetnia M, Lasram K, et al. Mutational founder effect in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa families from Southern Tunisia. Arch Dermatol Res. 2014; 306:405–411.
Article5. Nakazawa Y, Sasaki K, Mitsutake N, Matsuse M, Shimada M, Nardo T, et al. Mutations in UVSSA cause UV-sensitive syndrome and impair RNA polymerase IIo processing in transcription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair. Nat Genet. 2012; 44:586–592.
Article6. Baralle D, Baralle M. Splicing in action: assessing disease causing sequence changes. J Med Genet. 2005; 42:737–748.
Article7. Krawczak M, Reiss J, Cooper DN. The mutational spectrum of single base-pair substitutions in mRNA splice junctions of human genes: causes and consequences. Hum Genet. 1992; 90:41–54.
Article8. Nakano A, Chao SC, Pulkkinen L, Murrell D, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Pfendner E, et al. Laminin 5 mutations in junctional epidermolysis bullosa: molecular basis of Herlitz vs. non-Herlitz phenotypes. Hum Genet. 2002; 110:41–51.
Article9. Yuen WY, Lemmink HH, van Dijk-Bos KK, Sinke RJ, Jonkman MF. Herlitz junctional epidermolysis bullosa: diagnostic features, mutational profile, incidence and population carrier frequency in the Netherlands. Br J Dermatol. 2011; 165:1314–1322.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- KRT5 Gene Mutation in Patient with Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex with Mottled Pigmentation
- Localized Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita Limited to the Face
- A Case of Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex (Dowling-Meara 1 Type) in Newborn
- Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita: A Complete Remissions versus Patients with Long-term Persistent Activities
- Dominant Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa