Ann Dermatol.
2017 Apr;29(2):187-193. 10.5021/ad.2017.29.2.187.
The Effect of Micro-Spicule Containing Epidermal Growth Factor on Periocular Wrinkles
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. im1177@daum.net
- 2Paean Biotechnology Inc., Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 2394842
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2017.29.2.187
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Micro-needle patches have been recently used to increase skin permeability, which improves drug delivery, and for cosmetic purposes. However, these patches may often have limited efficacy due to insufficient skin penetration and reduced compliance caused by discomfort.
OBJECTIVE
We evaluated the efficacy and the safety of soluble micro-spicule containing epidermal growth factor (MS-EGF) for the treatment of periocular wrinkles.
METHODS
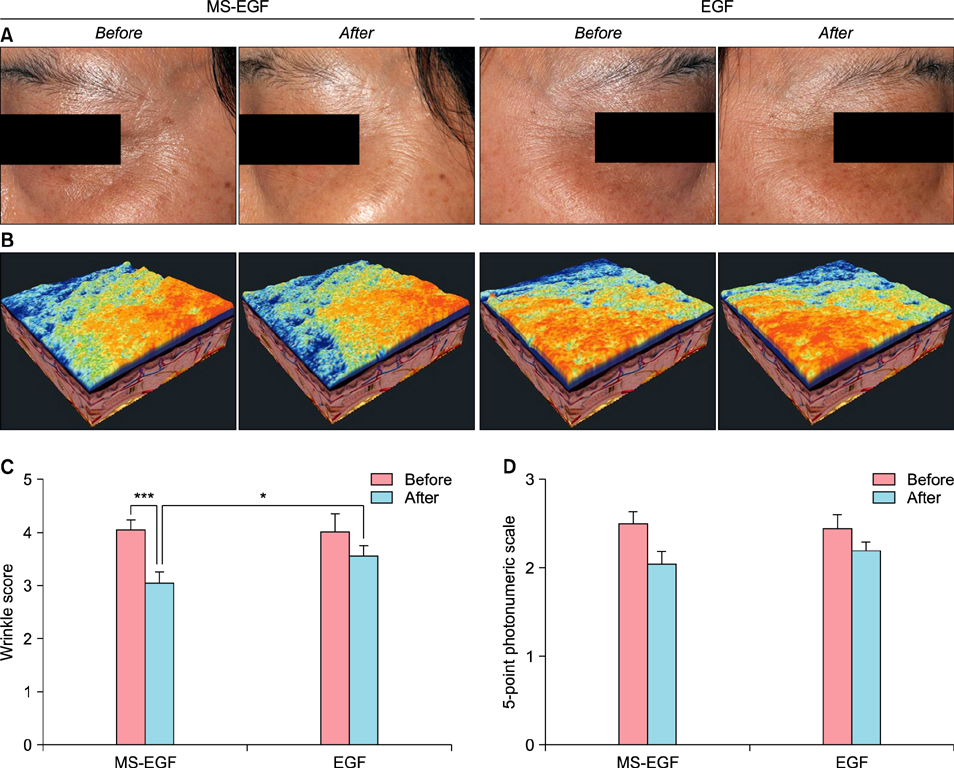
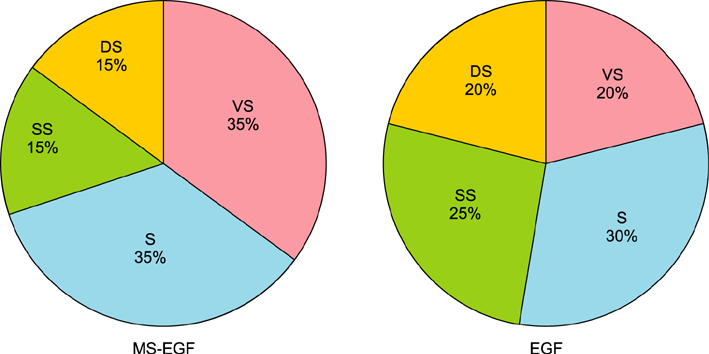
Twenty healthy volunteers aged 33 to 54 years were enrolled in a randomized, controlled, split-face study. For 4 weeks, a periocular wrinkle was treated daily with either a soluble MS-EGF cream or a cream containing EGF alone. All subjects underwent 8 weeks of follow-up. Efficacy was assessed using an ultrasonic measurement of dermal depth and density, digital skin image analysis, 5-point photonumeric scale for periocular wrinkles and subjective satisfaction.
RESULTS
MS-EGF group showed statistically significant increase of dermal depth and density compared to EGF alone group after 4 and 8 weeks. In addition, there was a marked improvement shown in clinical and 3-dimensional skin image in MS-EGF group. The treatments were well-tolerated; no significant side-effect was noted.
CONCLUSION
The MS-EGF formulation may represent an effective and biocompatible advance in the treatment of periocular wrinkles.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rinaldi A. Healing beauty? More biotechnology cosmetic products that claim drug-like properties reach the market. EMBO Rep. 2008; 9:1073–1077.2. Ooe M, Seki T, Miura T, Takada A. Comparative evaluation of wrinkle treatments. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2013; 37:424–433.
Article3. Narayan RJ. Transdermal delivery of insulin via microneedles. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2014; 10:2244–2260.
Article4. Farage MA, Miller KW, Elsner P, Maibach HI. Functional and physiological characteristics of the aging skin. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2008; 20:195–200.
Article5. Chauhan P, Shakya M. Modeling signaling pathways leading to wrinkle formation: identification of the skin aging target. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2009; 75:463–468.
Article6. Anchan RM, Reh TA, Angello J, Balliet A, Walker M. EGF and TGF-alpha stimulate retinal neuroepithelial cell proliferation in vitro. Neuron. 1991; 6:923–936.
Article7. Schlessinger J, Schreiber AB, Levi A, Lax I, Libermann T, Yarden Y. Regulation of cell proliferation by epidermal growth factor. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1983; 14:93–111.
Article8. Elias PM, Friend DS. The permeability barrier in mammalian epidermis. J Cell Biol. 1975; 65:180–191.
Article9. Elias PM, Friend DS, McNutt NS. Epidermal permeability barrier: transformation of lamellar granule-disks into intercellular sheets by a membrane fusion process. J Invest Dermatol. 1987; 88:459–460.
Article10. An JJ, Eum WS, Kwon HS, Koh JS, Lee SY, Baek JH, et al. Protective effects of skin permeable epidermal and fibroblast growth factor against ultraviolet-induced skin damage and human skin wrinkles. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2013; 12:287–295.
Article11. Elias PM. Epidermal lipids, barrier function, and desquamation. J Invest Dermatol. 1983; 80:Suppl. 44s–49s.
Article12. Prausnitz MR. Microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2004; 56:581–587.
Article13. van der Maaden K, Jiskoot W, Bouwstra J. Microneedle technologies for (trans)dermal drug and vaccine delivery. J Control Release. 2012; 161:645–655.
Article14. Doraiswamy A, Ovsianikov A, Gittard SD, Monteiro-Riviere NA, Crombez R, Montalvo E, et al. Fabrication of microneedles using two photon polymerization for transdermal delivery of nanomaterials. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2010; 10:6305–6312.
Article15. Carruthers A, Carruthers J, Hardas B, Kaur M, Goertelmeyer R, Jones D, et al. A validated grading scale for crow's feet. Dermatol Surg. 2008; 34:Suppl 2. S173–S178.
Article16. Gilchrest BA. A review of skin ageing and its medical therapy. Br J Dermatol. 1996; 135:867–875.
Article17. Binstock RH. Anti-aging medicine and research: a realm of conflict and profound societal implications. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2004; 59:B523–B533.18. Kogan A, Garti N. Microemulsions as transdermal drug delivery vehicles. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2006; 123-126:369–385.
Article19. Schramm J, Mitragotri S. Transdermal drug delivery by jet injectors: energetics of jet formation and penetration. Pharm Res. 2002; 19:1673–1679.20. Tokudome Y, Nakamura K, Itaya Y, Hashimoto F. Enhancement of skin penetration of hydrophilic and lipophilic compounds by pH-sensitive liposomes. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2015; 18:249–257.
Article21. Paudel KS, Milewski M, Swadley CL, Brogden NK, Ghosh P, Stinchcomb AL. Challenges and opportunities in dermal/transdermal delivery. Ther Deliv. 2010; 1:109–131.
Article22. Cai B, Xia W, Bredenberg S, Li H, Engqvist H. Bioceramic microneedles with flexible and self-swelling substrate. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015; 94:404–410.
Article23. Chu LY, Choi SO, Prausnitz MR. Fabrication of dissolving polymer microneedles for controlled drug encapsulation and delivery: bubble and pedestal microneedle designs. J Pharm Sci. 2010; 99:4228–4238.
Article24. Donnelly RF, Moffatt K, Alkilani AZ, Vicente-Pérez EM, Barry J, McCrudden MT, et al. Hydrogel-forming microneedle arrays can be effectively inserted in skin by self-application: a pilot study centred on pharmacist intervention and a patient information leaflet. Pharm Res. 2014; 31:1989–1999.
Article25. Kaur M, Ita KB, Popova IE, Parikh SJ, Bair DA. Microneedle-assisted delivery of verapamil hydrochloride and amlodipine besylate. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2014; 86:284–291.
Article26. Ita K. Transdermal delivery of drugs with microneedles-potential and challenges. Pharmaceutics. 2015; 7:90–105.
Article27. Park J, Seo J, Shin JU, Jeong DH, Kim JD, Lee KH. Efficacy of biodegradable microneedle patches on periorbital wrinkles. Korean J Dermatol. 2014; 52:597–607.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Corrigendum: The Effect of Micro-Spicule Containing Epidermal Growth Factor on Periocular Wrinkles
- Epidermal growth factor receptors increase in rabbit embryonal implantation
- Amplification of epidermal growth factor receptor gene in primary cervical cancer
- Amplification of epidermal growth factor receptor gene in primary cervical cancer
- The effect of GnRH analogue on epidermal growth factor receptor in uterine myoma