J Rheum Dis.
2017 Oct;24(5):318-320. 10.4078/jrd.2017.24.5.318.
Recurrent Aseptic Meningitis in Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease: A Not So Benign Disease?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea. noizegun@gmail.com
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2394349
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2017.24.5.318
Abstract
- No abstract available.
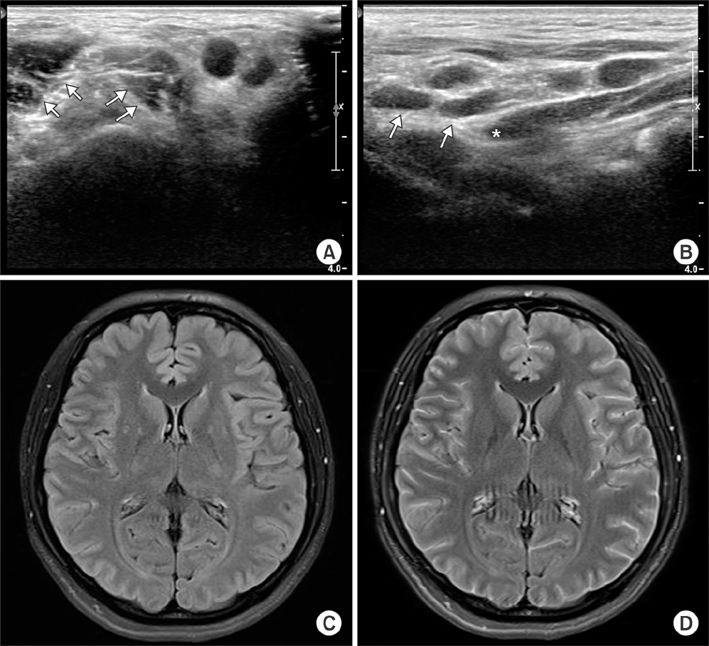
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jung IY, Ann HW, Kim JJ, Lee SJ, Kim J, Seong H, et al. The incidence and clinical characteristics by gender differences in patients with Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017; 96:e6332.2. Iguchi H, Sunami K, Yamane H, Konishi K, Takayama M, Nakai Y, et al. Apoptotic cell death in Kikuchi's disease: a TEM study. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1998; 538:250–253.3. Ohshima K, Shimazaki K, Kume T, Suzumiya J, Kanda M, Kikuchi M. Perforin and Fas pathways of cytotoxic T-cells in histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis. Histopathology. 1998; 33:471–478.4. Komagamine T, Nagashima T, Kojima M, Kokubun N, Nakamura T, Hashimoto K, et al. Recurrent aseptic meningitis in association with Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: case report and literature review. BMC Neurol. 2012; 12:112.5. Sato Y, Kuno H, Oizumi K. Histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis (Kikuchi's disease) with aseptic meningitis. J Neurol Sci. 1999; 163:187–191.6. Marunaka H, Orita Y, Tachibana T, Miki K, Makino T, Gion Y, et al. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: evaluation of prognostic factors and analysis of pathologic findings. Acta Otolaryngol. 2016; 136:944–947.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease with aseptic meningitis
- A Case of Kikuchi's Disease (Histiocytic Necrotizing Lymphadenitis) with Cutaneous Involvement Presenting As Aseptic Meningitis
- A Case of Recurrent Steroid-dependent Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease Successfully Treated with Hydroxychloroquine
- A Case Report of Benign Recurrent Aseptic Meningitis Mollaret`s Meningitis
- Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease, A Possible Complication of Rituximab Treatment