J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2017 Oct;52(5):403-410. 10.4055/jkoa.2017.52.5.403.
The Usefulness of Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis to Manage Comminuted Mid-Clavicle Fracture: A Comparison with Conventional Open Plating
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. drshoulder@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2393512
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2017.52.5.403
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to compare the clinical and radiological outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) with those of conventional open plating (COP) for treating comminuted mid-clavicular fractures and to evaluate the usefulness of MIPO.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty-nine patients who underwent surgical treatment for mid-clavicular comminuted fractures were analyzed retrospectively. Nineteen patients were treated with MIPO and twenty patients with COP. Radiological evaluation included time to union, fracture healing, and clavicular length difference measured as the proportional length difference with the unaffected side. Clinical assessment was performed using the simple shoulder test score, American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons score, and quick disability of the arm, shoulder and hand score. Moreover, the mean operation and radiation times, as well as exposure were compared.
RESULTS
All clavicles achieved bone union. The mean time to union was 12.1 weeks in the MIPO group, and 14.6 weeks in the COP group (p=0.587). There was no significant difference between the two groups regarding the functional and radiological outcomes at 2-year follow-up. A significantly shorter operation time was observed in the MIPO group than in the COP group (75.8 min vs. 106.9 min, p=0.002). More radiation time and exposure were identified in the MIPO group (52.8 s vs. 37.1 s, p=0.002; 209.4 mGy vs. 43.1 mGy, p=0.005).
CONCLUSION
Both COP and MIPO were shown to be effective treatment options for mid-clavicular comminuted fractures. MIPO may be a better alternative to COP due to shorter operation time and no need for a bone graft, although the functional and radiological outcomes were not significantly different. However, all surgeons should pay close attention to minimize radiation hazard.
MeSH Terms
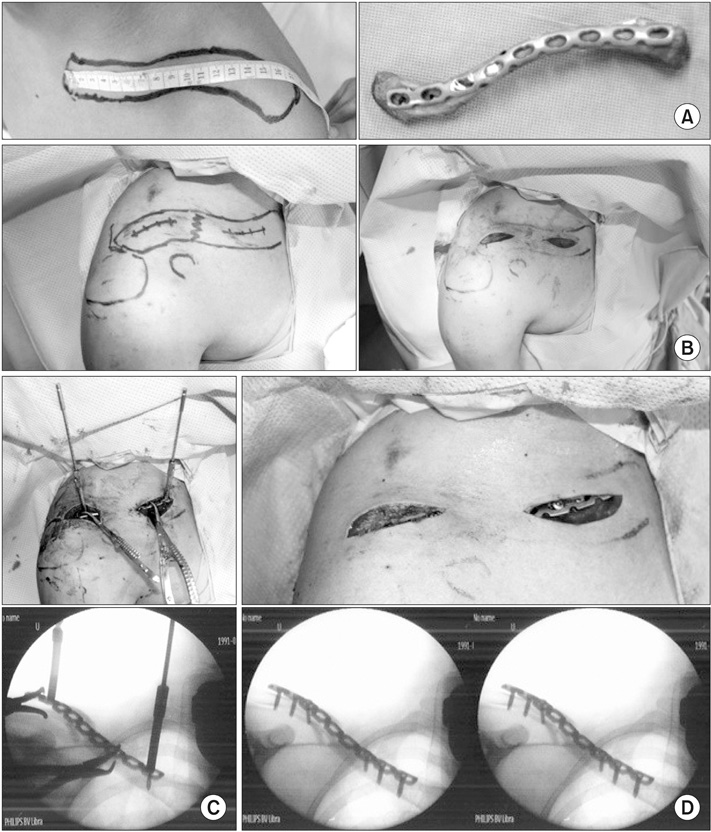
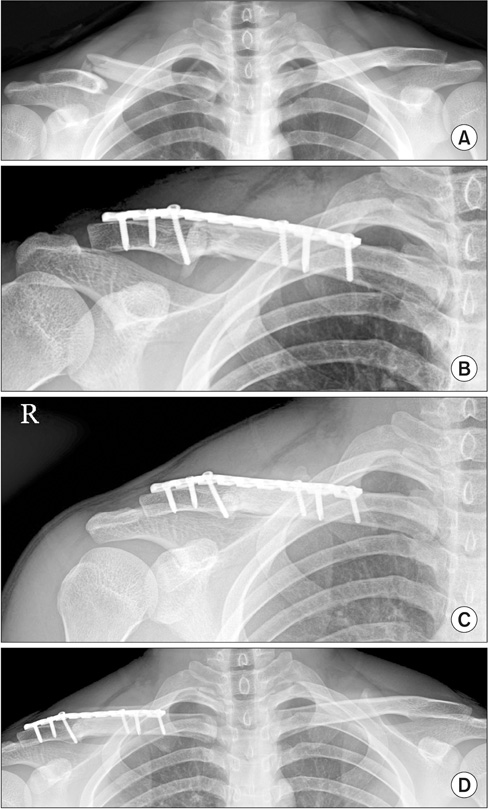
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Surgical Results of Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Fixation in the Treatment of Clavicle Shaft Fracture
Seong-Ho Yoo, Suk-Woong Kang, Jae-Seung Seo
J Korean Fract Soc. 2019;32(1):21-26. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.21.
Reference
-
1. Postacchini F, Gumina S, De Santis P, Albo F. Epidemiology of clavicle fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2002; 11:452–456.2. Robinson CM. Fractures of the clavicle in the adult. Epidemiology and classification. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998; 80:476–484.3. Neer CS 2nd. Nonunion of the clavicle. J Am Med Assoc. 1960; 172:1006–1011.4. Rowe CR. An atlas of anatomy and treatment of midclavicular fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1968; 58:29–42.5. McKee RC, Whelan DB, Schemitsch EH, McKee MD. Operative versus nonoperative care of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94:675–684.6. Robinson CM, Goudie EB, Murray IR, et al. Open reduction and plate fixation versus nonoperative treatment for displaced midshaft clavicular fractures: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013; 95:1576–1584.7. Canadian Orthopaedic Trauma Society. Nonoperative treatment compared with plate fixation of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. A multicenter, randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007; 89:1–10.8. Ferran NA, Hodgson P, Vannet N, Williams R, Evans RO. Locked intramedullary fixation vs plating for displaced and shortened mid-shaft clavicle fractures: a randomized clinical trial. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010; 19:783–789.9. Nordqvist A, Petersson CJ, Redlund-Johnell I. Mid-clavicle fractures in adults: end result study after conservative treatment. J Orthop Trauma. 1998; 12:572–576.10. Frigg A, Rillmann P, Perren T, Gerber M, Ryf C. Intramedullary nailing of clavicular midshaft fractures with the titanium elastic nail: problems and complications. Am J Sports Med. 2009; 37:352–359.11. Smekal V, Irenberger A, Struve P, Wambacher M, Krappinger D, Kralinger FS. Elastic stable intramedullary nailing versus nonoperative treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures-a randomized, controlled, clinical trial. J Orthop Trauma. 2009; 23:106–112.12. Zlowodzki M, Zelle BA, Cole PA, Jeray K, McKee MD;. Treatment of acute midshaft clavicle fractures: systematic review of 2144 fractures: on behalf of the evidence-based orthopaedic trauma working group. J Orthop Trauma. 2005; 19:504–507.13. Liu PC, Hsieh CH, Chen JC, Lu CC, Chuo CY, Chien SH. Infection after surgical reconstruction of a clavicle fracture using a reconstruction plate: a report of seven cases. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2008; 24:45–49.14. Duncan SF, Sperling JW, Steinmann S. Infection after clavicle fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005; 439:74–78.15. Jung GH, Park CM, Kim JD. Biologic fixation through bridge plating for comminuted shaft fracture of the clavicle: technical aspects and prospective clinical experience with a minimum of 12-month follow-up. Clin Orthop Surg. 2013; 5:327–333.16. Lee HJ, Oh CW, Oh JK, et al. Percutaneous plating for comminuted midshaft fractures of the clavicle: a surgical technique to aid the reduction with nail assistance. Injury. 2013; 44:465–470.17. Sohn HS, Kim BY, Shin SJ. A surgical technique for minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of clavicular midshaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2013; 27:e92–e96.18. Kim JJ, Oh HK, Bae JY, Kim JW. Radiological assessment of the safe zone for medial minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in the distal femur with computed tomography angiography. Injury. 2014; 45:1964–1969.19. Apivatthakakul T, Arpornchayanon O, Bavornratanavech S. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) of the humeral shaft fracture. Is it possible? A cadaveric study and preliminary report. Injury. 2005; 36:530–538.20. Röderer G, Erhardt J, Graf M, Kinzl L, Gebhard F. Clinical results for minimally invasive locked plating of proximal humerus fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2010; 24:400–406.21. Sohn HS, Shin SJ, Kim BY. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis using anterior-inferior plating of clavicular midshaft fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012; 132:239–244.22. Jiang H, Qu W. Operative treatment of clavicle midshaft fractures using a locking compression plate: comparison between mini-invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) technique and conventional open reduction. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012; 98:666–671.23. Sohn HS, Kim WJ, Shon MS. Comparison between open plating versus minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for acute displaced clavicular shaft fractures. Injury. 2015; 46:1577–1584.24. Radhi AM, Masbah O, Shukur MH, Shahril Y, Taiman K. Radiation exposure to operating theatre personnel during fluoroscopic-assisted orthopaedic surgery. Med J Malaysia. 2006; 61:Suppl A. 50–52.25. Kim JW, Oh CW, Byun YS, Kim JJ, Park KC. A prospective randomized study of operative treatment for noncomminuted humeral shaft fractures: conventional open plating versus minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis. J Orthop Trauma. 2015; 29:189–194.26. Polat A, Kose O, Canbora K, Yanık S, Guler F. Intramedullary nailing versus minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for distal extra-articular tibial fractures: a prospective randomized clinical trial. J Orthop Sci. 2015; 20:695–701.27. 1990 Recommendations of the international commission on radiological protection. Ann ICRP. 1991; 21:1–201.28. Mehlman CT, DiPasquale TG. Radiation exposure to the orthopaedic surgical team during fluoroscopy: "how far away is far enough?". J Orthop Trauma. 1997; 11:392–398.29. Tremains MR, Georgiadis GM, Dennis MJ. Radiation exposure with use of the inverted-c-arm technique in upper-extremity surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001; 83:674–678.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Outcomes of Locking Compression Plate Fixation through Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis in the Treatment of Distal Tibia Fracture
- Surgical Treatment of Clavicle Midshaft Fractures Using a Locking Compression Plate: Conventional Open Reduction and Plating with Internal Fixation versus Minimal Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis
- Operative Treatment of Humerus Shaft Fracture: Conventional Open Plating or Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis
- Treatment of Lateral Malleolar Fractures using Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis Technique
- Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Stabilization Using a Medial Locking Plate for Proximal Tibial Fractures: Technical Note