J Bacteriol Virol.
2017 Sep;47(3):111-121. 10.4167/jbv.2017.47.3.111.
Human Rhinoviruses: the Forgotten but Still Important Viruses
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biotechnology, the Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon-si, Gyeonggi-do, Korea. jhnam@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Division of VAX R&D, Life Science Research Institute, SK Chemicals, Seongnam-si, Gyeonggi-do, Korea.
- KMID: 2392959
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2017.47.3.111
Abstract
- Human rhinoviruses (HRVs) are responsible for many of the characteristic symptoms of the common cold, such as a sore throat, runny nose, nasal congestion, sneezing, and coughing. However, despite the high detection rate in children, most HRV infections are asymptomatic. As a result, these viruses are generally ignored, even though a close association between HRV infections in early life and the subsequent induction of asthma has been reported. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct further research into HRV diagnostics, treatments, epidemiology, and vaccines. This review describes recent studies of HRVs, including their genomic diversity, surveillance systems, taxonomy, and immune responses, as well as vaccines.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Price WH. The isolation of a new virus associcated with respiratory clinical disease in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956; 42:892–6.2). Pelon W, Mogabgab WJ, Phillips IA, Pierce WE. A cytopathogenic agent isolated from naval recruits with mild respiratory illnesses. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957; 94:262–7.
Article3). Savolainen C, Blomqvist S, Mulders MN, Hovi T. Genetic clustering of all 102 human rhinovirus prototype strains: serotype 87 is close to human enterovirus 70. J Gen Virol. 2002; 83:333–40.
Article4). Lau SK, Yip CC, Tsoi HW, Lee RA, So LY, Lau YL, et al. Clinical features and complete genome characterization of a distinct human rhinovirus (HRV) genetic cluster, probably representing a previously undetected HRV species, HRV-C, associated with acute respiratory illness in children. J Clin Microbiol. 2007; 45:3655–64.
Article5). Palmenberg AC, Rathe JA, Liggett SB. Analysis of the complete genome sequences of human rhinovirus. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125:1190–9.
Article6). Simmonds P, McIntyre C, Savolainen-Kopra C, Tapparel C, Mackay IM, Hovi T. Proposals for the classification of human rhinovirus species C into genotypically assigned types. J Gen Virol. 2010; 91:2409–19.
Article7). McIntyre CL, Savolainen-Kopra C, Hovi T, Simmonds P. Recombination in the evolution of human rhinovirus genomes. Arch Virol. 2013; 158:1497–515.
Article8). McIntyre CL, McWilliam Leitch EC, Savolainen-Kopra C, Hovi T, Simmonds P. Analysis of Genetic Diversity and Sites of Recombination in Human Rhinovirus Species C. J Virol. 2010; 84:10297–310.
Article9). Racaniello VR. Picornaviridae. The Viruses and Their Replication. Fields B, Knipe D, Howley P, Griffin D, editors. Field virology. 4th ed.Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins;2002. p. 685–722.10). Hanson PJ, Zhang HM, Hemida MG, Ye X, Qiu Y, Yang D. IRES-Dependent Translational Control during Virus-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis. Front Microbiol. 2012; 3:92.
Article11). Jahan N, Wimmer E, Mueller S. Polypyrimidine tract binding protein-1 (PTB1) is a determinant of the tissue and host tropism of a human rhinovirus/poliovirus chimera PV1 (RIPO). PLoS One. 2013; 8:e60791.12). Fernández-Miragall O, López de Quinto S, Martínez-Salas E. Relevance of RNA structure for the activity of picornavirus IRES elements. Virus Res. 2009; 139:172–82.
Article13). Kafasla P, Morgner N, Robinson CV, Jackson RJ. Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein stimulates the poliovirus IRES by modulating eIF4G binding. EMBO J. 2010; 29:3710–22.
Article14). Jacobs SE, Lamson DM, St George K, Walsh TJ. Human rhinoviruses. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2013; 26:135–62.
Article15). Thibaut HJ, Lacroix C, De Palma AM, Franco D, Decramer M, Neyts J. Toward antiviral therapy/prophylaxis for rhinovirus-induced exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: challenges, opportunities, and strategies. Rev Med Virol. 2015; 26:21–33.
Article16). Gern JE, Busse WW. Association of rhinovirus infections with asthma. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1999; 12:9–18.
Article17). Hayden FG. Rhinovirus and the lower respiratory tract. Rev Med Virol. 2004; 14:17–31.
Article18). Dougherty RH, Fahy JV. Acute exacerbations of asthma: epidemiology, biology and the exacerbation-prone phenotype. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009; 39:193–202.
Article19). Pérez-Losada M, Arenas M, Galán JC, Palero F, González-Candelas F. Recombination in viruses: mechanisms, methods of study, and evolutionary consequences. Infect Genet Evol. 2015; 30:296–307.
Article20). Duffy S, Shackelton LA, Holmes EC. Rates of evolutionary change in viruses: patterns and determinants. Nat Rev Genet. 2008; 9:267–76.
Article21). Royston L, Tapparel C. Rhinoviruses and Respiratory Enteroviruses: Not as Simple as ABC. Viruses. 2016; 8:16.
Article22). Hjelle B, Jenison S, Torrez-Martinez N, Yamada T, Nolte K, Zumwalt R, et al. A novel hantavirus associated with an outbreak of fatal respiratory disease in the southwestern United States: evolutionary relationships to known hantaviruses. J Virol. 1994; 68:592–6.
Article23). Kang W, Huang C, Bai X, Yang W, Li G. A preliminary genetic reassortment between Hantaan virus and Seoul virus strains. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2002; 23:46–9.24). Kim JA, Kim WK, No JS, Lee SH, Lee SY, Kim JH, et al. Genetic Diversity and Reassortment of Hantaan Virus Tripartite RNA Genomes in Nature, the Republic of Korea. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016; 10:e0004650.
Article25). Maljkovic Berry I, Melendrez MC, Li T, Hawksworth AW, Brice GT, Blair PJ, et al. Frequency of influenza H3N2 intra-subtype reassortment: attributes and implications of reassortant spread. BMC Biol. 2016; 14:117.
Article26). Schweiger B. Molecular characterization of human influenza viruses–a look back on the last 10 years. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2016; 119:167–78.27). Meng Z, Han R, Hu Y, Yuan Z, Jiang S, Zhang X, et al. Possible pandemic threat from new reassortment of influenza A(H7N9) virus in China. Euro Surveill. 2014; 19.
Article28). Sanjuán R, Nebot MR, Chirico N, Mansky LM, Belshaw R. Viral mutation rates. J Virol. 2010; 84:9733–48.
Article29). Lauring AS, Frydman J, Andino R. The role of mutational robustness in RNA virus evolution. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013; 11:327–36.
Article30). Korboukh VK, Lee CA, Acevedo A, Vignuzzi M, Xiao Y, Arnold JJ, et al. RNA virus population diversity, an optimum for maximal fitness and virulence. J Biol Chem. 2014; 289:29531–44.
Article31). Palmenberg AC, Spiro D, Kuzmickas R, Wang S, Djikeng A, Rathe JA, et al. Sequencing and analyses of all known human rhinovirus genomes reveal structure and evolution. Science. 2009; 324:55–9.
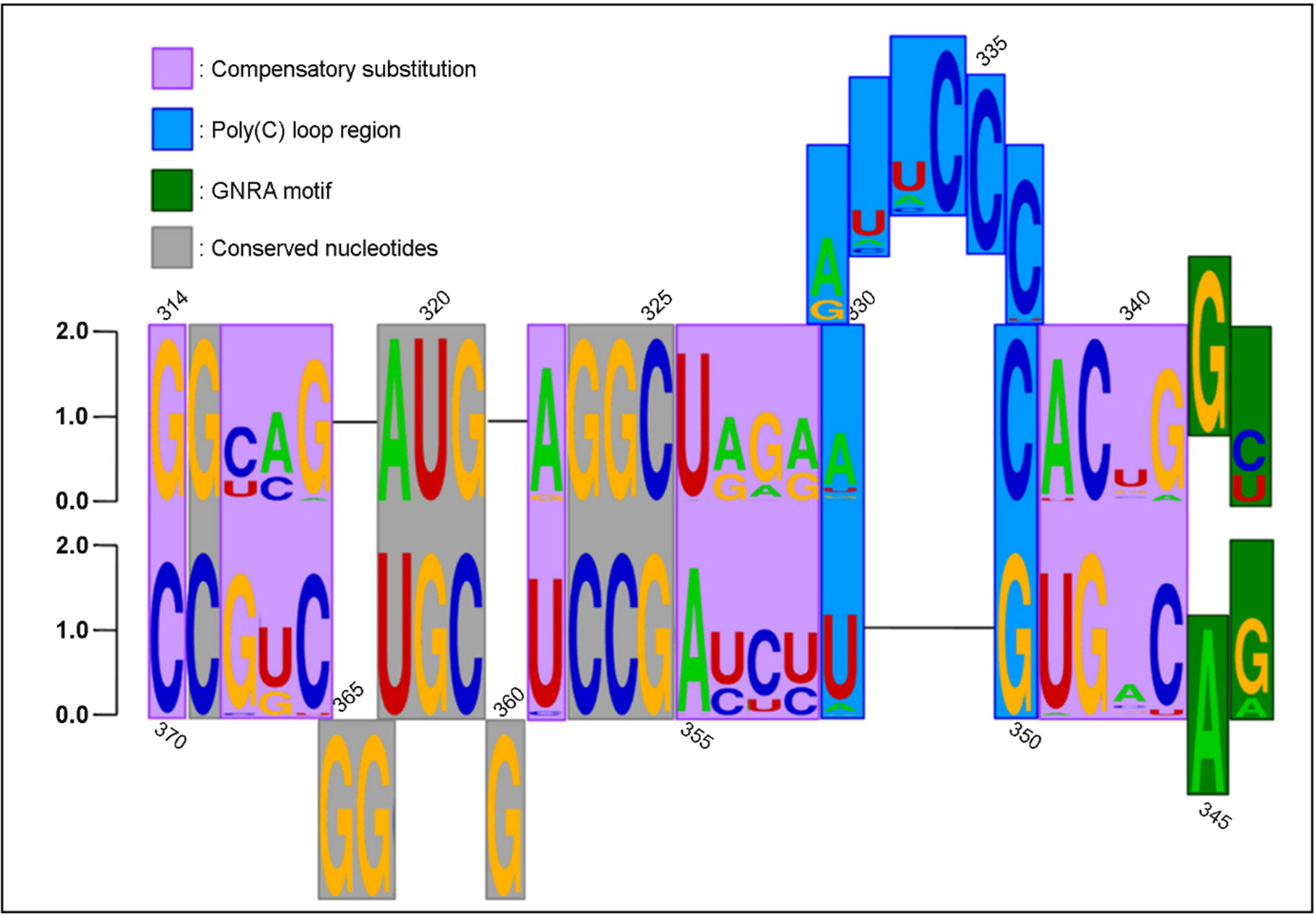
Article32). Kim H, Kim K, Kwon T, Kim DW, Kim SS, Kim YJ. Secondary structure conservation of the stem-loop IV sub-domain of internal ribosomal entry sites in human rhinovirus clinical isolates. Int J Infect Dis. 2015; 41:21–8.
Article33). Yozwiak NL, Skewes-Cox P, Gordon A, Saborio S, Kuan G, Balmaseda A, et al. Human enterovirus 109: a novel interspecies recombinant enterovirus isolated from a case of acute pediatric respiratory illness in Nicaragua. J Virol. 2010; 84:9047–58.
Article34). Lukashev AN. Role of recombination in evolution of enteroviruses. Rev Med Virol. 2005; 15:157–67.
Article35). Tan Y, Hassan F, Schuster JE, Simenauer A, Selvarangan R, Halpin RA, et al. Molecular Evolution and Intraclade Recombination of Enterovirus D68 during the 2014 Outbreak in the United States. J Virol. 2015; 90:1997–2007.
Article36). Kim H, Kim K, Kim DW, Jung HD, Min Cheong H, Kim KH, et al. Identification of Recombinant Human Rhinovirus A and C in Circulating Strains from Upper and Lower Respiratory Infections. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e68081.
Article37). Huang T, Wang W, Bessaud M, Ren P, Sheng J, Yan H, et al. Evidence of Recombination and Genetic Diversity in Human Rhinoviruses in Children with Acute Respiratory Infection. PLoS One. 2009; 4:e6355.
Article38). Lau SK, Yip CC, Lin AW, Lee RA, So LY, Lau YL, et al. Clinical and molecular epidemiology of human rhinovirus C in children and adults in Hong Kong reveals a possible distinct human rhinovirus C subgroup. J Infect Dis. 2009; 200:1096–103.
Article39). Xiang Z, Gonzalez R, Xie Z, Xiao Y, Liu J, Chen L, et al. Human rhinovirus C infections mirror those of human rhinovirus A in children with community-acquired pneumonia. J Clin Virol. 2010; 49:94–9.
Article40). Linsuwanon P, Payungporn S, Samransamruajkit R, Posuwan N, Makkoch J, Theanboonlers A, et al. High prevalence of human rhinovirus C infection in Thai children with acute lower respiratory tract disease. J Infect. 2009; 59:115–21.
Article41). Onyango CO, Welch SR, Munywoki PK, Agoti CN, Bett A, Ngama M, et al. Molecular epidemiology of human rhinovirus infections in Kilifi, coastal Kenya. J Med Virol. 2012; 84:823–31.
Article42). L'Huillier AG, Kaiser L, Petty TJ, Kilowoko M, Kyungu E, Hongoa P, et al. Molecular Epidemiology of Human Rhinoviruses and Enteroviruses Highlights Their Diversity in Sub-Saharan Africa. Viruses. 2015; 7:6412–23.43). Henquell C, Mirand A, Deusebis AL, Regagnon C, Archimbaud C, Chambon M, et al. Prospective genotyping of human rhinoviruses in children and adults during the winter of 2009–2010. J Clin Virol. 2012; 53:280–4.
Article44). Aponte FE, Taboada B, Espinoza MA, Arias-Ortiz MA, Monge-Martínez J, Rodríguez-Vázquez R, et al. Rhinovirus is an important pathogen in upper and lower respiratory tract infections in Mexican children. Virol J. 2015; 12:31.
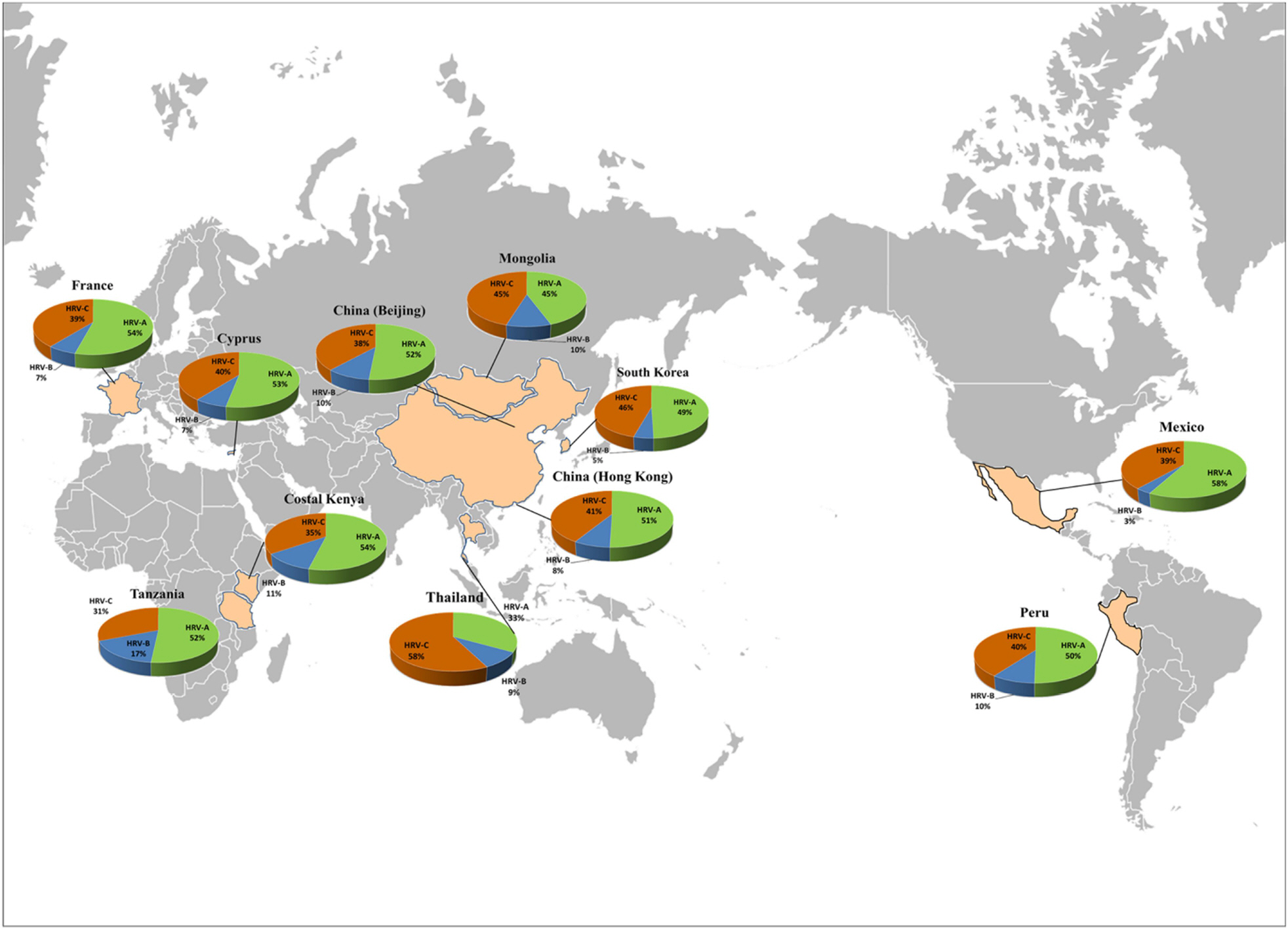
Article45). Tsatsral S, Xiang Z, Fuji N, Maitsetseg C, Khulan J, Oshitani H, et al. Molecular Epidemiology of the Human Rhinovirus Infection in Mongolia during 2008–2013. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2015; 68:280–7.46). Richter J, Nikolaou E, Panayiotou C, Tryfonos C, Koliou M, Christodoulou C. Molecular epidemiology of rhinoviruses in Cyprus over three consecutive seasons. Epidemiol Infect. 2015; 143:1876–83.
Article47). Howard LM, Johnson M, Gil AI, Griffin MR, Edwards KM, Lanata CF, et al. Molecular Epidemiology of Rhinovirus Detections in Young Children. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2016; 3:ofw001.
Article48). Public Health England. Surveillance of influenza and other respiratory viruses in the United Kingdom winter 2014 to 2015. England. 2015. Available from:. https://www.gov.uk/government/organisations/public-health-england.49). Public Health Agency of Canada. Respiratory Virus Detections/Isolations for the period August 24, 2014 August 29, 2015. Canada. 2015. Available from:. http://www.phac-aspc.gc.ca/irid-diir/index-eng.php.50). Environmental Science and Research. Virology annual report 2014. New Zealand. 2015. Available from:. https://surv.esr.cri.nz/virology/virology_annual_report.php.51). Korea Center and Disease Control and Prevention. Prevalence of Respiratory Viruses in Patients with Acute Respiratory Infections, 2014. Korea. 2015. Available from:. http://www.cdc.go.kr/CDC/info/.52). Wisdom A, Kutkowska AE, McWilliam Leitch EC, Gaunt E, Templeton K, Harvala H, et al. Genetics, recombination and clinical features of human rhinovirus species C (HRV-C) infections; interactions of HRV-C with other respiratory viruses. PLoS One. 2009; 4:e8518.
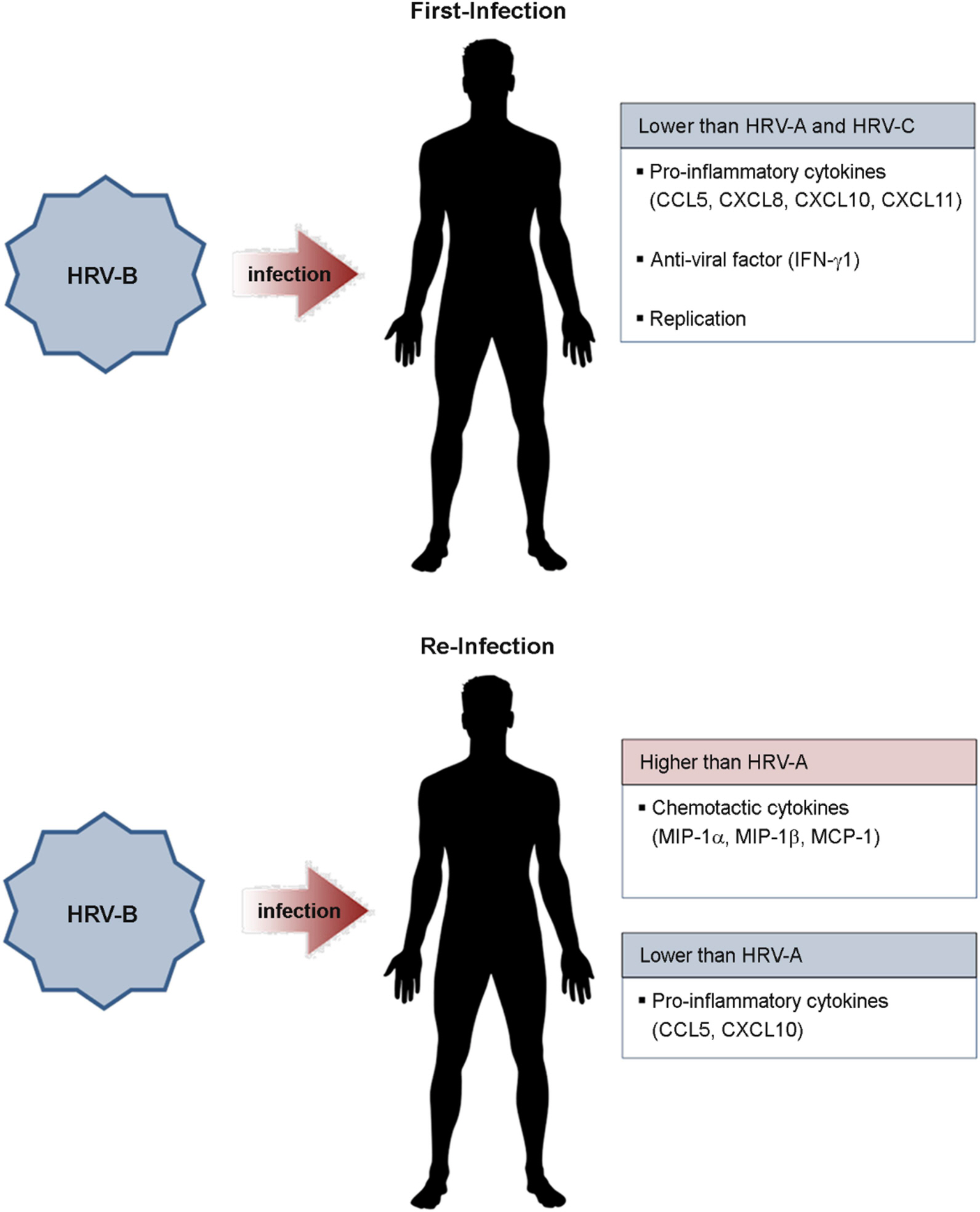
Article53). Rajan D, McCracken CE, Kopleman HB, Kyu SY, Lee FE-H, Lu X, et al. Human rhinovirus induced cytokine/chemokine responses in human airway epithelial and immune cells. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e114322.
Article54). Nakagome K, Bochkov YA, Ashraf S, Brockman-Schneider RA, Evans MD, Pasic TR, et al. Effects of rhinovirus species on viral replication and cytokine production. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014; 134:332–41.
Article55). Spurrell JC, Wiehler S, Zaheer RS, Sanders SP, Proud D. Human airway epithelial cells produce IP-10 (CXCL10) in vitro and in vivo upon rhinovirus infection. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2005; 289:L85–95.
Article56). Wark PA, Bucchieri F, Johnston SL, Gibson PG, Hamilton L, Mimica J, et al. IFN-gamma-induced protein 10 is a novel biomarker of rhinovirus-induced asthma exacerbations. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 120:586–93.57). Papadopoulos NG, Xepapadaki P, Mallia P, Brusselle G, Watelet JB, Xatzipsalti M, et al. Mechanisms of virus-induced asthma exacerbations: state-of-the-art. A GA2LEN and InterAirways document. Allergy. 2007; 62:457–70.
Article58). Miller EK, Hernandez JZ, Wimmenauer V, Shepherd BE, Hijano D, Libster R, et al. A mechanistic role for type III IFN-λ1 in asthma exacerbations mediated by human rhinoviruses. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012; 185:508–16.59). Staunton DE, Merluzzi VJ, Rothlein R, Barton R, Marlin SD, Springer TA. A cell adhesion molecule, ICAM-1, is the major surface receptor for rhinoviruses. Cell. 1989; 56:849–53.
Article60). Hofer F, Gruenberger M, Kowalski H, Machat H, Huettinger M, Kuechler E, et al. Members of the low density lipoprotein receptor family mediate cell entry of a minor-group common cold virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994; 91:1839–42.
Article61). Bochkov YA, Watters K, Ashraf S, Griggs TF, Devries MK, Jackson DJ, et al. Cadherin-related family member 3, a childhood asthma susceptibility gene product, mediates rhinovirus C binding and replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015; 112:5485–90.
Article62). Lee S, Nguyen MT, Currier MG, Jenkins JB, Strobert EA, Kajon AE, et al. A polyvalent inactivated rhinovirus vaccine is broadly immunogenic in rhesus macaques. Nat Commun. 2016; 7:12838.
Article63). Glanville N, McLean GR, Guy B, Lecouturier V, Berry C, Girerd Y, et al. Cross-serotype immunity induced by immunization with a conserved rhinovirus capsid protein. PLoS Pathog. 2013; 9:e1003669.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Human rhinoviruses and asthma in children
- Viral Infections and Associated Factors That Promote Acute Exacerbations of Asthma
- Rhinovirus-Infected Epithelial Cells Produce More IL-8 and RANTES Compared With Other Respiratory Viruses
- Characteristics of Viruses and the Infection Control
- Evaluation of a Multiplex Real-time PCR Assay for the Detection of Respiratory Viruses in Clinical Specimens