Korean J Pain.
2017 Oct;30(4):304-307. 10.3344/kjp.2017.30.4.304.
Treatment of hemifacial spasm in patient with hemifacial atrophy using combination therapy (ultrasound therapy and TENS): a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Oral Medicine and Radiology, ITS Dental College, Muradnagar, India. apalabaduni@gmail.com
- KMID: 2392908
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2017.30.4.304
Abstract
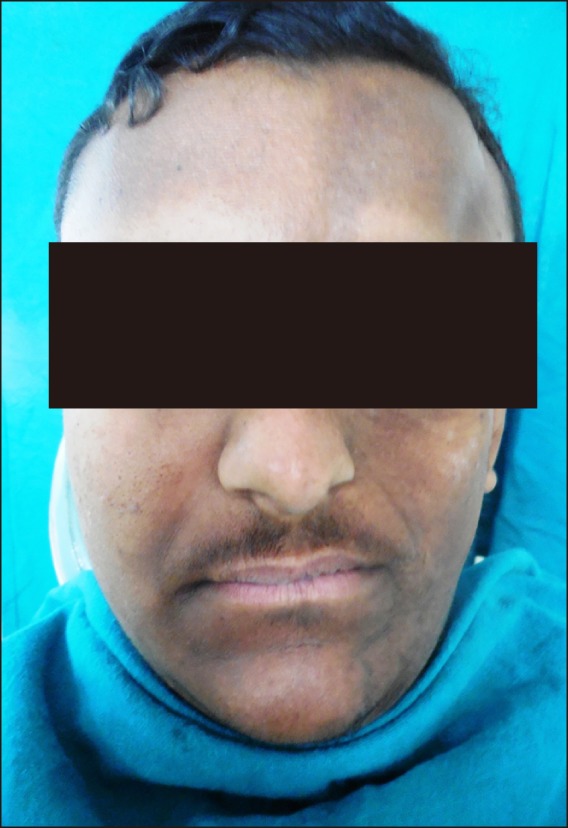
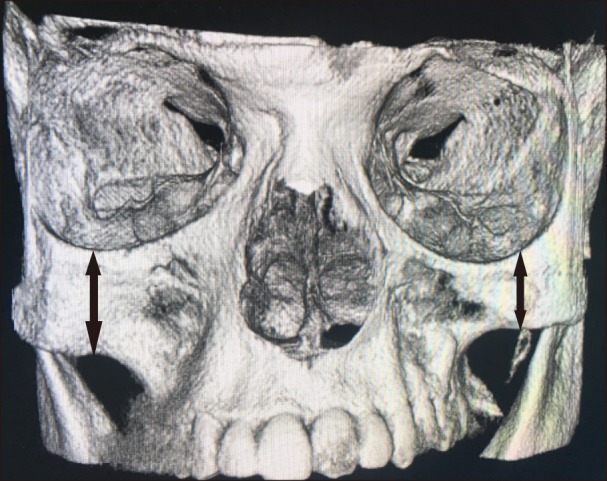
- A 19-year-old male patient presented with facial hemi-atrophy with unilateral spasms of the masseter and temporalis muscles. Ultrasound therapy and Transcutaneous Electric Nerve Stimulation therapy, known as combination therapy, were given on alternate days for 2 weeks. At the end of 2 weeks of combination therapy the patient reported a drastic reduction in the number of episodes of muscle spasm. The visual analog scale score for tenderness of the masseter and temporalis was also markedly reduced. No one has previously used combination therapy for the treatment of facial hemi-atrophy with hemi-facial spasms. The encouraging results of the combination therapy has prompted us to document this study.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pinheiro TP, Silva CC, Silveira CS, Botelho PC, Pinheiro Md, Pinheiro Jde J. Progressive hemifacial atrophy--case report. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2006; 11:E112–E114. PMID: 16505785.2. Patel H, Thakkar C, Patel K. Parry-Romberg syndrome: a rare entity. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2010; 9:247–250. PMID: 22190798.
Article3. Wartenberg R. Progressive facial hemiatrophy. Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1945; 54:75–96.
Article4. Sande A, Risbud M, Kshar A, Paranjpe AO. Progressive hemifacial atrophy. Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2013; 10:108–111. PMID: 23878573.5. Al-Aizari NA, Azzeghaiby SN, Al-Shamiri HM, Darwish S, Tarakji B. Oral manifestations of Parry-Romberg syndrome: a review of literature. Avicenna J Med. 2015; 5:25–28. PMID: 25878963.
Article6. Panda AK, Gopinath G, Singh S. Parry-Romberg syndrome with hemimasticatory spasm in pregnancy; a dystonia mimic. J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2014; 5:184–186. PMID: 24966565.
Article7. Goyal S, Goyal S. Pattern of dental malocclusion in orthodontic patients in rwanda: a retrospective hospital based study. Rwanda Med J. 2012; 69:13–18.8. Ebersbach G, Kabus C, Schelosky L, Terstegge L, Poewe W. Hemimasticatory spasm in hemifacial atrophy: diagnostic and therapeutic aspects in two patients. Mov Disord. 1995; 10:504–507. PMID: 7565834.
Article9. Kim HJ, Jeon BS, Lee KW. Hemimasticatory spasm associated with localized scleroderma and facial hemiatrophy. Arch Neurol. 2000; 57:576–580. PMID: 10768634.
Article10. Cersósimo MG, Bertoti A, Roca CU, Micheli F. Botulinum toxin in a case of hemimasticatory spasm with severe worsening during pregnancy. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2004; 27:6–8. PMID: 15090929.
Article11. Teive HA, Piovesan EJ, Germiniani FM, Camargo CH, Sa D, Scola RH, et al. Hemimasticatory spasm treated with botulinum toxin: case report. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2002; 60:288–289. PMID: 12068362.
Article12. Rosenstengel C, Matthes M, Baldauf J, Fleck S, Schroeder H. Hemifacial spasm: conservative and surgical treatment options. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2012; 109:667–673. PMID: 23264807.13. Nayyar P, Kumar P, Nayyar PV, Singh A. BOTOX: broadening the horizon of dentistry. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014; 8:ZE25–ZE29.14. Wang A, Jankovic J. Hemifacial spasm: clinical findings and treatment. Muscle Nerve. 1998; 21:1740–1747. PMID: 9843077.
Article15. Mukkannavar PB. Effect of combination therapy [TENS & ultrasound] and ischemic compression in the treatment of active myofascial trigger points. J Exerc Sci Physiother. 2008; 4:95–103.16. Kasat V, Gupta A, Ladda R, Kathariya M, Saluja H, Farooqui AA. Transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation (TENS) in dentistry: a review. J Clin Exp Dent. 2014; 6:e562–e568. PMID: 25674327.
Article17. Singh R, Rao K, Anap D, Iyer C, Khatri S. The short term effect of TheraBite® on temporomandibular dysfunction: a case study. Int J Phys Med Rehabil. 2013; 1:102.
Article18. Pal US, Kumar L, Mehta G, Singh N, Singh G, Singh M, et al. Trends in management of myofacial pain. Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2014; 5:109–116. PMID: 25937719.
Article19. Rajalakshmi A, Sathish KM, Ivvala AS, Mahalakshmi R. Effect of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in trapezitis. Int J Physiother Res. 2013; 1:205–207.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Botulinum Toxin Injection Treatment for Facial Spasm
- Effects of Botulinum Toxin Combined with Diltiazem on Blepharospasm and Hemifacial Spasm
- Treatment of Venous Origin Hemifacial Spasm by Microsurgical Decompression: Case Report
- Vestibular Paroxysmia and Hemifacial Spasm by Vascular Compression
- CT Guided Chemical Facial Nerve Block in the Treatment of Facial Spasm