Korean J Pain.
2010 Mar;23(1):46-50.
Epidural Blood Patches in a Patient With Multi-level Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage That Was Induced by Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, School of Medicine, Keimyung University, Daegu, Korea. mandell@naver.com
Abstract
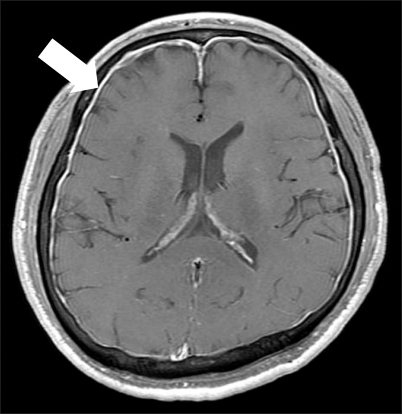
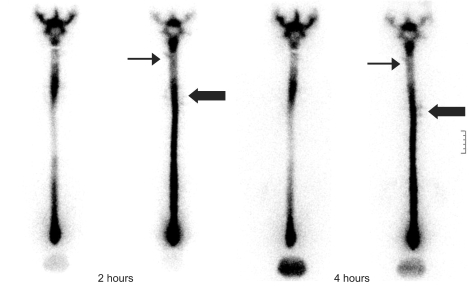
- Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) is considered to be a very rare disorder. It is characterized by an orthostatic headache that is aggravated with the patient in the upright position and it is relieved by the patient assuming the supine position. SIH is caused by a spontaneous spinal cerebrospinal fluid leakage without the patient having undergone trauma, surgery or dural puncture or having any other significant medical history. An autologous epidural blood patch (EBP) is effective in relieving SIH. We report here on a case of SIH with cerebrospinal fluid leakage at the upper cervical vertebral level and the middle thoracic vertebral level. The points of leakage were identified by radionuclide cisternography, and this patient was successfully managed by injecting an EBP at each level of leakage.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schievink WI, Maya MM, Moser F, Tourje J, Torbati S. Frequency of spontaneous intracranial hypotension in the emergency department. J Headache Pain. 2007; 8:325–328. PMID: 18071632.
Article2. Zaatreh M, Finkel A. Spontaneous intracranial hypotension. South Med J. 2002; 95:1342–1346. PMID: 12540006.
Article3. Kim KS, Lee DI, Kang WJ, Shin OY, Kwon MI. A case of cervical epidural blood patch for treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Korean J Pain. 2002; 15:198–203.4. Lee JI, Roh JH, Yoon DM, Lee YW. Spontaneous intracranial hypotension and epidural blood patch: a case report. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2005; 48:216–219.
Article5. Park JH, Yoon DM, Lee YC, Kim WO, Yoon KB. 10 times epidural blood patches for spontaneous intracranial hypotension: a case report. Korean J Pain. 2005; 18:60–63.
Article6. Berroir S, Loisel B, Ducros A, Boukobza M, Tzourio C, Valade D, et al. Early epidural blood patch in spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Neurology. 2004; 63:1950–1951. PMID: 15557521.
Article7. Schievink WI. Spontaneous spinal cerebrospinal fluid leaks. Cephalalgia. 2008; 28:1345–1356. PMID: 19037970.
Article8. Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society. The international classification of headache disorders: 2nd edition. Cephalalgia. 2004; 24(Suppl 1):8–160. PMID: 15595989.9. Mokri B, Posner JB. Spontaneous intracranial hypotension: the broadening clinical and imaging spectrum of CSF leaks. Neurology. 2000; 55:1771–1772. PMID: 11134370.
Article10. Hyun SH, Lee KH, Lee SJ, Cho YS, Lee EJ, Choi JY, et al. Potential value of radionuclide cisternography in diagnosis and management planning of spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2008; 110:657–661. PMID: 18457913.
Article11. Schievink WI, Maya MM, Louy C. Cranial MRI predicts outcome of spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Neurology. 2005; 64:1282–1284. PMID: 15824366.
Article12. Sainani NI, Lawande MA, Pungavkar SA, Desai M, Patkar DP, Mohanty PH. Spontaneous intracranial hypotension: a study of six cases with MR findings and literature review. Australas Radiol. 2006; 50:419–423. PMID: 16981936.
Article13. Mokri B, Hunter SF, Atkinson JL, Piepgras DG. Orthostatic headaches caused by CSF leak but with normal CSF pressures. Neurology. 1998; 51:786–790. PMID: 9748027.
Article14. Camann WR, Murray RS, Mushlin PS, Lambert DH. Effects of oral caffeine on postdural puncture headache. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Anesth Analg. 1990; 70:181–184. PMID: 2405733.15. Mokri B. Headaches caused by decreased intracranial pressure: diagnosis and management. Curr Opin Neurol. 2003; 16:319–326. PMID: 12858068.
Article16. Jung IS, Choe H, Han YJ, Son JS. Spontaneous intracranial hypotension treated with epidural blood patch: a case report. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2005; 49:581–584.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension: Detection of Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage by Early Dynamic Radionuclide Cisternography
- Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Treated with CT-guided Cervical Epidural Blood Patch : A case report
- Iatrogenic Development of Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage in Diagnosing Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
- Treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension with multiple leakage sites of cerebrospinal fluid : A case report
- Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Treated with Epidural Blood Patch