J Korean Acad Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs.
2017 Sep;26(3):248-259. 10.12934/jkpmhn.2017.26.3.248.
Mediating Effects of Cognitive Emotion Regulation on Influences of Self-differentiation and Family Function in High School Students' Problem Behavior
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, Graduate School, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2College of Nursing Science, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. sunghshin@khu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2392219
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12934/jkpmhn.2017.26.3.248
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was done to investigate the mediation effects of cognitive emotion regulation on influences of self-differentiation and family function in high school students' problem behavior.
METHODS
Study design was a cross-sectional descriptive analysis of causal research. A survey was conducted with 194 students in a C city high school. Data were analyzed using SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 21.0.
RESULTS
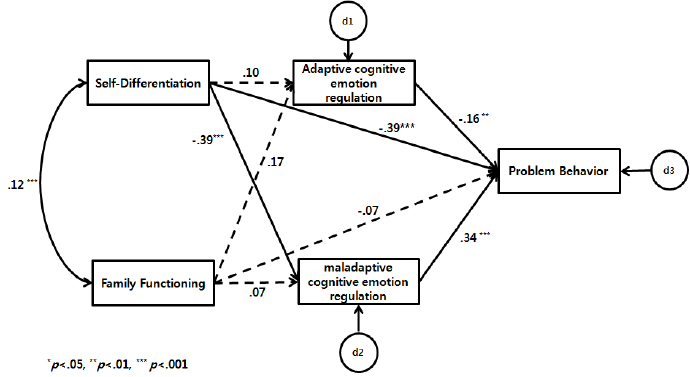
There were direct effects of self-differentiation (β= -.39, p<.001), adaptive cognitive emotion regulation strategies (β=-.16, p=.004) and maladaptive cognitive emotion regulation strategies (β=.34, p<.001) on problem behavior in these students. A mediator effect was found for self-differentiation, as it had a direct impact on the maladaptive cognitive emotion regulation strategy (β=-.15, p=.014), which then had a direct impact on problem behavior. However, family function had no direct impact on both the maladaptive cognitive emotion regulation strategy and the adaptive cognitive emotion regulation strategy and on problem behavior, no mediator effect was observed. Explanatory power of these variables for problem behavior was 48.0%.
CONCLUSION
Study findings suggest that to intervene for problem behavior in high school students, there is a need to develop and utilize programs that not only intervene for self-differentiation but also decrease high school students' use of non-adaptive cognitive emotion regulation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. National Youth Policy Institute of Korea. The First-Third Korean Children & Youth Panel Survey Data User Guide [Internet]. 2015. cited 2015 Nov 13. Available from: http://archive.nypi.re.kr/brdartcl/boardarticleList.do?brd_id=BDIDX_k9Fd9oFi29nooCcJ7kX1I4&srch_ctgry_idx=CTIDX00043&menu_nix=qZc474Ak.2. Chung IJ, Park JY, Kim EY. Factors predicting suicidal ideation and suicidal attempts of school youth and out-of-school youth. Ment Health Soc Work. 2010; 34:222–251.3. Gang MH, Kwon JS, Oh KO. Influencing factors of resilience of adolescents according to stress. Korean J Stress Res. 2012; 20(3):187–198.4. Oh YK, Lee HS. The effects of individual psychology, family environment and social environment factors on adolescents' behavior problems. J Korean Home Econ Educ Assoc. 2010; 22(4):51–64.5. Jung SH, Yoo JA. The effects of perceived neighborhood disorder on problem behavior among adolescents: the mediating effects of parent-child stress. J Korean Soc Child Welf. 2016; 56:1–32.6. Moon KS. The effect of academic stress on suicidal impulse in adolescence: mediating roles of parent and peer attachment. Korean J Child Stud. 2006; 27(5):143–157.7. Korean Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Survey of Youth Health Behavior [Internet]. 2016. cited 2016 Dec 27. Available from: http://cdc.go.kr/CDC/main.jsp.8. Kim CY, Jo HS. Self-differentiation, family function and stress level in high school students. J Korean Acad Child Health Nurs. 2008; 14(1):61–70.9. Han JC, Kim IK. The bullying and psychosocial dysfunction. Korean J Psychol Soc Issues. 2000; 6(2):103–114.10. Joo SJ. The effects of juvenile's self-differentiation on its delinquent disposition. J Korea Assoc Crim Psychol. 2012; 8(3):215–240.11. Lee HS. Effect of self-differentiation and family function on mental health in adolescents. J Korean Acad Child Health Nurs. 2010; 16(4):297–303. DOI: 10.4094/jkachn.2010.16.4.297.
Article12. Choi YS, Kim HY. Effect of adolescent's self-differentiation on the stress coping. J Soc Sci. 2005; 21:1–17.13. Chang KM. Associations between youth self-differentiation, perceived parental control, and psychological behavioral problems: mediating effects of self-differentiation. J Korea Acad Ind cooperation Soc. 2014; 15(2):845–854.
Article14. Yun EK, Shin SH. Comparison of the factors influencing young adolescents' aggression according to family structure. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2013; 43(3):321–330. DOI: 10.4040/jkan.2013.43.3.321.
Article15. Jung MS. The mediating effects of adaptive cognitive-emotion regulation strategies and positive affect on the relationship between acquired disabilities resilience, family resilience, and post-traumatic growth. J Rehabil Psychol. 2016; 23(2):349–366.16. Moon DG, Moon SB. A Structural relationship among the related variables of children's internalizing and externalizing problems. Korean J Child Stud. 2011; 32(5):49–65.
Article17. Nam YO, Kim JN. A study on psychosocial factors affecting adolescent problem behavior. J Adolesc Welf. 2010; 12(2):123–141.18. Kim SH. A study on relationships among the stressful events, cognitive emotion regulation strategies and psychological well-being. J Stud Guid Couns. 2004; 26:41–46.19. Cho SH. Self-differentiation and cognitive emotional control in adolescents and their influence on conflict resolution strategies [master's thesis]. Seoul: Sookmyung Womens University;2012. 65.20. Kim SA, Song HN. The effects of children's daily hassles and cognitive emotion regulation strategies on children's emotional and behavioral problems. J Hum Life Sci. 2012; 15:121–135.21. Kim MJ. Influences of self-differentiation and cognitive emotion regulation strategies on interpersonal problems. [master's thesis]. Seoul: The Catholic University of Korea;2010. 57.22. Kim HW, Lim JH, Lee JY. Family differentiation and worry of adolescents: the mediating effect of maladaptive perfectism and maladaptive cognitive emotion regulation. Korean J School Psychol. 2016; 13(2):267–293.
Article23. Mun SB. Basic concepts and applications of structural equating model. Seoul: Hakjisa;2009. p. 723.24. Je SB. The relationship between differentiation of self and dysfunction behavior: based on Bowen's family system theory [dissertation]. Seoul: Busan National University of Korea;1989. 115.25. Kim YH, Chung KH, Oh HS, Shin YJ, Yang YJ, Chung EH, et al. A study of mental health state and family function of parents with a mentally disabled person. J Korean Acad Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2009; 18(3):332–340.26. Eisenberg N, Sadovsky A, Spinrad TL, Fabes RA, Losoya SH, Valiente C, et al. The relations of problem behavior status to children's negative emotionality, effortful control, and impulsivity: concurrent relations and prediction of change. Dev Psychol. 2005; 41(1):193–211. DOI: 10.1037/0012-1649.41.1.193.
Article27. Kim DI, Choi SM, Hong SD. The relationship between psychological risk factors and problem behaviors of at-risk youth: validation of the mediating effect of environmental protective factors. Korea J Couns. 2007; 8(3):1121–1136.28. Lee JM, Cho YO. A study on factor of cyberbullying behavior depending on adolescent phase: a test of Thornberry's interaction theory. Inst Police Sci. 2016; 11(4):319–348.29. Kim JA. Application of logotherapy for enhance self-differentiation. J Korea Acad Ind cooperation Soc. 2008; 9(3):846–851.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Self-esteem, Depression, and Cognitive Emotion Regulation Strategies of University Students Residing in Dormitories
- Mediating Effect of Academic Emotion Regulation on the Relationship Between Self-Determined Learning Motivation and Learning Flow in Nursing Students in Remote Online Classes
- The Effect of Senior Elementary School Students’ Emotional Perception Clarity, Emotion Regulation, and Family Relationship on Non-Suicidal Self-Injury and Depression
- Self-differentiation, Family Function and Stress Level in High School Students
- Impact of Childhood Maltreatment on Cognitive Function and Its Relationship With Emotion Regulation in Young Adults