J Bone Metab.
2014 Feb;21(1):76-83.
Two Cases of Hypophosphatemic Osteomalacia After Long-term Low Dose Adefovir Therapy in Chronic Hepatitis B and Literature Review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Intermal Medicine, Dongsan Hospital, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. mdkim9111@dsmc.or.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Dongsan Hospital, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
Abstract
- Adefovir dipivoxil (ADV) is a nucleotide used as long-term therapy of chronic hepatitis B. Many published reports have shown that long-term high-dose therapy with adefovir can be associated with proximal renal tubular dysfunction resulting in significant hypophosphatemia, renal insufficiency and osteomalacia. We have encountered two patients who developed evidence of hypophosphatemic osteomalacia while on long-term low-dose adefovir therapy for chronic hepatitis B. We report on its clinical features and its potential resolution with cessation of the drug and supplementation with phosphate. We also reviewed the other published cases associated with hypophosphatemic osteomalacia after low-dose adefovir therapy. The symptoms and the hypophosphatemia improved after cessation of the drug and supplementation with phosphate in most cases. Patients taking adefovir long-term should receive regular investigation of the phosphate level and renal function.
MeSH Terms
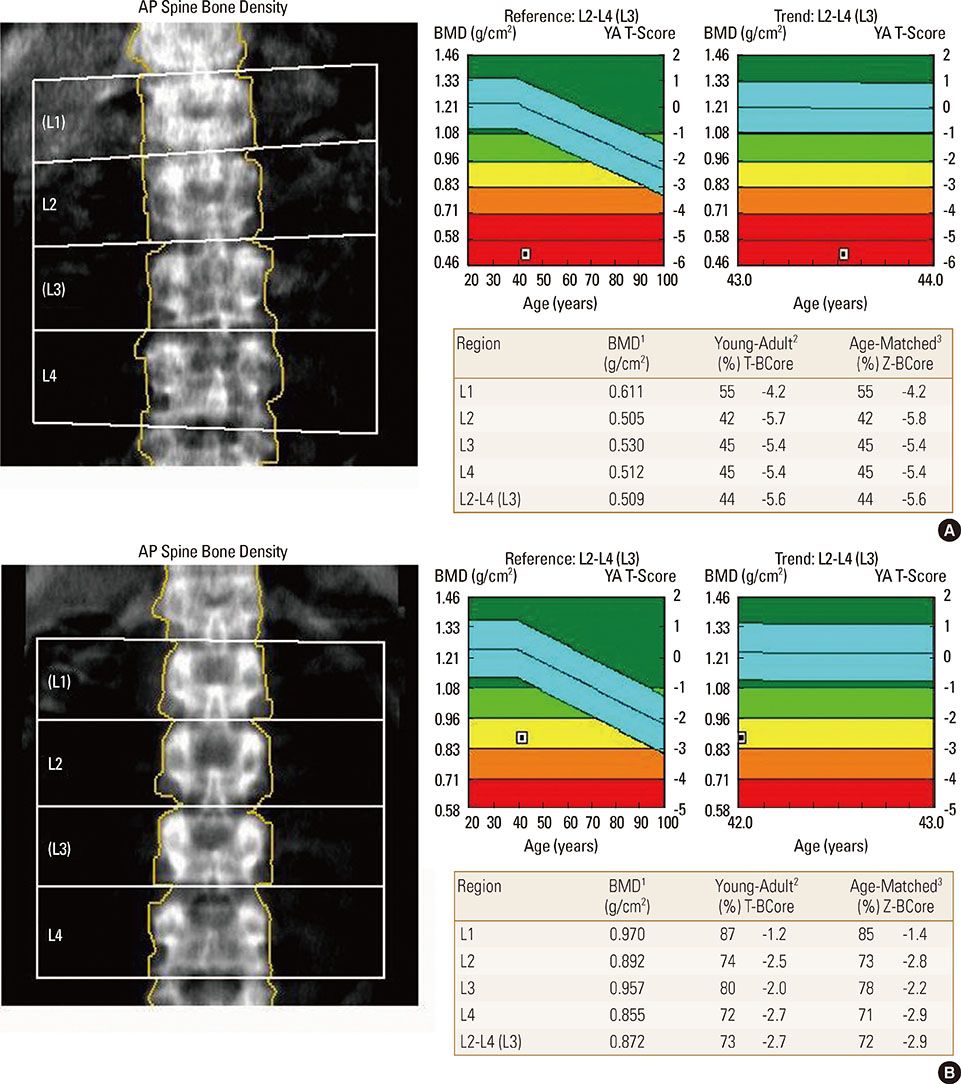
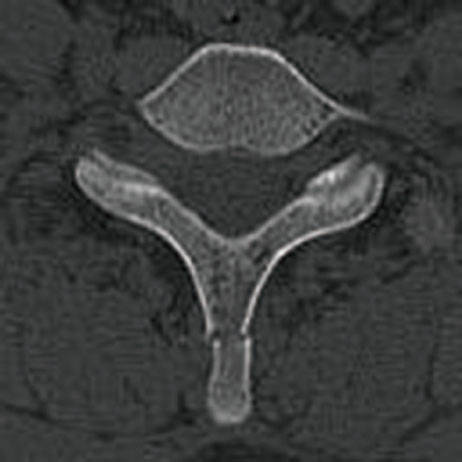
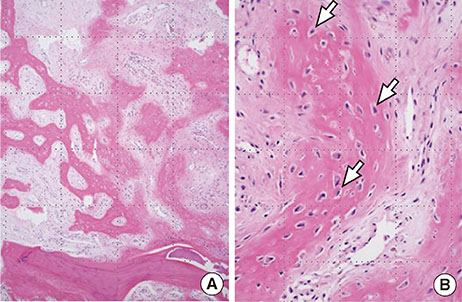
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee HJ, Choi JW, Kim TN, et al. A case of severe hypophosphatemia related to adefovir dipivoxil treatment in a patient with liver cirrhosis related to hepatitis B virus. Korean J Hepatol. 2008; 14:381–386.
Article2. Lee HC, Song YD, Ahn KJ, et al. A case adult onset hypophosphatemic osteomalacia. J Korean Soc Endocrinol. 1991; 6:75–81.3. Yoo KD, Jeong JH, Cho SK, et al. A case of hypophosphatemic osteomalacia associated with low-dose adefovir dipivoxil treatment. Korean J Med. 2010; 78:261–265.4. Lee KS, Kim DJ. Management of chronic hepatitis B. Korean J Hepatol. 2007; 13:447–488.
Article5. Tanji N, Tanji K, Kambham N, et al. Adefovir nephrotoxicity: possible role of mitochondrial DNA depletion. Hum Pathol. 2001; 32:734–740.
Article6. Izzedine H, Hulot JS, Launay-Vacher V, et al. Renal safety of adefovir dipivoxil in patients with chronic hepatitis B: two double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled studies. Kidney Int. 2004; 66:1153–1158.
Article7. Gara N, Zhao X, Collins MT, et al. Renal tubular dysfunction during long-term adefovir or tenofovir therapy in chronic hepatitis B. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012; 35:1317–1325.
Article8. Parfitt AM. Vitamin D and the pathogenesis of riskets and osteomalacia. In : Feldman D, Pike JW, Glorieux FH, editors. Vitamin D. 2nd ed. San Diego, CA: Elsevier Academic Press;2005. p. 1029–1048.9. Kwon SY, Ahn SY, Ko SY, et al. A case of osteomalacia related to adefovir in a patient with chronic hepatitis B. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2010; 56:117–120.
Article10. Wilson DR, York SE, Jaworski ZF, et al. Studies in hypophosphatemic vitamin D-refractory osteomalacia in adults. Medicine (Baltimore). 1965; 44:99–134.
Article11. Jung YK, Yeon JE, Choi JH, et al. Fanconi's syndrome associated with prolonged adefovir dipivoxil therapy in a hepatitis B virus patient. Gut Liver. 2010; 4:389–393.
Article12. Kim DH, Sung DH, Min YK. Hypophosphatemic osteomalacia induced by low-dose adefovir therapy: focus on manifestations in the skeletal system and literature review. J Bone Miner Metab. 2013; 31:240–246.
Article13. Girgis CM, Wong T, Ngu MC, et al. Hypophosphataemic osteomalacia in patients on adefovir dipivoxil. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2011; 45:468–473.
Article14. Law ST, Li KK, Ho YY. Acquired Fanconi syndrome associated with prolonged adefovir dipivoxil therapy in a chronic hepatitis B patient. Am J Ther. 2013; 20:e713–e716. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0b013e31820c4b20.
Article15. Sun XF, Zhang HB, Li XP, et al. A case of adefovir dipivoxil induced hypophosphataemic osteomalacia and literature review. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2011; 50:754–757.16. Li L, Dong GF, Zhang X, et al. Adefovir dipivoxil-induced Fanconi syndrome and hypophosphatemic osteomalacia associated with muscular weakness in a patient with chronic hepatitis B. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2011; 31:1956.17. Wu C, Zhang H, Qian Y, et al. Hypophosphatemic osteomalacia and renal Fanconi syndrome induced by low-dose adefovir dipivoxil: a case report and literature review suggesting ethnic predisposition. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2013; 38:321–326.
Article18. Tamori A, Enomoto M, Kobayashi S, et al. Add-on combination therapy with adefovir dipivoxil induces renal impairment in patients with lamivudine-refractory hepatitis B virus. J Viral Hepat. 2010; 17:123–129.
Article19. Minemura M, Tokimitsu Y, Tajiri K, et al. Development of osteomalacia in a post-liver transplant patient receiving adefovir dipivoxil. World J Hepatol. 2010; 2:442–446.
Article20. Shimohata H, Sakai S, Ogawa Y, et al. Osteomalacia due to Fanconi's syndrome and renal failure caused by long-term low-dose adefovir dipivoxil. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2013; 17:147–148.
Article21. Izzedine H, Kheder-Elfekih R, Housset P, et al. Adefovir dipivoxil-induced acute tubular necrosis and Fanconi syndrome in a renal transplant patient. AIDS. 2009; 23:544–545.
Article22. Wong T, Girgis CM, Ngu MC, et al. Hypophosphatemic osteomalacia after low-dose adefovir dipivoxil therapy for hepatitis B. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010; 95:479–480.
Article23. Fabbriciani G, de Socio GV, Massarotti M, et al. Adefovir induced hypophosphatemic osteomalacia. Scand J Infect Dis. 2011; 43:990–992.
Article24. Fontana RJ. Side effects of long-term oral antiviral therapy for hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2009; 49:S185–S195.
Article25. Izzedine H, Launay-Vacher V, Deray G. Antiviral drug-induced nephrotoxicity. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005; 45:804–817.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Three Cases of Osteomalacia with Fractures Induced by Adefovir in Chronic Hepatitis B
- An Uncommon Case of Bilateral Pathologic Hip Fractures: Antiviral Drug-induced Osteomalacia in a Patient with Hepatitis B
- A case of hypophosphatemic osteomalacia associated with low-dose adefovir dipivoxil treatment
- Recalcitrant Low Back Pain Diagnosed as Hypophosphatemic Osteomalacia Induced by Antiviral Medication
- A Case of Osteomalacia Related to Adefovir in a Patient with Chronic Hepatitis B