Ann Rehabil Med.
2012 Oct;36(5):681-687.
Effectiveness of Initial Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on the Newly Diagnosed Lateral or Medial Epicondylitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Daejeon Sun Hospital, Daejeon 301-725, Korea. rmactksk@naver.com
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Daejeon Sun Hospital, Daejeon 301-725, Korea.
- 3Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, School of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon 301-721, Korea.
- 4Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, School of Medicine, Kangwon National University and Hospital, Chuncheon 200-722, Korea.
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
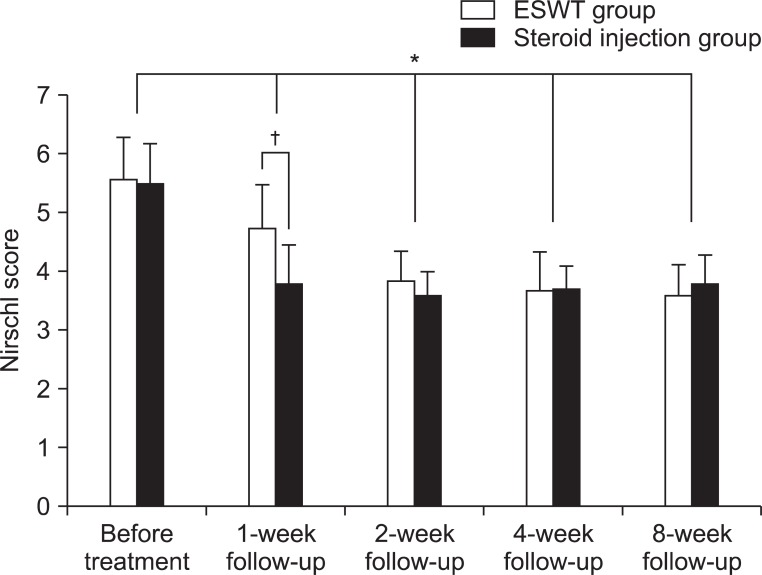
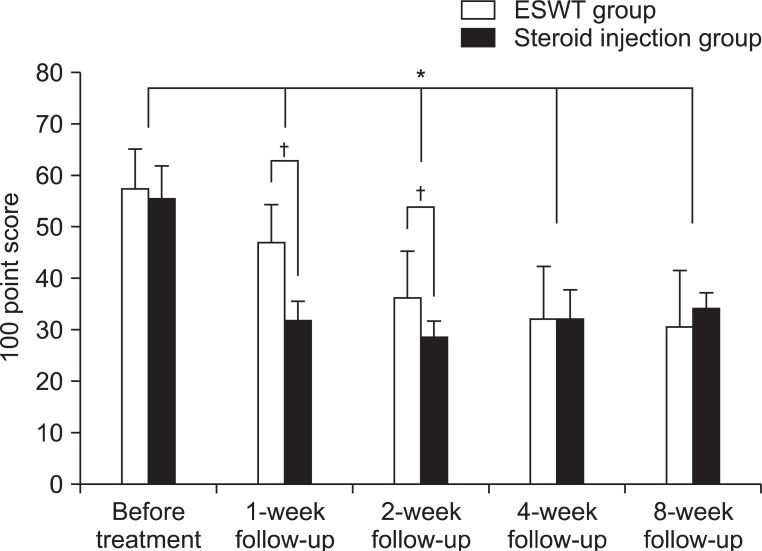
To evaluate the effectiveness of initial extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) for patients newly diagnosed with lateral or medial epicondylitis, compared to local steroid injection. METHOD: An analysis was conducted of twenty-two patients who were newly confirmed as lateral or medial epicondylitis through medical history and physical examination. The ESWT group (n=12) was treated once a week for 3 weeks using low energy (0.06-0.12 mJ/mm2, 2,000 shocks), while the local steroid injection group (n=10) was treated once with triamcinolone 10 mg mixed with 1% lidocaine solution. Nirschl score and 100 point score were assessed before and after the treatments of 1st, 2nd, 4th and 8th week. And Roles and Maudsley score was assessed one and eight weeks after the treatments.
RESULTS
Both groups showed significant improvement in Nirschl score and 100 point score during the entire period. The local steroid injection group improved more in Nirschl score at the first week and in 100 point score at the first 2 weeks, compared to those of the ESWT group. But the proportion of excellent and good grades of Roles and Maudsley score in the ESWT group increased more than that of local steroid injection group by the final 8th week.
CONCLUSION
The ESWT group improved as much as the local steroid injection group as treatment for medial and lateral epicondylitis. Therefore, ESWT can be a useful treatment option in patients for whom local steroid injection is difficult.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kraushaar BS, Nirschl RP. Tendinosis of the elbow (tennis elbow). Clinical features and findings of histological, immunohistochemical, and electron microscopy studies. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999; 81:259–278. PMID: 10073590.2. Boyd HB, Mcleod AC Jr. Tennis elbow. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973; 55:1183–1187. PMID: 4585946.
Article3. Friedlander HL, Reid RL, Cape RF. Tennis elbow. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1967; 51:109–116. PMID: 6027007.
Article4. Furia JP. Safety efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for chronic lateral epicondylitis. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2005; 34:13–19. PMID: 15707134.5. Shin JY, Seo KM, Kim DK, Kim BK, Kang SH. The effect of prolotherapy on lateral epicondylitis of elbow. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2002; 26:764–768.6. Connell DA, Ali KE, Ahmad M, Lambert S, Corbett S, Curtis M. Ultrasound-guided autologous blood injection for tennis elbow. Skeletal Radiol. 2006; 35:371–377. PMID: 16552606.
Article7. Wong SM, Hui AC, Tong PY, Poon DW, Yu E, Wong LK. Treatment of lateral epicondylitis with botulinum toxin: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 2005; 143:793–797. PMID: 16330790.8. Speed CA. Extracorporeal shock-wave therapy in the management of chronic soft-tissue conditions. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004; 86:165–171. PMID: 15046427.
Article9. Nirschl RP. Elbow tendinosis: tennis elbow. Clin Sports Med. 1992; 11:851–870. PMID: 1423702.10. Jung KH, Hwang JH, Chang HJ, Yoon YC, Park MJ, Yoo JC, Park WH. Low-energy extracorporeal shock wave therapy on chronic epicondylitis of the elbow: clinical and sonographic study. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2009; 33:77–83.11. Roles NC, Maudsley RH. Radial tunnel syndrome: resistant tennis elbow as nerve entrapment. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1972; 54:499–508. PMID: 4340924.12. Wang CJ, Chen HS. Shock wave therapy for patients with lateral epicondylitis of the elbow: a one- to two-year follow-up study. Am J Sports Med. 2002; 30:422–425. PMID: 12016085.13. Struijs PA, Smidt N, Arola H, van Dijk CN, Buchbinder R, Assendelft WJ. Orthotic devices for the treatment of tennis elbow. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001; (2):CD001821. PMID: 11406011.
Article14. Smidt N, van der Windt DA, Assendelft WJ, Deville WL, Korthals-de Bos IB, Bouter LM. Corticosteroid injections, physiotherapy, or a wait-and-see policy for lateral epicondylitis: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002; 359:657–662. PMID: 11879861.
Article15. Buchbinder R, Green S, Bell S, Barnsley L, Smidt N, Assendelft WJ. Surgery for lateral elbow pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002; (1):CD003525. PMID: 11869670.
Article16. Rompe JD, Hope C, Kullmer K, Heine J, Burger R. Analgesic effect of extracorporeal shock-wave therapy on chronic tennis elbow. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996; 78:233–237. PMID: 8666632.
Article17. Rompe JD, Kirkpatrick CJ, Kullmer K, Schwitalle M, Krischek O. Dose-related effects of shock waves on rabbit tendon Achillis. A sonographic and histological study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998; 80:546–552. PMID: 9619954.18. Takahashi N, Wada Y, Ohtori S, Saisu T, Moriya H. Application of shock waves to rat skin decreases calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in dorsal root ganglion neurons. Auton Neurosci. 2003; 107:81–84. PMID: 12963418.
Article19. Haake M, Konig IR, Decker T, Riedel C, Buch M, Muller HH. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the treatment of lateral epicondylitis: a randomized multicenter trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002; 84-A:1982–1991. PMID: 12429759.20. Oh JH, Yoon JP, Oh CH, Jo KH, Gong HS. Dose-related effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for lateral epicondylitis. J Korean Shoulder Elbow Soc. 2009; 12:21–26.21. Pettrone FA, McCall BR. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy without local anesthesia for chronic lateral epicondylitis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87:1297–1304. PMID: 15930540.
Article22. Labelle H, Guibert R, Newman N, Fallaha M, Rivard CH. Lack of scientific evidence for the treatment of lateral epicondylitis of the elbow. An attempted metaanalysis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992; 74:646–651. PMID: 1388172.
Article23. Verhaar JA, Wakenkamp GH, van Mameren H, Kester AD, van der Linden AJ. Local corticosteroid injection versus Cyriax-type physiotherapy for tennis elbow. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996; 78:128–132. PMID: 8898143.
Article24. Assendelft WJ, Hay EM, Adshead R, Bouter LM. Corticosteroid injections for lateral epicondylitis: a systematic overview. Br J Gen Pract. 1996; 46:209–216. PMID: 8703521.25. Kim JM, Kang SY, Hwang JH. The effect of exercise after local steroid injection on the rabbit Achilles tendon. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2002; 26:769–775.26. Kim SK, Kim JM, Park HS, Shin HJ, Hwang CH. Spontaneous bilateral Achilles tendon rupture after local steroid injection for carpal tunnel syndrome in a diabetic patient. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2009; 33:715–717.27. Speed CA, Nichols D, Richards C, Humphreys H, Wies JT, Burnet S, Hazleman BL. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for lateral epicondylitis-a double blind randomized controlled trial. J Orthop Res. 2002; 20:895–898. PMID: 12382950.
Article28. Stahl S, Kaufman T. The efficacy of an injection of steroids for medial epicondylitis. A prospective study of sixty elbows. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997; 79:1648–1652. PMID: 9384424.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Suggestions for Effective Extracorporeal Shock Wave Treatment Methods for Lateral Epicondylitis
- Dose Related Effect of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy in Lateral Epicondylitis
- Effect of Low-energy Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Calcifying Epicondylitis: Sonographic Follow-up
- Shockwave Therapy for Tennis Elbow
- Dose-related Effect of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Lateral Epicondylitis : Prospective Randomized Double Blind Comparative Study