Ann Rehabil Med.
2012 Oct;36(5):648-656.
Effect of Intradiscal Monopolar Pulsed Radiofrequency on Chronic Discogenic Back Pain Diagnosed by Pressure-Controlled Provocative Discography: A One Year Prospective Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Daegu 705-717, Korea. spineahn@ynu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Keimyung University Dongsan Center, Daegu 700-712, Korea.
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
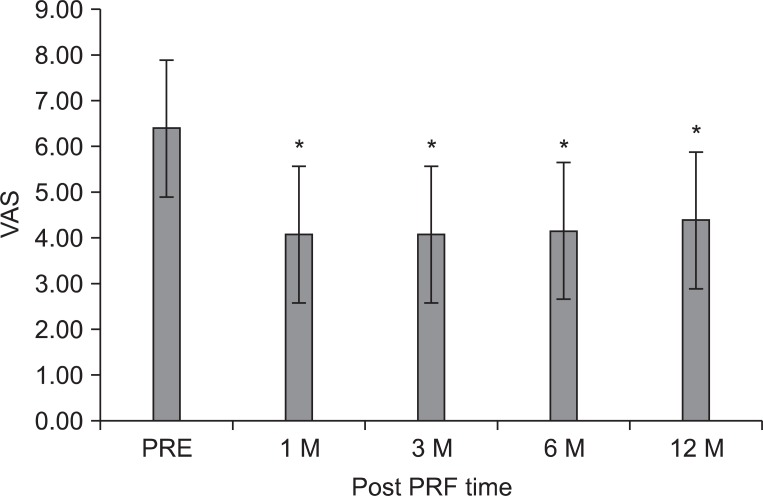
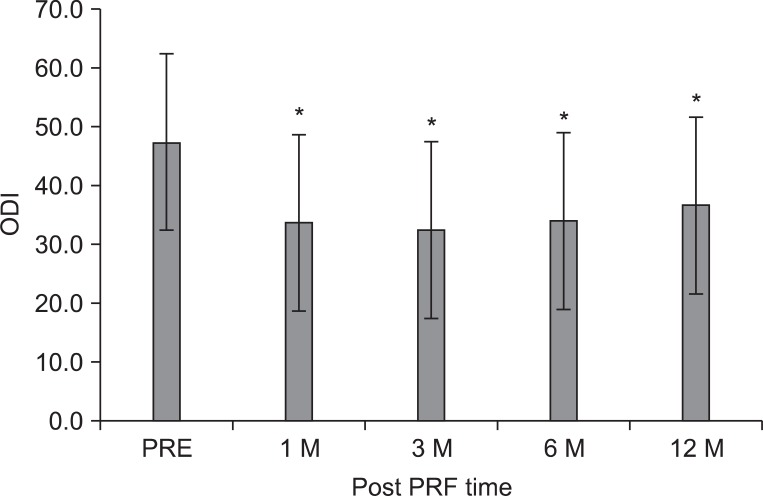
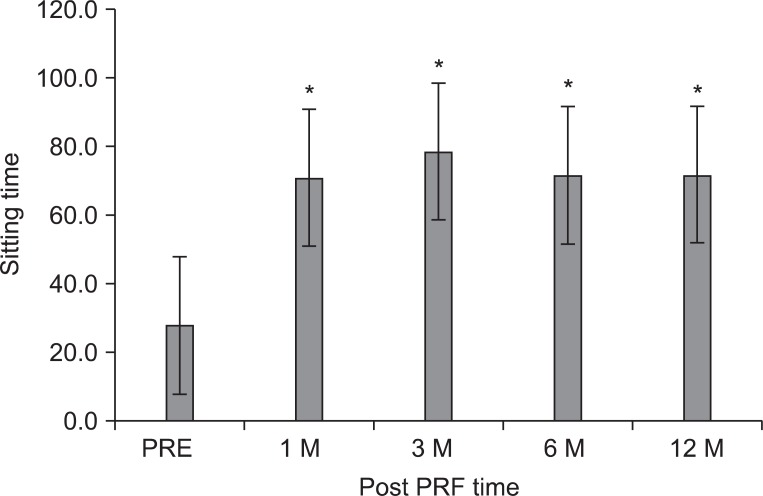
To investigate the efficacy and safety of percutaneous intradiscal monopolar pulsed radiofrequency (PRF) in patients with chronic disabling discogenic back pain. METHOD: Twenty-six subjects (7 males; mean age 43.2 years) with chronic back pain refractory to active rehabilitative management were recruited. All subjects underwent MRI for evaluation of Modic changes, and monopolar PRF (20 min at 60 V) at the center of target lumbar intervertebral disc confirmed by pressure-controlled provocative discography. Clinical outcomes were measured by the visual analogue scale (VAS), Oswestry disability index (ODI), and sitting tolerance time (ST) for 12 months after treatment. Successful clinical outcome was described as a minimum of 2 point reduction in VAS compared with the baseline at each follow-up period.
RESULTS
The mean VAS for low back pain reduced significantly from 6.4+/-1.1 at pre-treatment to 4.4+/-1.9 at 12 months (p<0.05). The mean ODI score was 47.3+/-15.4 points at pre-treatment and 36.7+/-19.5 at 12 months (p<0.001). The ST was 27.8+/-20.4 minutes at pre-treatment and 71.5+/-42.2 at 12 months (p<0.001). However, successful clinical outcome was achieved at 58%, 50%, and 42%, measured at 3, 6, and 12 months post-treatment. There were no significant relationship between the clinical outcome and Modic changes; no adverse events were recorded.
CONCLUSION
The results demonstrated that the application of intradiscal monopolar PRF might be relatively effective but limited; successful intervention for chronic refractory discogenic back pain is needed. To achieve the optimal outcome through intradiscal PRF, we suggested further studies about stimulation duration, mode, and intensity of PRF.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mooney V. Where is the lumbar pain coming from? Ann Med. 1989; 21:373–379. PMID: 2532527.
Article2. Schwarzer AC, Aprill CN, Derby R, Fortin J, Kine G, Bogduk N. The prevalence and clinical features of internal disc disruption in patients with chronic low back pain. Spine. 1995; 20:1878–1883. PMID: 8560335.
Article3. Crock HV. Internal disc disruption. A challenge to disc prolapse fifty years on. Spine. 1986; 11:650–653. PMID: 3787337.4. Kwan KM, Pang MK, Zhou S, Cowan SK, Kong RY, Pfordte T, Olsen BR, Sillence DO, Tam PP, Cheah KS. Abnormal compartmentalization of cartilage matrix components in mice lacking collagen X: implications for function. J Cell Biol. 1997; 136:459–471. PMID: 9015315.
Article5. Braithwaite I, White J, Saifuddin A, Renton P, Taylor BA. Vertebral end-plate (Modic) changes on lumbar spine MRI: correlation with pain reproduction at lumbar discography. Eur Spine J. 1998; 7:363–368. PMID: 9840468.
Article6. Modic MT, Steinberg PM, Ross JS, Masaryk TJ, Carter JR. Degenerative disk disease: assessment of changes in vertebral body marrow with MR imaging. Radiology. 1988; 166:193–199. PMID: 3336678.
Article7. Fayad F, Lefevre-Colau MM, Rannou F, Quintero N, Nys A, Macé Y, Poiraudeau S, Drapé JL, Revel M. Relation of inflammatory Modic changes to intradiscal steroid injection outcome in chronic low back pain. Eur Spine J. 2007; 16:925–931. PMID: 17216228.
Article8. Cao P, Jiang L, Zhuang C, Yang Y, Zhang Z, Chen W, Zheng T. Intradiscal injection therapy for degenerative chronic discogenic low back pain with end plate Modic changes. Spine J. 2011; 11:100–106. PMID: 20850390.
Article9. Freemont AJ, Peacock TE, Goupille P, Hoyland JA, O'Brien J, Jayson MI. Nerve ingrowth into diseased intervertebral disc in chronic back pain. Lancet. 1997; 350:178–181. PMID: 9250186.
Article10. Pagura JR. Percutaneous radiofrequency spinal rhizotomy. Appl Neurophysiol. 1983; 46:138–146. PMID: 6670863.
Article11. Choi HJ, Choi SK, Kim TS, Lim YJ. Pulsed radiofrequency neuromodulation treatment on the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve for the treatment of meralgia paresthetica. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2011; 50:151–153. PMID: 22053239.
Article12. Zhang J, Shi DS, Wang R. Pulsed radiofrequency of the second cervical ganglion (C2) for the treatment of cervicogenic headache. J Headache Pain. 2011; 12:569–571. PMID: 21611808.
Article13. Huang CC, Tsao SL, Cheng CY, Hsin MT, Chen CM. Treating frozen shoulder with ultrasound-guided pulsed mode radiofrequency lesioning of the suprascapular nerve: two cases. Pain Med. 2010; 11:1837–1840. PMID: 21040432.
Article14. Tsou HK, Chao SC, Wang CJ, Chen HT, Shen CC, Lee HT, Tsuei YS. Percutaneous pulsed radiofrequency applied to the L-2 dorsal root ganglion for treatment of chronic low-back pain: 3-year experience. J Neurosurg Spine. 2010; 12:190–196. PMID: 20121355.
Article15. Teixeira A, Sluijter ME. Intradiscal high-voltage, long-duration pulsed radiofrequency for discogenic pain: a preliminary report. Pain Med. 2006; 7:424–428. PMID: 17014601.
Article16. Rohof O. Intradiscal pulsed radiofrequency application following provocative discography for the management of degenerative disc disease and concordant pain: a pilot study. Pain Pract. 2012; 12:342–349. PMID: 22008239.
Article17. Kvarstein G, Mawe L, Indahl A, Hol PK, Tennoe B, Digernes R, Stubhaug A, Tonnessen TI, Beivik H. A randomized double-blind controlled trial of intra-annular radiofrequency thermal disc therapy--a 12-month follow-up. Pain. 2009; 145:279–286. PMID: 19647940.18. Urrutia G, Kovacs F, Nishishinya MB, Olabe J. Percutaneous thermocoagulation intradiscal techniques for discogenic low back pain. Spine. 2007; 32:1146–1154. PMID: 17471101.
Article19. Kim HI, Shin DA. Automated pressure-controlled discography with constant injection speed and real-time pressure measurement. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2009; 46:16–22. PMID: 19707489.
Article20. Gronblad M, Weinstein JN, Santavirta S. Immunohistochemical observations on spinal tissue innervation. A review of hypothetical mechanisms of back pain. Acta Orthop Scand. 1991; 62:614–622. PMID: 1837417.21. McCarthy PW, Carruthers B, Martin D, Petts P. Immunohistochemical demonstration of sensory nerve fibers and endings in lumbar intervertebral discs of the rat. Spine. 1991; 16:653–655. PMID: 1862405.
Article22. Pauza KJ, Howell S, Dreyfuss P, Peloza JH, Dawson K, Bogduk N. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of intradiscal electrothermal therapy for the treatment of discogenic low back pain. Spine J. 2004; 4:27–35. PMID: 14749191.
Article23. Wetzel FT, McNally TA, Phillips FM. Intradiscal electrothermal therapy used to manage chronic discogenic low back pain: new directions and interventions. Spine. 2002; 27:2621–2626. PMID: 12436005.24. Shah RV, Lutz GE, Lee J, Doty SB, Rodeo S. Intradiskal electrothermal therapy: a preliminary histologic study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2001; 82:1230–1237. PMID: 11552196.
Article25. Yilmaz C, Kabatas S, Cansever T, Gulsen S, Coven I, Caner H, Altinors N. Radiofrequency facet joint neurotomy in treatment of facet syndrome. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2010; 23:480–485. PMID: 20124916.
Article26. Rosen S, Falco F. Radiofrequency stimulation of intervertebral discs. Pain Physician. 2003; 6:435–438. PMID: 16871294.
Article27. Smith HP, McWhorter JM, Challa VR. Radiofrequency neurolysis in a clinical model. Neuropathological correlation. J Neurosurg. 1981; 55:246–253. PMID: 7252548.28. Cahana A, Vutskits L, Muller D. Acute differential modulation of synaptic transmission and cell survival during exposure to pulsed and continuous radiofrequency energy. J Pain. 2003; 4:197–202. PMID: 14622704.
Article29. Higuchi Y, Nashold BS Jr, Sluijter M, Cosman E, Pearlstein RD. Exposure of the dorsal root ganglion in rats to pulsed radiofrequency currents activates dorsal horn lamina I and II neurons. Neurosurgery. 2002; 50:850–856. PMID: 11904038.
Article30. Hagiwara S, Iwasaka H, Takeshima N, Noguchi T. Mechanisms of analgesic action of pulsed radiofrequency on adjuvant-induced pain in the rat: roles of descending adrenergic and serotonergic systems. Eur J Pain. 2009; 13:249–252. PMID: 18539061.
Article31. Erdine S, Bilir A, Cosman ER, Cosman ER Jr. Ultrastructural changes in axons following exposure to pulsed radiofrequency fields. Pain Pract. 2009; 9:407–417. PMID: 19761513.
Article32. Kim HI, Shin DA. Automated pressure-controlled discography with constant injection speed and real-time pressure measurement. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2009; 46:16–22. PMID: 19707489.
Article33. Shin DA, Kim SH, Han IB, Rhim SC, Kim HI. Factors influencing manometric pressure during pressure-controlled discography. Spine. 2009; 34:E790–E793. PMID: 19829241.
Article34. Luoma K, Vehmas T, Gronblad M, Kerttula L, Kaapa E. Relationship of Modic type 1 change with disc degeneration: a prospective MRI study. Skeletal Radiol. 2009; 38:237–244. PMID: 19096840.
Article35. Kresina TF, Malemud CJ, Moskowitz RW. Analysis of osteoarthritic cartilage using monoclonal antibodies reactive with rabbit proteoglycan. Arthritis Rheum. 1986; 29:863–871. PMID: 2427091.
Article36. Cao P, Jiang L, Zhuang C, Yang Y, Zhang Z, Chen W, Zheng T. Intradiscal injection therapy for degenerative chronic discogenic low back pain with end plate Modic changes. Spine J. 2011; 11:100–106. PMID: 20850390.
Article37. Zhuang CY, Cao P, Zheng T, Yang YQ, Zhang ZW, Chen W. Intradiscal interventional therapy for degenerative chronic discogenic low back pain with end-plate Modic changes. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2009; 89:2490–2494. PMID: 20137437.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intradiscal Electrothermotherapy(IDET) in Patients with Chronic Discogenic Low Back Pain; Preliminary Report
- Diagnostic Relevance of Pressure-Controlled Discography
- Provocative Discography Following Focal Selective Coagulation in a Patient with Chronic Lumbar Discogenic Pain
- Effect of Intradiscal Methylene Blue Injection for the Chronic Discogenic Low Back Pain: One Year Prospective Follow-up Study
- Discitis after Intradiscal Radiofrequency Themocoagulation in Patient with Chronic Discogenic Low Back Pain