Korean Circ J.
2016 Sep;46(5):601-609. 10.4070/kcj.2016.46.5.601.
J Wave Syndromes: History and Current Controversies
- Affiliations
-
- 1Tianjin Key Laboratory of Ionic-Molecular Function of Cardiovascular disease, Department of Cardiology, Tianjin Institute of Cardiology, The Second Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin, China.
- 2Department of cardiology, The Second Hospital of Jiaxing, Jiaxing, China.
- 3Lankenau Institute for Medical Research and Lankenau Medical Center, Wynnewood, Pennsylvania, USA. YanG@mlhs.org
- 4The First Affiliated Hospital, Medical School of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, China.
- KMID: 2389614
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2016.46.5.601
Abstract
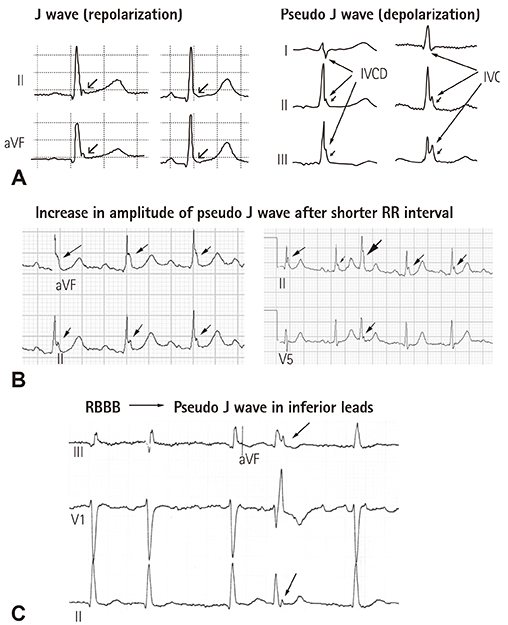
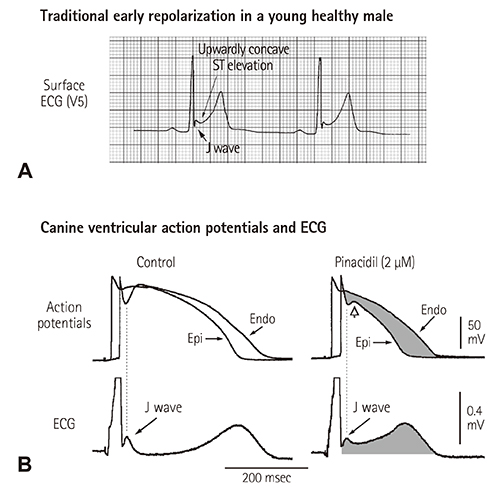
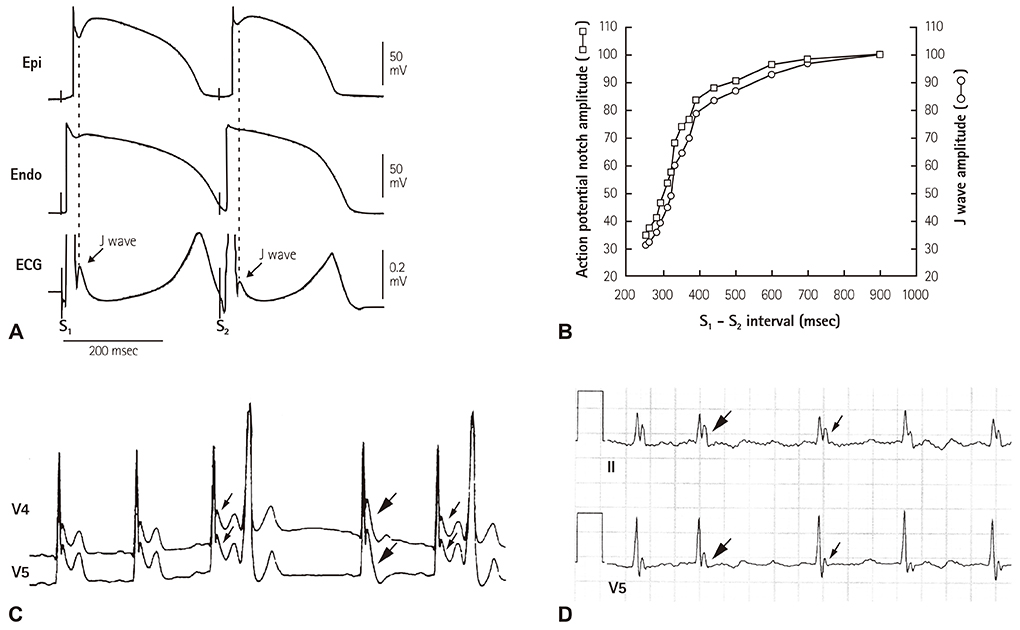
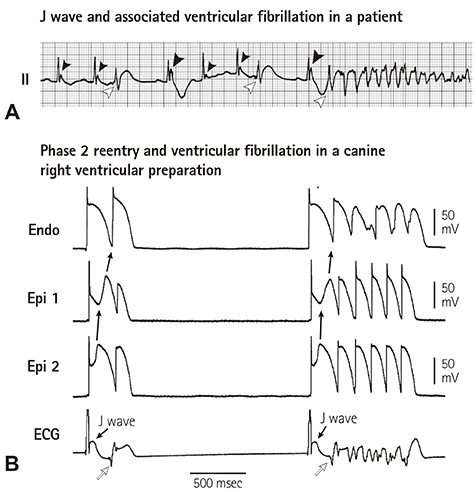
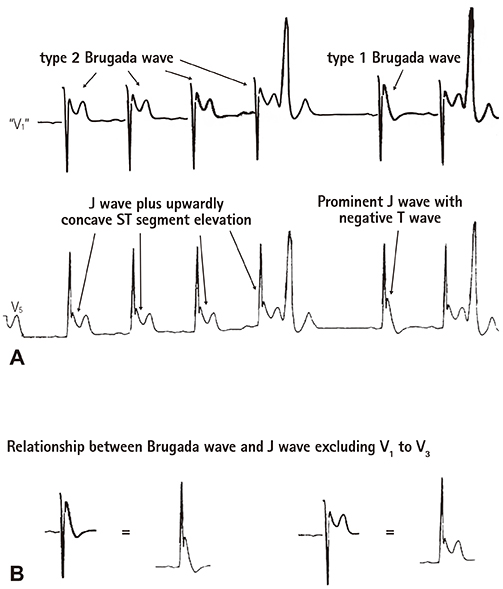
- The concept of J wave syndromes was first proposed in 2004 by Yan et al for a spectrum of electrocardiographic (ECG) manifestations of prominent J waves that are associated with a potential to predispose affected individuals to ventricular fibrillation (VF). Although the concept of J wave syndromes is widely used and accepted, there has been tremendous debate over the definition of J wave, its ionic and cellular basis and arrhythmogenic mechanism. In this review article, we attempted to discuss the history from which the concept of J wave syndromes (JWS) is evolved and current controversies in JWS.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Multicenter Cohort Analysis Unveil Inherited Arrhythmia in Korea
Il-young Oh
Korean Circ J. 2023;53(10):708-709. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2023.0214.
Reference
-
1. Yan GX, Yao QH, Wang DQ, Cui CC. J wave and J wave syndromes (in Chinese). Chin J Card Arrhythm. 2004; 8:360–365.2. Shipley RA, Hallaran WR. The four lead electrocardiogram in 200 normal men and women. Am Heart J. 1936; 11:325–345.3. Osborn JJ. Experimental hypothermia; respiratory and blood pH changes in relation to cardiac function. Am J Physiol. 1953; 175:389–398.4. Yan GX, Antzelevitch C. Cellular basis for the electrocardiographic J wave. Circulation. 1996; 93:372–379.5. Badri M, Patel A, Yan GX. Cellular and ionic basis of J-wave syndromes. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2015; 25:12–21.6. Antzelevitch C, Yan GX. J-wave syndromes: Brugada and early repolarization syndromes. Heart Rhythm. 2015; 12:1852–1866.7. Brugada P, Brugada J. Right bundle branch block, persistent ST segment elevation and sudden cardiac death: a distinct clinical and electrocardiographic syndrome. A multicenter report. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1992; 20:1391–1396.8. Kalla H, Yan GX, Marinchak R. Ventricular fibrillation in a patient with prominent J (Osborn) waves and ST segment elevation in the inferior electrocardiographic leads: a Brugada syndrome variant? J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2000; 11:95–98.9. Takagi M, Aihara N, Takaki H, et al. Clinical characteristics of patients with spontaneous or inducible ventricular fibrillation without apparent heart disease presenting with J wave and ST segment elevation in inferior leads. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2000; 11:844–848.10. Qi X, Sun F, An X, Yang J. A case of Brugada syndrome with ST segment elevation through entire precordial leads. Chin J Cardiol. 2004; 32:272–273.11. Shu J, Zhu T, Yang L, Cui C, Yan GX. ST-segment elevation in the early repolarization syndrome, idiopathic ventricular fibrillation, and the Brugada syndrome: cellular and clinical linkage. J Electrocardiol. 2005; 38:26–32.12. Hlaing T, DiMino T, Kowey PR, Yan GX. ECG repolarization waves: their genesis and clinical implications. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2005; 10:211–223.13. Haissaguerre M, Derval N, Sacher F, et al. Sudden cardiac arrest associated with early repolarization. N Engl J Med. 2008; 358:2016–2023.14. Antzelevitch C, Yan GX. J-wave syndromes. from cell to bedside. J Electrocardiol. 2011; 44:656–661.15. Li GL, Yang L, Cui CC, Sun CF, Yan GX. J wave syndromes: a decade of progress. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015; 128:969–975.16. Wasserburger RH, Alt WJ. The normal RS-T segment elevation variant. Am J Cardiol. 1961; 8:184–192.17. Gussak I, Antzelevitch C. Early repolarization syndrome: clinical characteristics and possible cellular and ionic mechanisms. J Electrocardiol. 2000; 33:299–309.18. Priori SG, Wilde AA, Horie M, et al. HRS/EHRA/APHRS expert consensus statement on the diagnosis and management of patients with inherited primary arrhythmia syndromes: document endorsed by HRS, EHRA, and APHRS in May 2013 and by ACCF, AHA, PACES, and AEPC in June 2013. Heart Rhythm. 2013; 10:1932–1963.19. Macfarlane PW, Antzelevitch C, Haissaguerre M, et al. The Early Repolarization Pattern: A Consensus Paper. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015; 66:470–477.20. Surawicz B, Macfarlane PW. Inappropriate and confusing electrocardiographic terms: J-wave syndromes and early repolarization. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011; 57:1584–1586.21. Bastiaenen R, Behr ER. Benign or malignant, early or delayed: the changing face of early repolarization. Europace. 2012; 14:5–7.22. Klatsky AL, Oehm R, Cooper RA, Udaltsova N, Armstrong MA. The early repolarization normal variant electrocardiogram: correlates and consequences. Am J Med. 2003; 115:171–177.23. Tikkanen JT, Anttonen O, Junttila MJ, et al. Long-term outcome associated with early repolarization on electrocardiography. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:2529–2537.24. Sinner MF, Reinhard W, Müller M, et al. Association of early repolarization pattern on ECG with risk of cardiac and all-cause mortality: a population-based prospective cohort study (MONICA/KORA). PLoS Med. 2010; 7:e1000314.25. Wu SH, Lin XX, Cheng YJ, Qiang CC, Zhang J. Early repolarization pattern and risk for arrhythmia death: a meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013; 61:645–650.26. Husfeldt E, Secher O. Ventricular fibrillation during hypothermia successfully treated by rewarming and electroshock. Thorax. 1956; 11:67–70.27. Caldini P. Ventricular fibrillation in induced hypothermia. Postgrad Med J. 1959; 35:538–542.28. Johnson P, Lesage A, Floyd WL, Young WG Jr, Sealy WC. Prevention of ventricular fibrillation during profound hypothermia by quinidine. Ann Surg. 1960; 151:490–495.29. Yan GX, Antzelevitch C. Cellular basis for the Brugada syndrome and other mechanisms of arrhythmogenesis associated with ST-segment elevation. Circulation. 1999; 100:1660–1666.30. Otto CM, Tauxe RV, Cobb LA, et al. Ventricular fibrillation causes sudden death in Southeast Asian immigrants. Ann Intern Med. 1984; 101:45–47.31. Aizawa Y, Tamura M, Chinushi M, et al. Idiopathic ventricular fibrillation and bradycardia-dependent intraventricular block. Am Heart J. 1993; 126:1473–1474.32. Aizawa Y, Sato M, Kitazawa H, et al. Tachycardia-dependent augmentation of "notched J waves" in a general patient population without ventricular fibrillation or cardiac arrest: not a repolarization but a depolarization abnormality? Heart Rhythm. 2015; 12:376–383.33. Antzelevitch C, Yan GX. J wave syndromes. Heart Rhythm. 2010; 7:549–558.34. Belhassen B, Glick A, Viskin S. Excellent long-term reproducibility of the electrophysiologic efficacy of quinidine in patients with idiopathic ventricular fibrillation and Brugada syndrome. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2009; 32:294–301.35. Yan GX, Lankipalli RS, Burke JF, Musco S, Kowey PR. Ventricular repolarization components on the electrocardiogram: cellular basis and clinical significance. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003; 42:401–409.36. Nademanee K, Veerakul G, Chandanamattha P, et al. Prevention of ventricular fibrillation episodes in Brugada syndrome by catheter ablation over the anterior right ventricular outflow tract epicardium. Circulation. 2011; 123:1270–1279.37. Szél T, Antzelevitch C. Abnormal repolarization as the basis for late potentials and fractionated electrograms recorded from epicardium in experimental models of Brugada syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014; 63:2037–2045.38. Nademanee K, Raju H, de Noronha SV, et al. Fibrosis, connexin-43, and conduction abnormalities in the Brugada syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015; 66:1976–1986.39. Gussak I, Bjerregaard P, Egan TM, Chaitman BR. ECG phenomenon called the J wave. History, pathophysiology, and clinical significance. J Electrocardiol. 1995; 28:49–58.40. Tikkanen JT, Junttila MJ, Anttonen O, et al. Early repolarization: electrocardiographic phenotypes associated with favorable long-term outcome. Circulation. 2011; 123:2666–2673.