Korean Circ J.
2017 Sep;47(5):769-775. 10.4070/kcj.2017.0059.
The Mid-term Results of Thoracoscopic Closure of Atrial Septal Defects
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. bestsurgeon@gmail.com
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2389609
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2017.0059
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
Recently, minimally invasive surgical (MIS) techniques including robot-assisted operations have been widely applied in cardiac surgery. The thoracoscopic technique is a favorable MIS option for patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs). Accordingly, we report the mid-term results of thoracoscopic ASD closure without robotic assistance.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
We included 66 patients who underwent thoracoscopic ASD closure between June 2006 and July 2014. Mean age was 27±9 years. The mean size of the ASD was 25.9±6.3 mm. Eleven patients (16.7%) had greater than mild tricuspid regurgitation (TR). The TR pressure gradient was 32.4±8.6 mmHg.
RESULTS
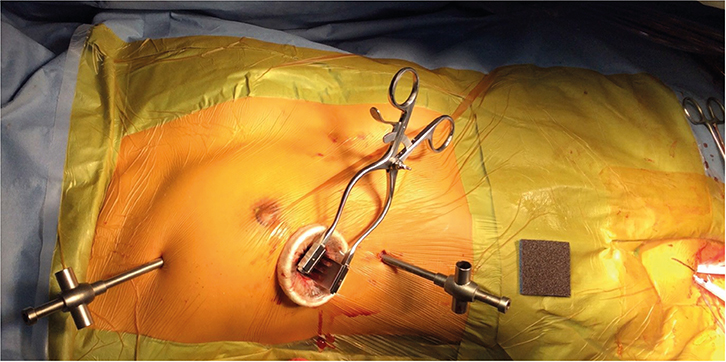
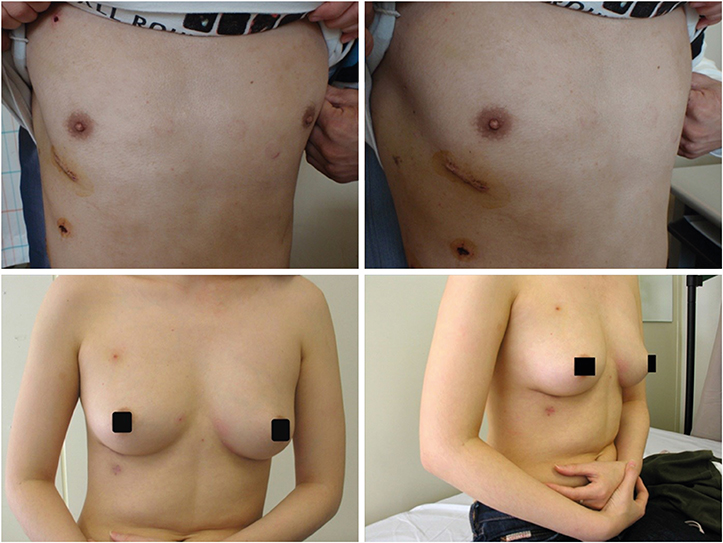
Fifty-two (78.8%) patients underwent closure with a pericardial patch and 14 (21.2%) underwent direct suture closure. Concomitant procedures included tricuspid valve repair in 8 patients (12.1%), mitral valve repair in 4 patients (6.1%), and right isthmus block in 1 patient (1.5%). The mean length of the right thoracotomy incision was 4.5±0.9 cm. The mean cardiopulmonary bypass time was 159±43 minutes, and the mean aortic cross clamp time was 79±29 minutes. The mean hospital stay lasted 6.1±2.6 days. There were no early deaths. There were 2 reoperations. One was due to ASD patch detachment and the other was due to residual mitral regurgitation after concomitant mitral valve repair. However, there have been no reoperations since July 2010. There were 2 pneumothoraxes requiring chest tube re-insertion. There was one wound dehiscence in an endoscopic port. The mean follow-up duration was 33±31 months. There were no deaths, residual shunts, or reoperations during follow-up.
CONCLUSION
Thoracoscopic ASD closure without robotic assistance is feasible, suggesting that this method is a reliable MIS option for patients with ASDs.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Cardiopulmonary Bypass
Chest Tubes
Follow-Up Studies
Heart Septal Defects, Atrial*
Humans
Length of Stay
Methods
Minimally Invasive Surgical Procedures
Mitral Valve
Mitral Valve Insufficiency
Pneumothorax
Sutures
Thoracic Surgery
Thoracic Surgery, Video-Assisted
Thoracoscopes
Thoracotomy
Tricuspid Valve
Tricuspid Valve Insufficiency
Wounds and Injuries
Figure
Reference
-
1. Khan JH, McElhinney DB, Reddy VM, Hanley FL. Repair of secundum atrial septal defect: limiting the incision without sacrificing exposure. Ann Thorac Surg. 1998; 66:1433–1435.2. Jun TG, Park PW, Lee YT, et al. Full sternotomy with minimal skin incision for congenital heart surgery. Cardiovasc Surg. 2002; 10:595–599.3. Bichell DP, Geva T, Bacha EA, Mayer JE, Jonas RA, del Nido PJ. Minimal access approach for the repair of atrial septal defect: the initial 135 patients. Ann Thorac Surg. 2000; 70:115–118.4. Black MD, Freedom RM. Minimally invasive repair of atrial septal defects. Ann Thorac Surg. 1998; 65:765–767.5. Kim H, Kim SH, Kim YH, et al. The comparision of right anterolateral thoracotomy and median sternotomy in the atrial septal defect repair. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003; 36:1–6.6. Ryan WH, Cheirif J, Dewey TM, Prince SL, Mack MJ. Safety and efficacy of minimally invasive atrial septal defect closure. Ann Thorac Surg. 2003; 75:1532–1534.7. Poyrazoglu HH, Avsar MK, Demir S, Karakaya Z, Güler T, Tor F. Atrial septal defect closure: comparison of vertical axillary minithoracotomy and median sternotomy. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2013; 46:340–345.8. Morgan JA, Peacock JC, Kohmoto T, et al. Robotic techniques improve quality of life in patients undergoing atrial septal defect repair. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004; 77:1328–1333.9. Argenziano M, Oz MC, Kohmoto T, et al. Totally endoscopic atrial septal defect repair with robotic assistance. Circulation. 2003; 108:Suppl 1. II191–II194.10. Xiao C, Gao C, Yang M, et al. Totally robotic atrial septal defect closure: 7-year single-institution experience and follow-up. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2014; 19:933–937.11. Däbritz S, Sachweh J, Walter M, Messmer BJ. Closure of atrial septal defects via limited right anterolateral thoracotomy as a minimal invasive approach in female patients. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 1999; 15:18–23.12. Butera G, Romagnoli E, Carminati M, et al. Treatment of isolated secundum atrial septal defects: impact of age and defect morphology in 1,013 consecutive patients. Am Heart J. 2008; 156:706–712.13. Torracca L, Ismeno G, Alfieri O. Totally endoscopic computer-enhanced atrial septal defect closure in six patients. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001; 72:1354–1357.14. Vistarini N, Aiello M, Mattiucci G, et al. Port-access minimally invasive surgery for atrial septal defects: a 10-year single-center experience in 166 patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010; 139:139–145.15. Wimmer-Greinecker G, Dogan S, Aybek T, et al. Totally endoscopic atrial septal repair in adults with computer-enhanced telemanipulation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003; 126:465–468.16. Masura J, Gavora P, Podnar T. Long-term outcome of transcatheter secundum-type atrial septal defect closure using Amplatzer septal occluders. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005; 45:505–507.17. Kim KH, Song J, Kang IS, Chang SA, Huh J, Park SW. Balloon occlusive diameter of non-circular atrial septal defects in transcatheter closure with amplatzer septal occluder. Korean Circ J. 2013; 43:681–685.18. Menkis AH, Kodera K, Kiaii B, Swinamer SA, Rayman R, Boyd WD. Robotic surgery, the first 100 cases: where do we go from here? Heart Surg Forum. 2004; 7:1–4.19. Kim JE, Jung SH, Kim GS, et al. Surgical outcomes of congenital atrial septal defect using da VinciTM Surgical Robot System. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2013; 46:93–97.20. Ma ZS, Dong MF, Yin QY, Feng ZY, Wang LX. Totally thoracoscopic repair of atrial septal defect without robotic assistance: a single-center experience. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011; 141:1380–1383.21. Liu G, Qiao Y, Ma L, Ni L, Zeng S, Li Q. Totally thoracoscopic surgery for the treatment of atrial septal defect without of the robotic da Vinci surgical system. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2013; 8:119.22. Yao DK, Chen H, Ma LL, Ma ZS, Wang LX. Totally endoscopic atrial septal repair with or without robotic assistance: a systematic review and meta-analysis of case series. Heart Lung Circ. 2013; 22:433–440.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Procedural, Early and Long-Term Outcomes after Transcatheter Atrial Septal Defects Closure: Comparison between Large and Very Large Atrial Septal Defect Groups
- Totally Thoracoscopic Ablation for Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation after Atrial Septal Defect Device Closure
- Comprehensive understanding of atrial septal defects by imaging studies for successful transcatheter closure
- Emergent Surgical Intervention for Embolization of Atrial Septal Defect Closure Device
- Transcatheter Closure of Secundum Atrial Septal Defect with the Amplatzer Septal Occluder