Ann Rehabil Med.
2017 Apr;41(2):231-238. 10.5535/arm.2017.41.2.231.
Effect of Vallecular Ballooning in Stroke Patients With Dysphagia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Myongji Hospital, Goyang, Korea. rallo1080@naver.com
- KMID: 2389481
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2017.41.2.231
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate the improvement of dysphagia after balloon dilatation and balloon swallowing at the vallecular space with a Foley catheter in stroke patients.
METHODS
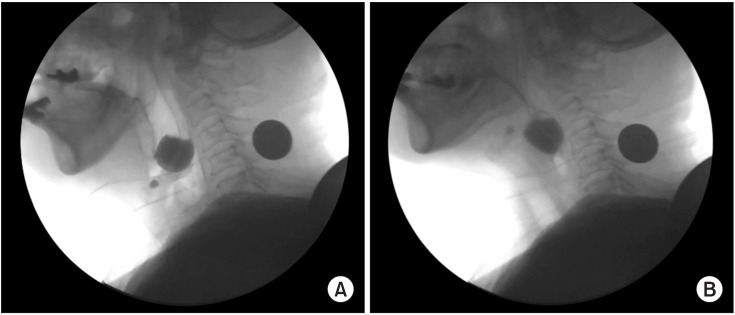
This study was conducted between May 1, 2012 and December 31, 2015, and involved 30 stroke patients with complaints of difficulty in swallowing. All patients underwent videofluoroscopic swallowing study (VFSS) before and after vallecular ballooning. VFSS was performed with a 4 mL semisolid bolus. For vallecular ballooning, two trainings were performed for at least 10 minutes, including backward stretching of the epiglottis and swallowing of a balloon located in the vallecular space, by checking the movement of the Foley catheter tip in real time using VFSS.
RESULTS
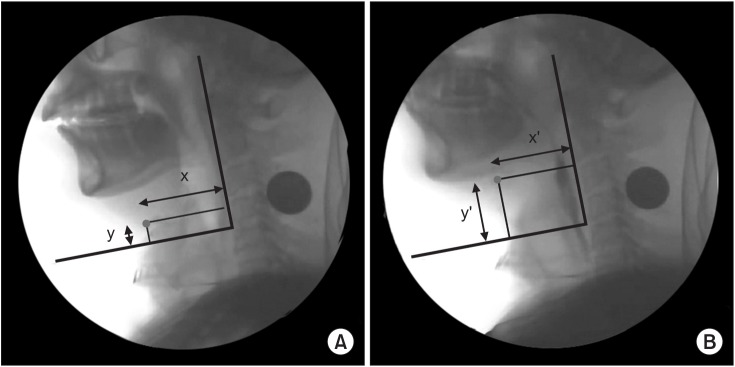
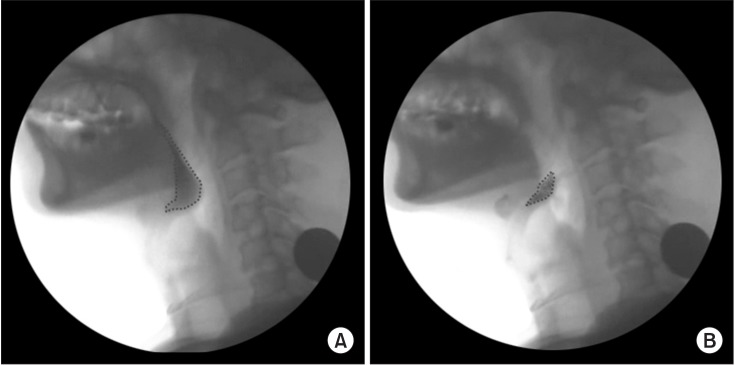
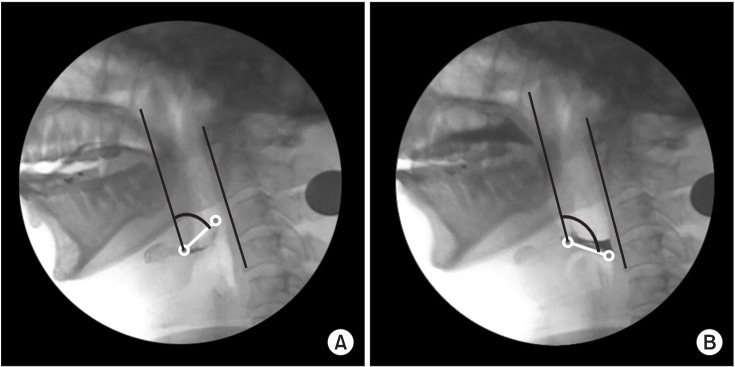
After examination of the dysphagia improvement pattern before and after vallecular ballooning, laryngeal elevation (x-axis: pre 2.62±1.51 mm and post 3.54±1.93 mm, p=0.038; y-axis: pre 17.11±4.24 mm and post 22.11±3.46 mm, p=0.036), pharyngeal transit time (pre 5.76±6.61 s and post 4.08±5.49 s, p=0.043), rotation of the epiglottis (pre 53.24°±26.77° and post 32.45°±24.60°, p<0.001), and post-swallow pharyngeal remnant (pre 41.31%±23.77% and post 32.45%±24.60%, p=0.002) showed statistically significant differences. No significant difference was observed in the penetration-aspiration scale score (pre 4.73±1.50 and post 4.46±1.78, p=0.391).
CONCLUSION
For stroke patients with dysmotility of the epiglottis and post-swallowing residue, vallecular ballooning can be considered as an alternative method that can be applied without risk of aspiration in dysphagia treatment.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Efficacy of a 4-Week Swallowing Rehabilitation Program Combined With Pyriform Sinus Ballooning in Patients With Post-stroke Dysphagia
Yong Kyun Kim, Kyun Yeon Lee, Sang-Heon Lee
Ann Rehabil Med. 2018;42(4):542-550. doi: 10.5535/arm.2018.42.4.542.
Reference
-
1. Fink BR, Martin RW, Rohrmann CA. Biomechanics of the human epiglottis. Acta Otolaryngol. 1979; 87:554–559. PMID: 463526.
Article2. Ekberg O, Sigurjonsson SV. Movement of the epiglottis during deglutition: a cineradiographic study. Gastrointest Radiol. 1982; 7:101–107. PMID: 7084590.3. Garon BR, Huang Z, Hommeyer M, Eckmann D, Stern GA, Ormiston C. Epiglottic dysfunction: abnormal epiglottic movement patterns. Dysphagia. 2002; 17:57–68. PMID: 11820387.
Article4. Ekberg O. Epiglottic dysfunction during deglutition in patients with dysphagia. Arch Otolaryngol. 1983; 109:376–380. PMID: 6847497.
Article5. Perlman AL, Grayhack JP, Booth BM. The relationship of vallecular residue to oral involvement, reduced hyoid elevation, and epiglottic function. J Speech Hear Res. 1992; 35:734–741. PMID: 1405528.
Article6. Heo SY, Kim KM. Immediate effects of Kinesio Taping on the movement of the hyoid bone and epiglottis during swallowing by stroke patients with dysphagia. J Phys Ther Sci. 2015; 27:3355–3357. PMID: 26696697.
Article7. Kim YK, Kim MT, Kim SK. The effect of balloon dilation at the vallecular using videofluoroscopic swallowing study on patient who has a dysphagia. Ann Rehabil Med. 2013; 37:426–429. PMID: 23869342.
Article8. Kim YK, Choi JH, Yoon JG, Lee JW, Cho SS. Improved dysphagia after decannulation of tracheostomy in patients with brain injuries. Ann Rehabil Med. 2015; 39:778–785. PMID: 26605176.
Article9. Cook IJ, Dodds WJ, Dantas RO, Kern MK, Massey BT, Shaker R, et al. Timing of videofluoroscopic, manometric events, and bolus transit during the oral and pharyngeal phases of swallowing. Dysphagia. 1989; 4:8–15. PMID: 2640180.
Article10. Logemann JA. Evaluation and treatment of swallowing disorders. 2nd ed. Austin: Pro-ED;1998. p. 38–50.11. Ertekin C, Aydogdu I. Neurophysiology of swallowing. Clin Neurophysiol. 2003; 114:2226–2244. PMID: 14652082.
Article12. Ding R, Larson CR, Logemann JA, Rademaker AW. Surface electromyographic and electroglottographic studies in normal subjects under two swallow conditions: normal and during the Mendelsohn manuever. Dysphagia. 2002; 17:1–12. PMID: 11820381.
Article13. Welch MV, Logemann JA, Rademaker AW, Kahrilas PJ. Changes in pharyngeal dimensions effected by chin tuck. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1993; 74:178–181. PMID: 8431103.14. Baek SS, Park SB, Lee SG, Lee KM, Kim SH. The effect of neck posture in swallowing of stroke patients. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 1997; 21:8–12.15. Robbins J, Kays SA, Gangnon RE, Hind JA, Hewitt AL, Gentry LR, et al. The effects of lingual exercise in stroke patients with dysphagia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007; 88:150–158. PMID: 17270511.
Article16. Heitmiller RF, Tseng E, Jones B. Prevalence of aspiration and laryngeal penetration in patients with unilateral vocal fold motion impairment. Dysphagia. 2000; 15:184–187. PMID: 11014880.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Epidemiology, Natural Recovery, Long-term Outcome of Post Stroke Dysphagia
- Dysphagia Pattern according to Stroke Location
- Application of Non-invasive Brain Stimulation on Dysphagia after Stroke
- Efficacy of a 4-Week Swallowing Rehabilitation Program Combined With Pyriform Sinus Ballooning in Patients With Post-stroke Dysphagia
- The Effect of Balloon Dilation at the Vallecular Using Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Study on Patient Who Has a Dysphagia