Ann Dermatol.
2017 Aug;29(4):438-445. 10.5021/ad.2017.29.4.438.
Analysis of Serum Cytokine Profile in Pemphigus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology and Cutaneous Biology Research Institute, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kimsc@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2388942
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2017.29.4.438
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Pemphigus is a group of autoimmune blistering diseases affecting skin and mucous membranes. While pemphigus is an autoantibody mediated disease, the role of T cells and cytokines in the pathogenesis is being increasingly recognized.
OBJECTIVE
This study was conducted to observe alterations in the serum cytokine levels of patients with pemphigus vulgaris (PV), pemphigus foliaceous (PF), paraneoplastic pemphigus (PNP) and compare with bullous pemphigoid (BP) and healthy subjects.
METHODS
A total of 75 subjects (28 PV, 13 PF, 7 PNP, 7 BP, and 20 healthy controls) were included, all patients in active disease state. Serum levels of interferon (IFN)-γ, interleukin (IL)-4, IL-6, IL-17A, IL-10, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and IL-8 were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
RESULTS
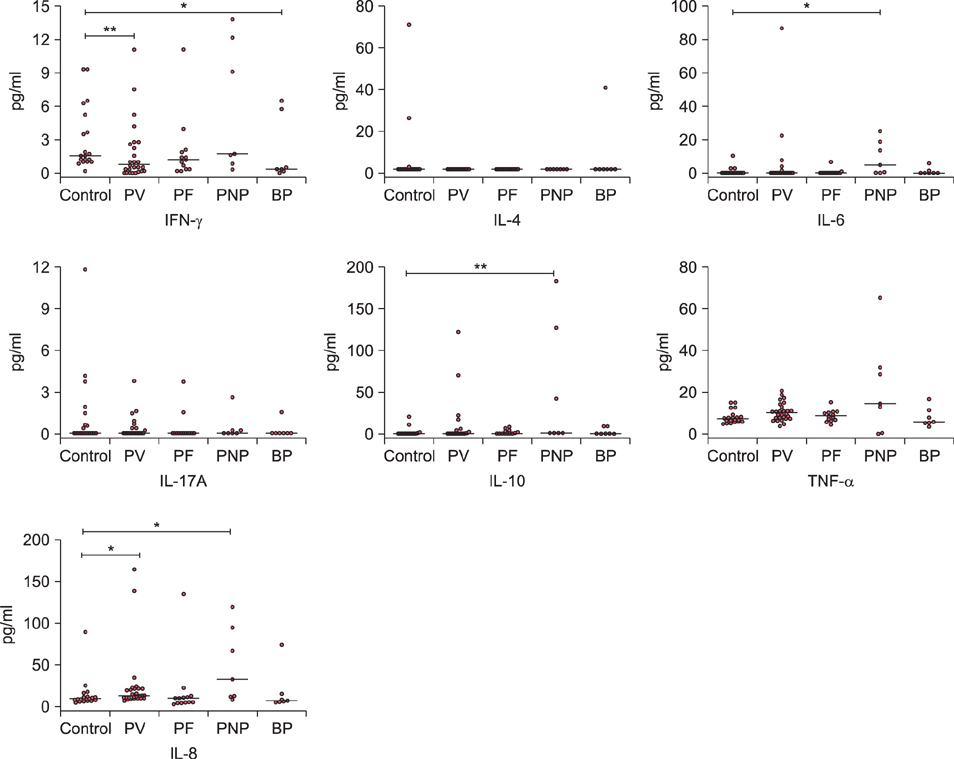
The median concentration of IFN-γ was lower in PV and BP patients compared to control (0.77, 0.34 and 1.63 pg/ml, respectively). IL-6 and IL-10 was significantly higher in PNP patients compared to control (4.92 and 0.24 pg/ml for IL-6, 0.86 and <0.12 pg/ml for IL-10, respectively). IL-8 was increased significantly in PV and PNP patients compared with control (11.85, 31.5 and 8.31 pg/ml, respectively). For IL-4, IL-17A and TNF-α, no significant difference was observed between the five groups.
CONCLUSION
The decreased level of IFN-γ in PV may imply suppressed Th1 response in the active disease stage. A Th2 predominant response is suggested in the active stage of PNP, with elevated serum levels of IL-6 and IL-10. Increased level of proinflammatory cytokine IL-8 is observed in the sera of PV and PNP patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Autoimmunity
Blister
Cytokines
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Healthy Volunteers
Humans
Interferons
Interleukin-10
Interleukin-17
Interleukin-4
Interleukin-6
Interleukin-8
Interleukins
Mucous Membrane
Pemphigoid, Bullous
Pemphigus*
Skin
T-Lymphocytes
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Cytokines
Interferons
Interleukin-10
Interleukin-17
Interleukin-4
Interleukin-6
Interleukin-8
Interleukins
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hertl M, Veldman C. Pemphigus--paradigm of autoantibody-mediated autoimmunity. Skin Pharmacol Appl Skin Physiol. 2001; 14:408–418.2. Robinson ND, Hashimoto T, Amagai M, Chan LS. The new pemphigus variants. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999; 40:649–671. quiz 672-673.
Article3. Anhalt GJ, Kim SC, Stanley JR, Korman NJ, Jabs DA, Kory M, et al. Paraneoplastic pemphigus. An autoimmune mucocutaneous disease associated with neoplasia. N Engl J Med. 1990; 323:1729–1735.
Article4. Takahashi H, Kuwana M, Amagai M. A single helper T cell clone is sufficient to commit polyclonal naive B cells to produce pathogenic IgG in experimental pemphigus vulgaris. J Immunol. 2009; 182:1740–1745.
Article5. Giordano CN, Sinha AA. Cytokine networks in Pemphigus vulgaris: An integrated viewpoint. Autoimmunity. 2012; 45:427–439.
Article6. Satyam A, Khandpur S, Sharma VK, Sharma A. Involvement of T(H)1/T(H)2 cytokines in the pathogenesis of autoimmune skin disease-Pemphigus vulgaris. Immunol Invest. 2009; 38:498–509.
Article7. Arakawa M, Dainichi T, Yasumoto S, Hashimoto T. Lesional Th17 cells in pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus. J Dermatol Sci. 2009; 53:228–231.
Article8. Alecu M, Alecu S, Coman G, Gălăţescu E, Ursaciuc C. ICAM-1, ELAM-1, TNF-alpha and IL-6 in serum and blister liquid of pemphigus vulgaris patients. Roum Arch Microbiol Immunol. 1999; 58:121–130.9. López-Robles E, Avalos-Díaz E, Vega-Memije E, Hojyo-Tomoka T, Villalobos R, Fraire S, et al. TNFalpha and IL-6 are mediators in the blistering process of pemphigus. Int J Dermatol. 2001; 40:185–188.
Article10. Feliciani C, Toto P, Amerio P. In vitro C3 mRNA expression in Pemphigus vulgaris: complement activation is increased by IL-1alpha and TNF-alpha. J Cutan Med Surg. 1999; 3:140–144.
Article11. Feliciani C, Toto P, Amerio P, Pour SM, Coscione G, Shivji G, et al. In vitro and in vivo expression of interleukin-1alpha and tumor necrosis factor-alpha mRNA in pemphigus vulgaris: interleukin-1alpha and tumor necrosis factor-alpha are involved in acantholysis. J Invest Dermatol. 2000; 114:71–77.
Article12. Baroni A, Perfetto B, Ruocco E, Greco R, Criscuolo D, Ruocco V. Cytokine pattern in blister fluid and sera of patients with pemphigus. Dermatology. 2002; 205:116–121.
Article13. Keskin DB, Stern JN, Fridkis-Hareli M, Razzaque Ahmed A. Cytokine profiles in pemphigus vulgaris patients treated with intravenous immunoglobulins as compared to conventional immunosuppressive therapy. Cytokine. 2008; 41:315–321.
Article14. Choi Y, Nam KH, Lee JB, Lee JY, Ihm CW, Lee SE, et al. Retrospective analysis of 12 Korean patients with paraneoplastic pemphigus. J Dermatol. 2012; 39:973–981.
Article15. D'Auria L, Bonifati C, Mussi A, D'Agosto G, De Simone C, Giacalone B, et al. Cytokines in the sera of patients with pemphigus vulgaris: interleukin-6 and tumour necrosis factor-alpha levels are significantly increased as compared to healthy subjects and correlate with disease activity. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1997; 8:383–387.16. Nishifuji K, Amagai M, Kuwana M, Iwasaki T, Nishikawa T. Detection of antigen-specific B cells in patients with pemphigus vulgaris by enzyme-linked immunospot assay: requirement of T cell collaboration for autoantibody production. J Invest Dermatol. 2000; 114:88–94.
Article17. Takahashi H, Amagai M, Nishikawa T, Fujii Y, Kawakami Y, Kuwana M. Novel system evaluating in vivo pathogenicity of desmoglein 3-reactive T cell clones using murine pemphigus vulgaris. J Immunol. 2008; 181:1526–1535.
Article18. Nawijn MC, Dingjan GM, Ferreira R, Lambrecht BN, Karis A, Grosveld F, et al. Enforced expression of GATA-3 in transgenic mice inhibits Th1 differentiation and induces the formation of a T1/ST2-expressing Th2-committed T cell compartment in vivo. J Immunol. 2001; 167:724–732.
Article19. Zheng WP, Flavell RA. The transcription factor GATA-3 is necessary and sufficient for Th2 cytokine gene expression in CD4 T cells. Cell. 1997; 89:587–596.
Article20. Hertl M, Amagai M, Sundaram H, Stanley J, Ishii K, Katz SI. Recognition of desmoglein 3 by autoreactive T cells in pemphigus vulgaris patients and normals. J Invest Dermatol. 1998; 110:62–66.
Article21. Veldman C, Stauber A, Wassmuth R, Uter W, Schuler G, Hertl M. Dichotomy of autoreactive Th1 and Th2 cell responses to desmoglein 3 in patients with pemphigus vulgaris (PV) and healthy carriers of PV-associated HLA class II alleles. J Immunol. 2003; 170:635–642.
Article22. Lin MS, Swartz SJ, Lopez A, Ding X, Fernandez-Vina MA, Stastny P, et al. Development and characterization of desmoglein-3 specific T cells from patients with pemphigus vulgaris. J Clin Invest. 1997; 99:31–40.
Article23. Kaneko F, Minagawa T, Takiguchi Y, Suzuki M, Itoh N. Role of cell-mediated immune reaction in blister formation of bullous pemphigoid. Dermatology. 1992; 184:34–39.
Article24. Wakugawa M, Nakamura K, Hino H, Toyama K, Hattori N, Okochi H, et al. Elevated levels of eotaxin and interleukin-5 in blister fluid of bullous pemphigoid: correlation with tissue eosinophilia. Br J Dermatol. 2000; 143:112–116.
Article25. Bhol KC, Rojas AI, Khan IU, Ahmed AR. Presence of interleukin 10 in the serum and blister fluid of patients with pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigoid. Cytokine. 2000; 12:1076–1083.
Article26. Giomi B, Caproni M, Calzolari A, Bianchi B, Fabbri P. Th1, Th2 and Th3 cytokines in the pathogenesis of bullous pemphigoid. J Dermatol Sci. 2002; 30:116–128.
Article27. Rizzo C, Fotino M, Zhang Y, Chow S, Spizuoco A, Sinha AA. Direct characterization of human T cells in pemphigus vulgaris reveals elevated autoantigen-specific Th2 activity in association with active disease. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2005; 30:535–540.
Article28. Bettelli E, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK. T(H)-17 cells in the circle of immunity and autoimmunity. Nat Immunol. 2007; 8:345–350.
Article29. Veldman C, Höhne A, Dieckmann D, Schuler G, Hertl M. Type I regulatory T cells specific for desmoglein 3 are more frequently detected in healthy individuals than in patients with pemphigus vulgaris. J Immunol. 2004; 172:6468–6475.
Article30. Iyer SS, Cheng G. Role of interleukin 10 transcriptional regulation in inflammation and autoimmune disease. Crit Rev Immunol. 2012; 32:23–63.
Article31. Cho MJ, Ellebrecht CT, Payne AS. The dual nature of interleukin-10 in pemphigus vulgaris. Cytokine. 2015; 73:335–341.
Article32. Yang M, Rui K, Wang S, Lu L. Regulatory B cells in autoimmune diseases. Cell Mol Immunol. 2013; 10:122–132.
Article33. Nousari HC, Kimyai-Asadi A, Anhalt GJ. Elevated serum levels of interleukin-6 in paraneoplastic pemphigus. J Invest Dermatol. 1999; 112:396–398.
Article34. Yee C, Biondi A, Wang XH, Iscove NN, de Sousa J, Aarden LA, et al. A possible autocrine role for interleukin-6 in two lymphoma cell lines. Blood. 1989; 74:798–804.
Article35. O'Toole EA, Mak LL, Guitart J, Woodley DT, Hashimoto T, Amagai M, et al. Induction of keratinocyte IL-8 expression and secretion by IgG autoantibodies as a novel mechanism of epidermal neutrophil recruitment in a pemphigus variant. Clin Exp Immunol. 2000; 119:217–224.36. Sjögren F, Anderson C. Sterile trauma to normal human dermis invariably induces IL1beta, IL6 and IL8 in an innate response to "danger". Acta Derm Venereol. 2009; 89:459–465.
Article37. De Jongh CM, Verberk MM, Withagen CE, Jacobs JJ, Rustemeyer T, Kezic S. Stratum corneum cytokines and skin irritation response to sodium lauryl sulfate. Contact Dermatitis. 2006; 54:325–333.
Article38. Strickland I, Rhodes LE, Flanagan BF, Friedmann PS. TNF-alpha and IL-8 are upregulated in the epidermis of normal human skin after UVB exposure: correlation with neutrophil accumulation and E-selectin expression. J Invest Dermatol. 1997; 108:763–768.
Article39. Lee WJ, Chae SY, Ryu HS, Jang YH, Lee SJ, Kim DW. Inflammatory cytokine expression and sebum production after exposure of cultured human sebocytes to ultraviolet a radiation and light at wavelengths of 650 nm and 830 nm. Ann Dermatol. 2015; 27:163–170.
Article40. Pardo J, Mercader P, Mahiques L, Sanchez-Carazo JL, Oliver V, Fortea JM. Infliximab in the management of severe pemphigus vulgaris. Br J Dermatol. 2005; 153:222–223.
Article41. Daulat S, Detweiler JG, Pandya AG. Development of pemphigus vulgaris in a patient with psoriasis treated with etanercept. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2009; 23:483–484.
Article42. Fiorentino DF, Garcia MS, Rehmus W, Kimball AB. A pilot study of etanercept treatment for pemphigus vulgaris. Arch Dermatol. 2011; 147:117–118.
Article43. Hall RP 3rd, Fairley J, Woodley D, Werth VP, Hannah D, Streilein RD, et al. A multicentre randomized trial of the treatment of patients with pemphigus vulgaris with infliximab and prednisone compared with prednisone alone. Br J Dermatol. 2015; 172:760–768.
Article