Anesth Pain Med.
2017 Jul;12(3):275-280. 10.17085/apm.2017.12.3.275.
Comparison of the endotracheal tube intracuff pressure with cylindrical and tapered cuffs during nitrous oxide exposure: a randomized single-blinded clinical study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea. dragona1@dumc.or.kr
- KMID: 2388847
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2017.12.3.275
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
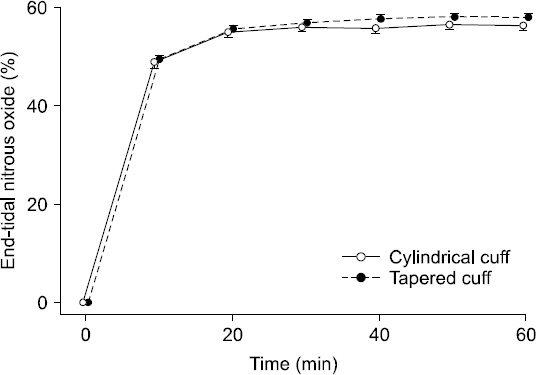
Tracheal complications caused by excessive mucosal pressure from an inflated endotracheal tube are major concerns during anesthesia; hence, an intracuff pressure of 20-30 cmHâ‚‚O is recommended as a clinically acceptable intracuff pressure. Diffusion of nitrous oxide (Nâ‚‚O) into the endotracheal tube cuff increases the intracuff pressure, which may also be influenced by the cuff shape. Therefore, we investigated whether the intracuff pressure of a tapered cuff was different from that of a cylindrical cuff in patients undergoing general anesthesia using 60% Nâ‚‚O.
METHODS
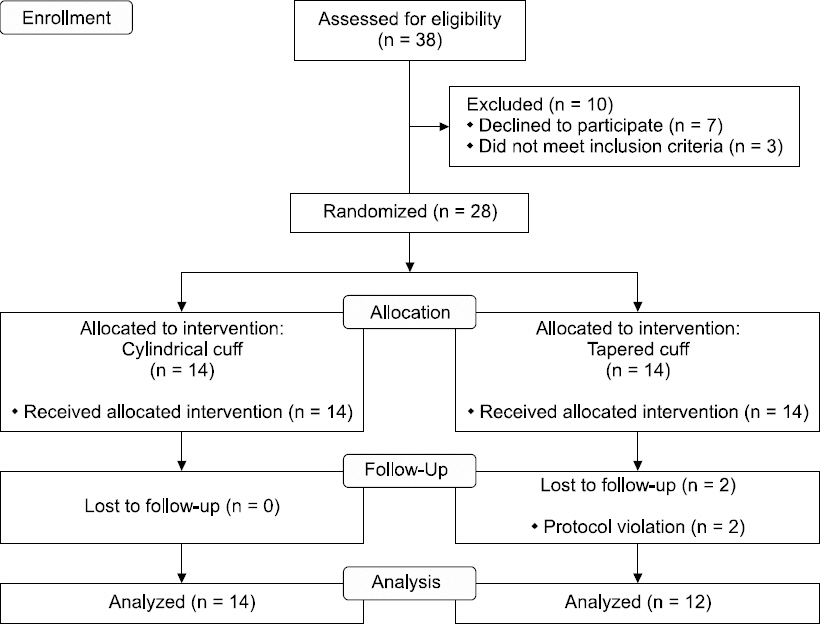
Twenty-six patients who underwent general anesthesia using 60% Nâ‚‚O in supine position were randomly allocated to the cylindrical cuff group (Group C) or tapered cuff group (Group T). The baseline intracuff pressure was set at 20 cmHâ‚‚O, and measured every 10 minutes for 60 minutes.
RESULTS
The primary outcome was the intracuff pressure at 60 minutes after Nâ‚‚O exposure, which was 40 cmHâ‚‚O in Group C (95% CI 36-44) and 40 cmHâ‚‚O (95% CI 35-45) in Group T (P = 0.895). The lower confidence limit of the intracuff pressures in both groups exceeded 30 cmHâ‚‚O at 60 minutes of Nâ‚‚O exposure, which is the upper limit for clinically acceptable intracuff pressure (20-30 cmHâ‚‚O).
CONCLUSIONS
There was no significant difference in the intracuff pressures between cylindrical and tapered cuffs. Continuous or frequent monitoring is recommended regardless of the duration of the 60% Nâ‚‚O exposure because the intracuff pressure can exceed 30 cmHâ‚‚O within an hour.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Priebe HJ. Could “safe practice” be compromising safe practice? Should anesthetists have to deflate the cuff of the endotracheal tube before extubation? Minerva Anestesiol. 2016; 82:236–9. PMID: 26126979.2. Combes X, Schauvliege F, Peyrouset O, Motamed C, Kirov K, Dhonneur G, et al. Intracuff pressure and tracheal morbidity: influence of filling with saline during nitrous oxide anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 2001; 95:1120–4. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-200111000-00015. PMID: 11684980.3. Dobrin P, Canfield T. Cuffed endotracheal tubes: mucosal pressures and tracheal wall blood flow. Am J Surg. 1977; 133:562–8. DOI: 10.1016/0002-9610(77)90008-3.4. Seegobin RD, van Hasselt GL. Endotracheal cuff pressure and tracheal mucosal blood flow: endoscopic study of effects of four large volume cuffs. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1984; 288:965–8. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.288.6422.965.5. American Thoracic Society Infectious Diseases Society of America. Guidelines for the management of adults with hospital-acquired, ventilator-associated, and healthcare-associated pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005; 171:388–416. DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200405-644ST. PMID: 15699079.6. Hockey CA, van Zundert AA, Paratz JD. Does objective measurement of tracheal tube cuff pressures minimise adverse effects and maintain accurate cuff pressures? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2016; 44:560–70. PMID: 27608338.7. Stanley TH. Nitrous oxide and pressures and volumes of high- and low-pressure endotracheal-tube cuffs in intubated patients. Anesthesiology. 1975; 42:637–40. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-197505000-00035. PMID: 1130733.8. Tu HN, Saidi N, Leiutaud T, Bensaid S, Menival V, Duvaldestin P. Nitrous oxide increases endotracheal cuff pressure and the incidence of tracheal lesions in anesthetized patients. Anesth Analg. 1999; 89:187–90. DOI: 10.1097/00000539-199907000-00033.9. Dullenkopf A, Gerber AC, Weiss M. Nitrous oxide diffusion into tracheal tube cuffs: comparison of five different tracheal tube cuffs. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2004; 48:1180–4. DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2004.00483.x. PMID: 15352966.10. Kako H, Krishna SG, Ramesh AS, Merz MN, Elmaraghy C, Grischkan J, et al. The relationship between head and neck position and endotracheal tube intracuff pressure in the pediatric population. Paediatr Anaesth. 2014; 24:316–21. DOI: 10.1111/pan.12487. PMID: 24238105.11. Kim D, Jeon B, Son JS, Lee JR, Ko S, Lim H. The changes of endotracheal tube cuff pressure by the position changes from supine to prone and the flexion and extension of head. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2015; 68:27–31. DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2015.68.1.27. PMID: 25664152. PMCID: PMC4318861.12. Kim HC, Lee YH, Kim E, Oh EA, Jeon YT, Park HP. Comparison of the endotracheal tube cuff pressure between a tapered- versus a cylindrical-shaped cuff after changing from the supine to the lateral flank position. Can J Anaesth. 2015; 62:1063–70. DOI: 10.1007/s12630-015-0394-z. PMID: 25894912.13. Tsuboi S, Miyashita T, Yamaguchi Y, Yamamoto Y, Sakamaki K, Goto T. The TaperGuard™ endotracheal tube intracuff pressure increase is less than that of the Hi-Lo™ tube during nitrous oxide exposure: a model trachea study. Anesth Analg. 2013; 116:609–12. DOI: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e318279b399. PMID: 23400983.14. Hounsome J, Nicholson A, Greenhalgh J, Cook TM, Smith AF, Lewis SR. Nitrous oxide-based versus nitrous oxide-free general anaesthesia and accidental awareness during general anaesthesia in surgical patients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016; 8:CD011052. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011052.pub2.15. Kim D, Oh J, Choi W, Kwon YJ, Ko S. The economic evaluation of nitrous oxide in sevoflurane anesthesia. Anesth Pain Med. 2017; 12:23–7. DOI: 10.17085/apm.2017.12.1.23.16. Leslie K, Myles PS, Kasza J, Forbes A, Peyton PJ, Chan MT, et al. Nitrous Oxide and Serious Long-term Morbidity and Mortality in the Evaluation of Nitrous Oxide in the Gas Mixture for Anaesthesia (ENIGMA)-II Trial. Anesthesiology. 2015; 123:1267–80. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000908. PMID: 26501387.17. Ahmad NL, Norsidah AM. Change in endotracheal tube cuff pressure during nitrous oxide anaesthesia: a comparison between air and distilled water cuff inflation. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2001; 29:510–4. PMID: 11669433.18. Faul F, Erdfelder E, Lang AG, Buchner A. G*Power 3: a flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav Res Methods. 2007; 39:175–91. DOI: 10.3758/BF03193146. PMID: 17695343.19. Mehta S. Effects of nitrous oxide and oxygen on tracheal tube cuff gas volumes. Br J Anaesth. 1981; 53:1227–31. DOI: 10.1093/bja/53.11.1227. PMID: 7326169.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intracuff Pressure Change during Inhalation Anesthesia
- Endotracheal Tube Cuff Volume and Pressure Changes in the Use of Nitrous Oxide
- A Study of Cuff Pressure in the Endotracheal Tube
- The Effects of Nitrous Oxide on Volume and Pressure of Endotracheal Tube Cuffs during General Inhalation Anesthesia
- Regulation of Endotracheal Cuff Pressure