Anesth Pain Med.
2017 Jul;12(3):271-274. 10.17085/apm.2017.12.3.271.
Learning curve of skilled anesthesiologists for endotracheal intubation using Optiscopeâ„¢
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea. hjanesthesia@empas.com
- KMID: 2388846
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2017.12.3.271
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Optiscopeâ„¢ is a semi-rigid fiberscope for endotracheal intubation. A camera attached to the distal end of the stylet shows the laryngeal view through an adjustable LCD-monitor attached at the handle. The aim of this study was to evaluate the learning curve of skilled anesthesiologists in the use of Optiscopeâ„¢.
METHODS
Eighty-patients with normal airways were randomly assigned to four anesthesiologists, who did not have previous experience of intubation with Optiscopeâ„¢. After induction of general anesthesia, the four investigators performed 20 intubations each, using the Optiscopeâ„¢. Time to intubation (TTI), number of intubation attempts, and reasons of prolonged TTI were evaluated.
RESULTS
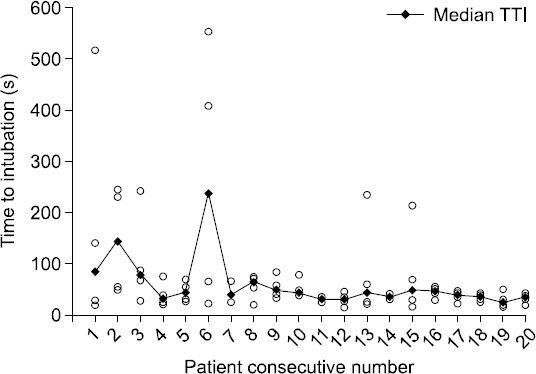
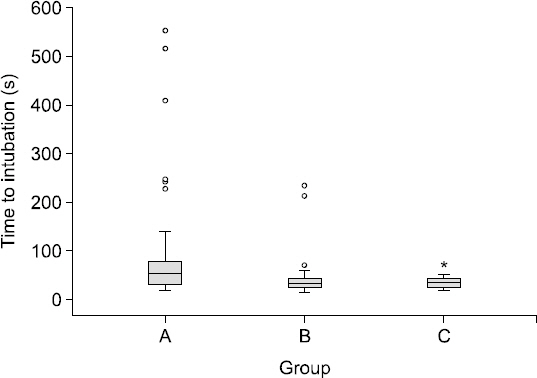
The success rate of intubation was 98.8%. The TTI was significantly faster in 16th-20th patients (35.0 s, interquartile range 27.3-41.4) than in the first 10 patients (54.1 s, interquartile range 31.2-75.5) (P = 0.006). All patients after the 16th intubation were intubated at the first attempt. Frequent problems encountered were difficulty in getting the stylet tip under the epiglottis, and mucous secretion obscuring the laryngeal anatomy.
CONCLUSIONS
Optiscopeâ„¢ is an effective device for endotracheal intubation. About 15 intubations in patients with normal airways provided clinically adequate experience to the skilled anesthesiologists. Additional maneuver of airway opening such as jaw thrust and sufficient removal of oral secretion, are suggested to reduce TTI.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Benumof JL. Management of the difficult adult airway. With special emphasis on awake tracheal intubation. Anesthesiology. 1991; 75:1087–110. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-199112000-00021. PMID: 1824555.2. Jun JH, Kim JK, Lee EJ. Awake endotracheal intubation using a video-assisted intubating stylet in a patient with a large supraglottic mass: A case report. Anesth Pain Med. 2015; 10:219–22. DOI: 10.17085/apm.2015.10.3.219.3. Kim ES, Shin YD, Lee KS, Baek DH. The use of Pentax-AWS for a difficult airway due to post-thyroidectomy hematoma: A case report. Anesth Pain Med. 2009; 4:272–5.4. Kim HJ, Choi YS, Park SH, Jo JH. Difficult endotracheal intubation secondary to tracheal deviation and stenosis in a patient with severe kyphoscoliosis: a case report. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2016; 69:386–9. DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2016.69.4.386. PMID: 27482317. PMCID: PMC4967635.5. Corbanese U, Morossi M. The Bonfils intubation fibrescope: clinical evaluation and consideration of the learning curve. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2009; 26:622–4. DOI: 10.1097/EJA.0b013e328328f572. PMID: 19300272.6. Ko DD, Kang H, Yang SY, Shin HY, Baek CW, Jung YH, et al. A comparison of hemodynamic changes after endotracheal intubation by the Optiscope™ and the conventional laryngoscope. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2012; 63:130–5. DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2012.63.2.130. PMID: 22949980. PMCID: PMC3427805.7. Rai MR, Dering A, Verghese C. The Glidescope system: a clinical assessment of performance. Anaesthesia. 2005; 60:60–4. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.2004.04013.x. PMID: 15601274.8. Savoldelli GL, Schiffer E, Abegg C, Baeriswyl V, Clergue F, Waeber JL. Learning curves of the Glidescope, the McGrath and the Airtraq laryngoscopes: a manikin study. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2009; 26:554–8. DOI: 10.1097/EJA.0b013e3283269ff4. PMID: 19522050.9. Bein B, Yan M, Tonner PH, Scholz J, Steinfath M, Dörges V. Tracheal intubation using the Bonfils intubation fibrescope after failed direct laryngoscopy. Anaesthesia. 2004; 59:1207–9. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.2004.03967.x. PMID: 15549980.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Circulatory Changes during Fiberoptic Endotracheal Intubation
- Endotracheal intubation by inexperienced trainees using the Clarus Video System: learning curve and orodental trauma perspectives
- Comparison of the rate of successful endotracheal intubation between the "sniffing" and "ramped" positions in patients with an expected difficult intubation: a prospective randomized study
- Prediction of Difficulty in Endotracheal Intubation in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Comparison of Modified Mallampati Test and Upper Lip Bite Test
- Granulomas of the Vocal Cords Following Endotracheal Anesthesia - Case report