Investig Clin Urol.
2017 May;58(3):171-178. 10.4111/icu.2017.58.3.171.
A preliminary oncologic outcome and postoperative complications in patients undergoing robot-assisted radical cystectomy: Initial experience
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Juntendo University Graduate School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan. shorie@juntendo.ac.jp
- 2Department of Urology, Teikyo University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan.
- 3Department of Urology, Juntendo Nerima Hospital, Tokyo, Japan.
- KMID: 2388061
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/icu.2017.58.3.171
Abstract
- PURPOSE
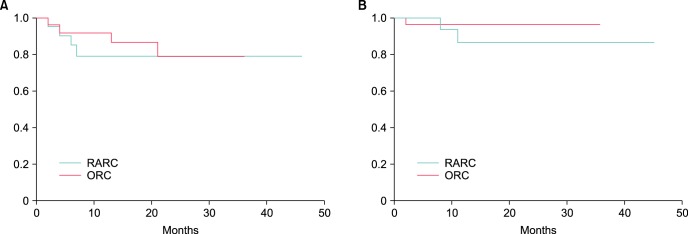
Robot-assisted radical cystectomy (RARC) was originally intended to replace open radical cystectomy (ORC) as a minimally invasive surgery for patients with invasive bladder cancer. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the advantages of robotic surgery, comparing perioperative and oncologic outcomes between RARC and ORC.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between June 2012 and August 2016, 49 bladder cancer patients were given a radical cystectomy, 21 robotically and 28 by open procedure. We compared the clinical variables between the RARC and ORC groups.
RESULTS
In the RARC group, the median estimated blood loss (EBL) during cystectomy, total EBL, operative time during cystectomy, and total operative time were 0 mL, 457.5 mL, 199 minutes, and 561 minutes, respectively. EBL during cystectomy (p<0.001), total EBL (p<0.001), and operative time during cystectomy (p=0.003) in the RARC group were significantly lower compared with the ORC group. Time to resumption of a regular diet (p<0.001) and length of stay (p=0.017) were also significantly shorter compared with the ORC group. However, total operative time in the RARC group (median, 561 minutes) was significantly longer compared with the ORC group (median, 492.5 minutes; p=0.015).
CONCLUSIONS
This Japanese study presented evidence that RARC yields benefits in terms of BL and time to regular diet, while consuming greater total operative time. RARC may be a minimally invasive surgical alternative to ORC with less EBL and shorter length of stay.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jensen JB, Ulhøi BP, Jensen KM. Extended versus limited lymph node dissection in radical cystectomy: impact on recurrence pattern and survival. Int J Urol. 2012; 19:39–47. PMID: 22050425.
Article2. Roghmann F, Trinh QD, Braun K, von Bodman C, Brock M, Noldus J, et al. Standardized assessment of complications in a contemporary series of European patients undergoing radical cystectomy. Int J Urol. 2014; 21:143–149. PMID: 23906282.
Article3. Challacombe BJ, Bochner BH, Dasgupta P, Gill I, Guru K, Herr H, et al. The role of laparoscopic and robotic cystectomy in the management of muscle-invasive bladder cancer with special emphasis on cancer control and complications. Eur Urol. 2011; 60:767–775. PMID: 21620562.
Article4. Hayn MH, Hussain A, Mansour AM, Andrews PE, Carpentier P, Castle E, et al. The learning curve of robot-assisted radical cystectomy: results from the International Robotic Cystectomy Consortium. Eur Urol. 2010; 58:197–202. PMID: 20434830.
Article5. Atmaca AF, Canda AE, Gok B, Akbulut Z, Altinova S, Balbay MD. Open versus robotic radical cystectomy with intracorporeal Studer diversion. JSLS. 2015; 19:e2014.
Article6. Kader AK, Richards KA, Krane LS, Pettus JA, Smith JJ, Hemal AK. Robot-assisted laparoscopic vs open radical cystectomy: comparison of complications and perioperative oncological outcomes in 200 patients. BJU Int. 2013; 112:E290–E294. PMID: 23815802.
Article7. Styn NR, Montgomery JS, Wood DP, Hafez KS, Lee CT, Tallman C, et al. Matched comparison of robotic-assisted and open radical cystectomy. Urology. 2012; 79:1303–1308. PMID: 22516354.
Article8. Sung HH, Ahn JS, Seo SI, Jeon SS, Choi HY, Lee HM, et al. A comparison of early complications between open and robot-assisted radical cystectomy. J Endourol. 2012; 26:670–675. PMID: 22011001.
Article9. Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz M, Wittekind C, editors. International Union Against Cancer (UICC). TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours. 7th ed. Hoboken (NJ): Wiley-Blackwell;2010.10. Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg. 2004; 240:205–213. PMID: 15273542.11. Shigemura K, Yamanaka N, Imanishi O, Yamashita M. Wallace direct versus anti-reflux Le Duc ureteroileal anastomosis: comparative analysis in modified Studer orthotopic neobladder reconstruction. Int J Urol. 2012; 19:49–53. PMID: 22004164.
Article12. R Development Core Team. R. a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna (Austria): R Foundation for Statistical Computing;2011.13. Li K, Lin T, Fan X, Xu K, Bi L, Duan Y, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies reporting early outcomes after robot-assisted radical cystectomy versus open radical cystectomy. Cancer Treat Rev. 2013; 39:551–560. PMID: 23273846.
Article14. Wu WC, Smith TS, Henderson WG, Eaton CB, Poses RM, Uttley G, et al. Operative blood loss, blood transfusion, and 30-day mortality in older patients after major noncardiac surgery. Ann Surg. 2010; 252:11–17. PMID: 20505504.
Article15. Bak DJ, Lee YJ, Woo MJ, Chung JW, Ha YS, Kim HT, et al. Complications and oncologic outcomes following robot-assisted radical cystectomy: what is the real benefit? Investig Clin Urol. 2016; 57:260–267.
Article16. Yuh BE, Nazmy M, Ruel NH, Jankowski JT, Menchaca AR, Torrey RR, et al. Standardized analysis of frequency and severity of complications after robot-assisted radical cystectomy. Eur Urol. 2012; 62:806–813. PMID: 22705382.
Article17. Goh AC, Gill IS, Lee DJ, de Castro Abreu AL, Fairey AS, Leslie S, et al. Robotic intracorporeal orthotopic ileal neobladder: replicating open surgical principles. Eur Urol. 2012; 62:891–901. PMID: 22920581.
Article18. Collins JW, Tyritzis S, Nyberg T, Schumacher MC, Laurin O, Adding C, et al. Robot-assisted radical cystectomy (RARC) with intracorporeal neobladder - what is the effect of the learning curve on outcomes? BJU Int. 2014; 113:100–107. PMID: 24053710.
Article19. Novotny V, Froehner M, Koch R, Zastrow S, Heberling U, Leike S, et al. Age, American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status classification and Charlson score are independent predictors of 90-day mortality after radical cystectomy. World J Urol. 2016; 34:1123–1129. PMID: 26658887.
Article20. Izquierdo L, Peri L, Leon P, Ramírez-Backhaus M, Manning T, Alcaraz A, et al. The role of cystectomy in elderly patients - a multicentre analysis. BJU Int. 2015; 116(Suppl 3):73–79. PMID: 26333289.
Article21. Guillotreau J, Miocinovic R, Gamé X, Forest S, Malavaud B, Kaouk J, et al. Outcomes of laparoscopic and robotic radical cystectomy in the elderly patients. Urology. 2012; 79:585–590. PMID: 22386404.
Article22. Coward RM, Smith A, Raynor M, Nielsen M, Wallen EM, Pruthi RS. Feasibility and outcomes of robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical cystectomy for bladder cancer in older patients. Urology. 2011; 77:1111–1114. PMID: 21333341.
Article23. Chen EC, Papa N, Lawrentschuk N, Bolton D, Sengupta S. Incidence and risk factors of venous thromboembolism after pelvic uro-oncologic surgery: a single center experience. BJU Int. 2016; 117(Suppl 4):50–53. PMID: 26486818.24. Chang SS, Cookson MS, Baumgartner RG, Wells N, Smith JA Jr. Analysis of early complications after radical cystectomy: results of a collaborative care pathway. J Urol. 2002; 167:2012–2016. PMID: 11956429.
Article25. Collins JW, Patel H, Adding C, Annerstedt M, Dasgupta P, Khan SM, et al. Enhanced recovery after robot-assisted radical cystectomy: EAU Robotic Urology Section Scientific Working Group Consensus View. Eur Urol. 2016; 70:649–660. PMID: 27234997.
Article26. Mir MC, Zargar H, Bolton DM, Murphy DG, Lawrentschuk N. Enhanced recovery after surgery protocols for radical cystectomy surgery: review of current evidence and local protocols. ANZ J Surg. 2015; 85:514–520. PMID: 25781409.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Cystectomy
- Erectile Function and Long-term Oncologic Outcomes of Nerve-Sparing Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy: Comparison With Open Radical Cystectomy
- Initial experience with Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy compared to the conventional method: is it a suitable option for robotic prostatectomy beginners?
- The Feasibility of Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Cystectomy with Pelvic Lymphadenectomy: from the Viewpoint of Extended Pelvic Lymphadenectomy
- Gender-related outcomes in robot-assisted radical cystectomy: A multi-institutional study