J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2017 Jul;60(4):424-432. 10.3340/jkns.2016.0910.003.
The Incidence and Characteristics of Patients with Small Ruptured Aneurysms (<5 mm) in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Busan-Ulsan Regional Cardio-Cerebrovascular Center, Medical Science Research Center, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea. nsparkhs@dau.ac.kr
- KMID: 2387880
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.0910.003
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Small unruptured aneurysms (<5 mm) are known for their very low risk of rupture, and are recommended to be treated conservatively. However, we encounter many patients with small ruptured aneurysms in the clinical practice. We aimed to investigate the incidence and characteristics of patients with small ruptured aneurysms.
METHODS
We reviewed all patients admitted to our hospital with subarachnoid hemorrhage from January 2005 to December 2015. The patients were divided into two groups: those with aneurysms <5 mm (group S) and those with aneurysms ≥5 mm (group L). The patient's age and sex, size and location of aneurysms, and risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, alcohol use, and smoking were compared between the two groups.
RESULTS
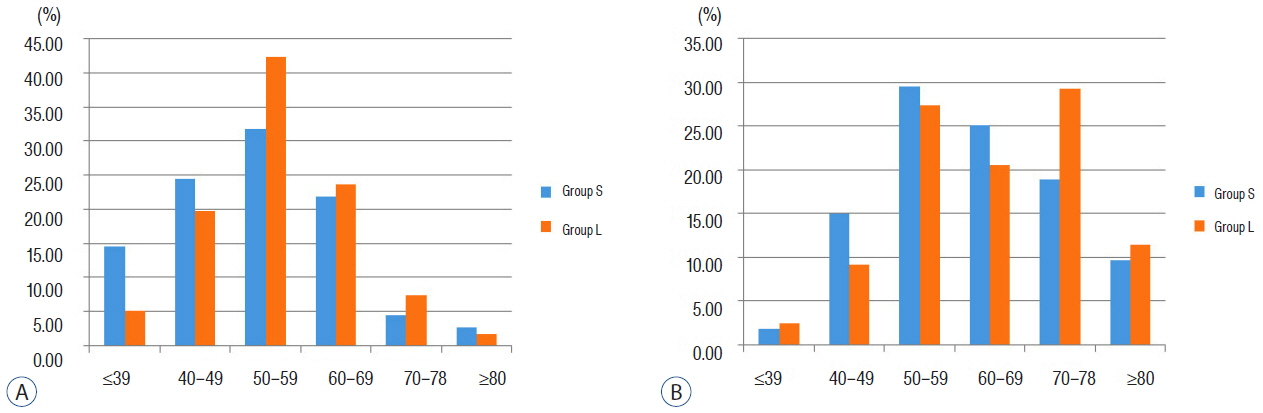
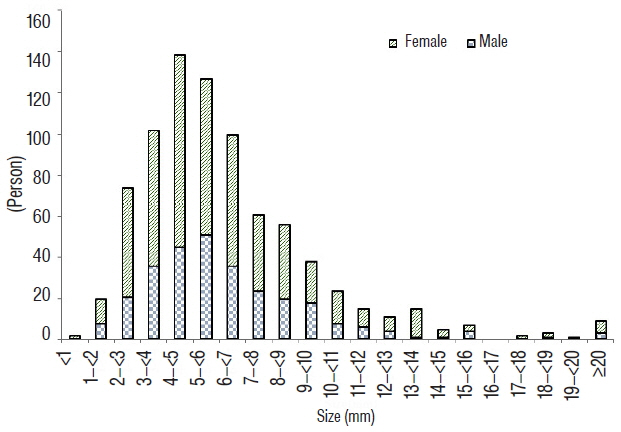
Eight-hundred eleven patients were diagnosed with ruptured aneurysms, and 337 (41.6%) were included in group S. The mean size of all aneurysms was 6.10±2.99 mm (range, 0.7-37.7); aneurysms with a diameter of 4-5 mm accounted for the largest subgroup of all aneurysms. Female sex was significantly associated with the incidence of small ruptured aneurysms (odds ratio [OR] 1.50, 95% confidence intervals [CI] 1.02-2.19, p=0.037). Despite female predominance in the incidence of small ruptured aneurysms, the proportion of small ruptured aneurysms in young (<50 years) men was high. In men, there were no significant differences regarding the location of the aneurysms between group S and group L (p=0.267), with the most frequent location being the anterior communicating artery (ACoA) in both group S (50.9%) and group L (51.4%). However, in women, there were significant differences regarding the location of the aneurysms between group S and group L (p=0.023), with the most frequent locations being the ACoA (33.0%) in group S, and the posterior communicating artery (30.6%) in group L. In women, two locations were significantly associated with small (<5 mm) ruptured aneurysms: the ACoA (OR 2.14, 95% CI 1.01-4.54, p=0.047) and anterior cerebral artery (OR 3.54, 95% CI 1.19-10.54, p=0.023). Multiplicity and smoking were significantly associated with large (≥5 mm) ruptured aneurysms in women. The use of alcohol was related to small ruptured aneurysms in men over 50 years of age (OR 2.23, 95% CI 1.03-4.84, p=0.042).
CONCLUSION
In this study, small (<5 mm) ruptured aneurysms exhibited different incidences by age, sex, location, and risk factors such as multiplicity, smoking, and alcohol use.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Relationship between Circadian Variation in Ictus of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Physical Activity
Jong Min Lee, Na Young Jung, Min Soo Kim, Eun Suk Park, Jun Bum Park, Hong Bo Sim, In Uk Lyo, Soon Chan Kwon
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2019;62(5):519-525. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2019.0061.Could A1 Aplasia or Hypoplasia Affect the Morphology and Rupture Risk of Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysm?
Sung Chan Park, Na Young Jung, Eun Suk Park, Soon Chan Kwon
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2022;65(4):531-538. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2021.0283.
Reference
-
References
1. Beck J, Rohde S, Berkefeld J, Seifert V, Raabe A. Size and location of ruptured and unruptured intracranial aneurysms measured by 3-dimensional rotational angiography. Surg Neurol. 65:18–25. discussion 25–27. 2006.
Article2. Cebral JR, Raschi M. Suggested connections between risk factors of intracranial aneurysms: a review. Ann Biomed Eng. 41:1366–1383. 2013.
Article3. Dolati P, Pittman D, Morrish WF, Wong J, Sutherland GR. The frequency of subarachnoid hemorrhage from very small cerebral aneurysms (< 5 mm): a population-based study. Cureus. 7:e279. 2015.
Article4. Fogelholm R, Murros K. Cigarette smoking and subarachnoid haemorrhage: a population-based case-control study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 50:78–80. 1987.
Article5. Hop JW, Rinkel GJ, Algra A, van Gijn J. Case-fatality rates and functional outcome after subarachnoid hemorrhage: a systematic review. Stroke. 28:660–664. 1997.
Article6. Inagawa T. Incidence and risk factors for multiple intracranial saccular aneurysms in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage in Izumo city, Japan. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 151:1623–1630. 2009.
Article7. International Study of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms Investigators. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms--risk of rupture and risks of surgical intervention. N Engl J Med. 339:1725–1733. 1998.8. Ishibashi T, Murayama Y, Saguchi T, Ebara M, Arakawa H, Irie K, et al. Justification of unruptured intracranial aneurysm repair: a single-center experience. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 34:1600–1605. 2013.
Article9. Jeong HW, Seo JH, Kim ST, Jung CK, Suh SI. Clinical practice guideline for the management of intracranial aneurysms. Neurointervention. 9:63–71. 2014.
Article10. Joo SW, Lee SI, Noh SJ, Jeong YG, Kim MS, Jeong YT. What is the significance of a large number of ruptured aneurysms smaller than 7 mm in diameter? J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 45:85–89. 2009.
Article11. Juvela S, Hillbom M, Numminen H, Koskinen P. Cigarette smoking and alcohol consumption as risk factors for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 24:639–646. 1993.
Article12. Juvela S, Poussa K, Porras M. Factors affecting formation and growth of intracranial aneurysms: a long-term follow-up study. Stroke. 32:485–491. 2001.
Article13. Kataoka K, Taneda M, Asai T, Yamada Y. Difference in nature of ruptured and unruptured cerebral aneurysms. Lancet. 355:203. 2000.
Article14. Keedy A. An overview of intracranial aneurysms. Mcgill J Med. 9:141–146. 2006.
Article15. Komotar RJ, Mocco J, Solomon RA. Guidelines for the surgical treatment of unruptured intracranial aneurysms: the first annual J. Lawrence pool memorial research symposium--controversies in the management of cerebral aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 62:183–193. discussion 193–194. 2008.16. Lee GJ, Eom KS, Lee C, Kim DW, Kang SD. Rupture of very small intracranial aneurysms: incidence and clinical characteristics. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 17:217–222. 2015.
Article17. Longstreth WT Jr, Nelson LM, Koepsell TD, van Belle G. Cigarette smoking, alcohol use, and subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 23:1242–1249. 1992.
Article18. Ohashi Y, Horikoshi T, Sugita M, Yagishita T, Nukui H. Size of cerebral aneurysms and related factors in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Surg Neurol. 61:239–245. discussion 245–247. 2004.
Article19. Orz Y, Kobayashi S, Osawa M, Tanaka Y. Aneurysm size: a prognostic factor for rupture. Br J Neurosurg. 11:144–149. 1997.
Article20. Qureshi AI, Suarez JI, Parekh PD, Sung G, Geocadin R, Bhardwaj A, et al. Risk factors for multiple intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 43:22–26. discussion 26–27. 1998.
Article21. Qureshi AI, Sung GY, Suri MF, Straw RN, Guterman LR, Hopkins LN. Factors associated with aneurysm size in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage: effect of smoking and aneurysm location. Neurosurgery. 46:44–50. 2000.
Article22. Rahman M, Ogilvy CS, Zipfel GJ, Derdeyn CP, Siddiqui AH, Bulsara KR, et al. Unruptured cerebral aneurysms do not shrink when they rupture: multicenter collaborative aneurysm study group. Neurosurgery. 68:155–160. discussion 160–161. 2011.
Article23. Seibert B, Tummala RP, Chow R, Faridar A, Mousavi SA, Divani AA. Intracranial aneurysms: review of current treatment options and outcomes. Front Neurol. 2:45. 2011.
Article24. Silva ÂR, Câmara RL, Valença MM. Carotid siphon geometry and variants of the circle of Willis in the origin of carotid aneurysms. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 70:917–921. 2012.
Article25. Sonobe M, Yamazaki T, Yonekura M, Kikuchi H. Small unruptured intracranial aneurysm verification study: SUAVe study, Japan. Stroke. 41:1969–1977. 2010.
Article26. Tabuchi S. Relationship between postmenopausal estrogen deficiency and aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Behav Neurol. 2015:720141. 2015.
Article27. Turan N, Heider RA, Zaharieva D, Ahmad FU, Barrow DL, Pradilla G. Sex differences in the formation of intracranial aneurysms and incidence and outcome of subarachnoid hemorrhage: review of experimental and human studies. Transl Stroke Res. 7:12–19. 2016.
Article28. Uchiyama S. Japanese guidelines for the management of stroke 2009. Nihon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi. 48:633–636. 2011.
Article29. van Gijn J, Kerr RS, Rinkel GJ. Subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet. 369:306–318. 2007.
Article30. Weir B, Disney L, Karrison T. Sizes of ruptured and unruptured aneurysms in relation to their sites and the ages of patients. J Neurosurg. 96:64–70. 2002.
Article31. Wiebers DO, Whisnant JP, Huston J 3rd, Meissner I, Brown RD Jr, Piepgras DG, et al. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: natural history, clinical outcome, and risks of surgical and endovascular treatment. Lancet. 362:103–110. 2003.
Article32. Wiebers DO, Whisnant JP, Sundt TM Jr, O’Fallon WM. The significance of unruptured intracranial saccular aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 66:23–29. 1987.
Article33. Yonekura M. Importance of prospective studies for deciding on a therapeutic guideline for unruptured cerebral aneurysm. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 82:21–25. 2002.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Rupture of Very Small Intracranial Aneurysms: Incidence and Clinical Characteristics
- Ruptured Very Small Cerebral Aneurysms and the Usefulness of Coil Embolization
- True Posterior Communicating Artery Aneurysms with High Risk of Rupture despite Very Small Diameter
- Hemorrhagic Risk of Unsecured, Unruptured Aneurysms during Hypervolemic Hypertensive Therapy in Patient with Multiple Intracranial Aneurysms
- Frequency and Characteristics of Paraclinoid Aneurysm in Ruptured Cerebral Aneurysms