Ann Surg Treat Res.
2017 Jun;92(6):440-443. 10.4174/astr.2017.92.6.440.
Colon perforation due to embolization coil for internal iliac aneurysm
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. choisjn@chonnam.ac.kr
- KMID: 2387419
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2017.92.6.440
Abstract
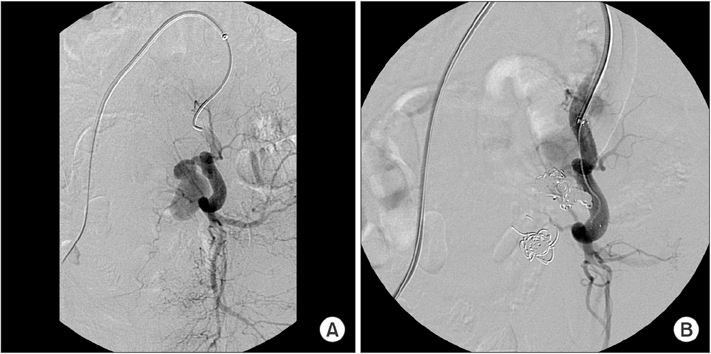
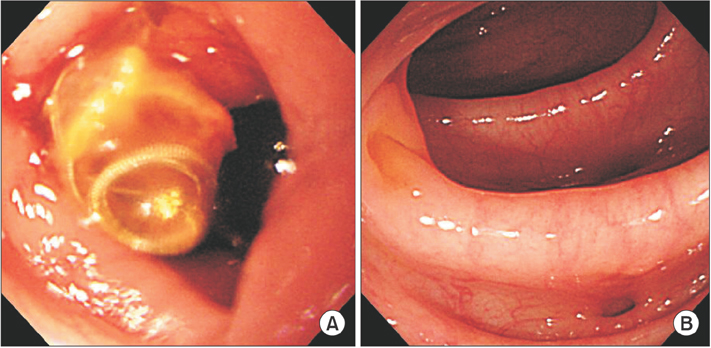
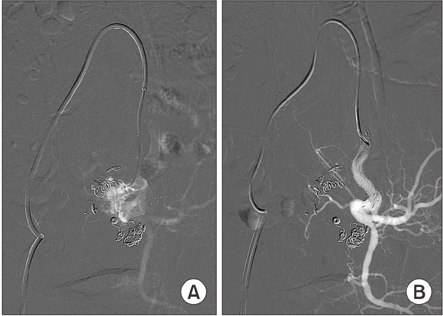
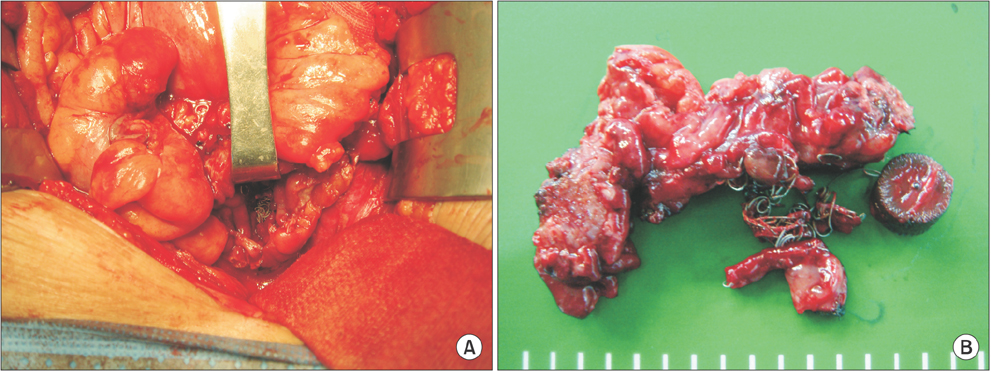
- Coil migration is an extremely rare but hazardous complication of aneurysmal coil embolization. Only 1 case report has described coil migration following endovascular exclusion to gastrointestinal (GI) tract. We report the experience of a case of colon penetration caused by embolization coil placed for internal iliac aneurysm. A 66-year-old man visited the Emergency Department for hematochezia that had persisted for 3 months. Stent insertion and coil embolization of left internal iliac artery aneurysm had been performed on the patient 18 months ago. Colonoscopy was performed. It suggested penetration of sigmoid colon by embolization coil and diverticulum. Angiography revealed extravasation of contrast media at left internal iliac artery. Covered stent deployment was done in the left internal iliac artery. One week after the stent insertion, the patient underwent anterior resection, aneurysm resection, and coil removal. The patient recovered without complications. He was discharged at 2 weeks after the operation.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dix FP, Titi M, Al-Khaffaf H. The isolated internal iliac artery aneurysm: a review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2005; 30:119–129.2. Melki JP, Fichelle JM, Cormier F, Marzelle J, Cormier JM. Embolization of hypogastric artery aneurysm: 17 cases. Ann Vasc Surg. 2001; 15:312–320.3. Sahgal A, Veith FJ, Lipsitz E, Ohki T, Suggs WD, Rozenblit AM, et al. Diameter changes in isolated iliac artery aneurysms 1 to 6 years after endovascular graft repair. J Vasc Surg. 2001; 33:289–284.4. Pitoulias GA, Donas KP, Schulte S, Horsch S, Papadimitriou DK. Isolated iliac artery aneurysms: endovascular versus open elective repair. J Vasc Surg. 2007; 46:648–654.5. Parry DJ, Kessel D, Scott DJ. Simplifying the internal iliac artery aneurysm. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2001; 83:302–308.6. Salam TA, Lumsden AB, Martin LG, Smith RB 3rd. Nonoperative management of visceral aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms. Am J Surg. 1992; 164:215–219.7. Dinter DJ, Rexin M, Kaehler G, Neff W. Fatal coil migration into the stomach 10 years after endovascular celiac aneurysm repair. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2007; 18(1 Pt 1):117–120.8. Skipworth JR, Morkane C, Raptis DA, Kennedy L, Johal K, Pendse D, et al. Coil migration: a rare complication of endovascular exclusion of visceral artery pseudoaneurysms and aneurysms. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2011; 93:e19–e23.9. Draghetti MJ, Salvo AF. Gas in the mesenteric veins as a nonfatal complication of diverticulitis: report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum. 1999; 42:1497–1498.10. Rothman BJ, Cloogman H, Wong D. Colovenous fistula complicating diverticulitis. Demonstration by contrast enema. Am J Gastroenterol. 1981; 75:464–468.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ferromagnetic Artifact Due to Metallic Embolic Fragment after Endosaccular Coil Embolization: A Case Report
- Vascular Perforation During Coil Embolization of an Intracranial Aneurysm: the Incidence, Mechanism, and Clinical Outcome
- Interventional Procedures of the Isolated Iliac Arterial Aneurysm
- Coil Embolization of Aneurysm Followed by Stereotactic Aspiration of Hematoma in a Patient with Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysm Presenting with SAH and ICH
- Spontaneous Occluded Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysm during Coil Embolization Treated with One Coil Insertion into Remaining Stump