J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2017 Jul;58(7):776-781. 10.3341/jkos.2017.58.7.776.
Clinical Characteristics of Idiopathic Orbital Inflammation Accompanied with Paranasal Sinusitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1The Institute of Vision Research, Department of Ophthalmology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yoonjs@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 2387150
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2017.58.7.776
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To investigate the clinical characteristics of idiopathic orbital inflammatory disease (IOI) with paranasal sinusitis.
METHODS
This study is a retrospective, comparative case series of patients who were diagnosed with IOI between January 2009 and December 2016. This study included patients with available medical and radiologic data at diagnosis and who participated in follow-up for more than 12 months after treatment. The patients were divided into two groups according to accompaniment of paranasal sinusitis and were compared.
RESULTS
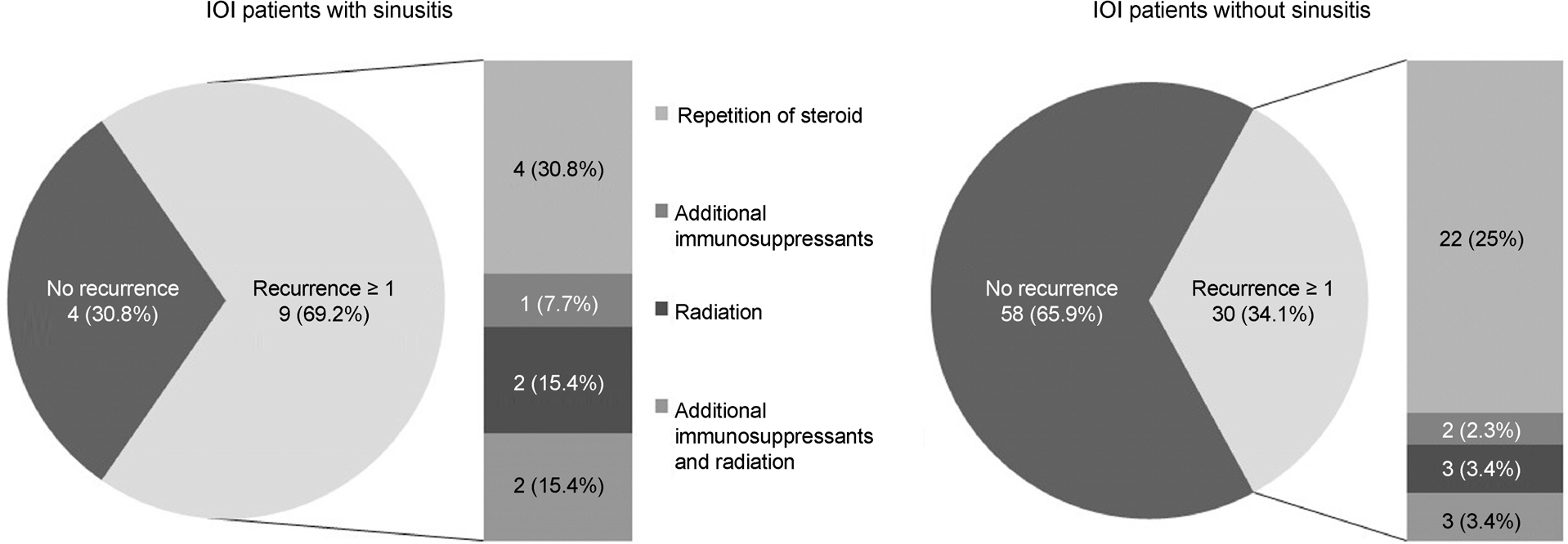
Among 101 patients with IOI, 13 (12.9%) were identified to have paranasal sinusitis. The incidence of pain was higher in patients with sinusitis (69.2%) than in patients without sinusitis (25.0%, p = 0.003). More patients with paranasal sinusitis experienced recurrence after systemic steroid therapy (69.2%) than in the other group (34.1%, p = 0.033). Additional immunosuppressants and/or radiation therapy were needed only in 9.1% patients without sinusitis but in 38.5% patients with sinusitis (p = 0.039).
CONCLUSIONS
IOI patients with sinusitis showed a significantly higher recurrence rate. More careful follow-up of patients during steroid tapering and treatment of sinusitis might be helpful to prevent recurrence of IOI.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Yuen SJ, Rubin PA. Idiopathic orbital inflammation: distribution, clinical features, and treatment outcome. Arch ophthalmol. 2003; 121:491–9.2. Mombaerts I, Goldschmeding R, Schlingemann RO, Koornneef L. What is orbital pseudotumor? Surv Ophthalmol. 1996; 41:66–78.
Article3. Rubin PA, Foster CS. Etiology and management of idiopathic orbi-tal inflammation. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004; 138:1041–3.
Article4. Takano K, Yajima R, Seki N. . A study of infraorbital nerve swelling associated with immunoglobulin G4 Mikulicz's disease. Mod Rheumatol. 2014; 24:798–801.
Article5. Hardy TG, McNab AA, Rose GE. Enlargement of the infraorbital nerve: an important sign associated with orbital reactive lymphoid hyperplasia or immunoglobulin g4-related disease. Ophthalmology. 2014; 121:1297–303.6. Lee KH, Han SH, Yoon JS. Implications of enlarged infraorbital nerve in idiopathic orbital inflammatory disease. Br J Ophthalmol. 2016; 100:1295–300.
Article7. Leibovitch I, Goldberg RA, Selva D. Paranasal sinus inflammation and non-specific orbital inflammatory syndrome: an uncommon association. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2006; 244:1391–7.
Article8. Eshaghian J, Anderson RL. Sinus involvement in inflammatory or-bital pseudotumor. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981; 99:627–30.
Article9. Yan J, Wu Z, Li Y. 36 case idiopathic orbital inflammatory pseudo-tumor with sinus involvement. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Ke Za Zhi. 2002; 16:410–1.10. Li J, Ge X, Ma JM. Relationship between dacryoadenitis subtype of idiopathic orbital inflammatory pseudotumor and paranasal sinusitis. Int J Ophthalmol. 2016; 9:444–7.
Article11. Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK. . Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol. 2012; 25:1181–92.12. Sung MS, Oh HJ, Ko BY, Yoon KC. Clinical features and results of steroid therapy for orbital inflammatory pseudotumor. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013; 54:185–91.
Article13. Park SJ, Sin SJ, Lee DG, Jang JW. Pseudotumor : distribution, clin-ical features, treatment outcomes. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:1379–86.e1.
Article14. DeConde AS, Soler ZM. Chronic rhinosinusitis: Epidemiology and burden of disease. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2016; 30:134–9.
Article15. Piao Y, Wang C, Yu W. . Concomitant occurrence of Mikulicz's disease and immunoglobulin G4-related chronic rhinosinusitis: a clinicopathological study of 12 cases. Histopathology. 2016; 68:502–12.
Article16. McNicholas MM, Power WJ, Griffin JF. Idiopathic inflammatory pseudotumour of the orbit: CT features correlated with clinical outcome. Clin Radiol. 1991; 44:3–7.
Article17. Smith TL, Kern R, Palmer JN. . Medical therapy vs surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis: a prospective, multi-institutional study with 1-year follow-up. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2013; 3:4–9.
Article18. Bassiouni A, Naidoo Y, Wormald PJ. When FESS fails: the in-flammatory load hypothesis in refractory chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope. 2012; 122:460–6.
Article19. Bassiouni A, Naidoo Y, Wormald PJ. Does mucosal remodeling in chronic rhinosinusitis result in irreversible mucosal disease? Laryngoscope. 2012; 122:225–9.
Article20. Mombaerts I, Cameron JD, Chanlalit W, Garrity JA. Surgical de-bulking for idiopathic dacryoadenitis: a diagnosis and a cure. Ophthalmology. 2014; 121:603–9.21. Menger MD, Vollmar B. Surgical trauma: hyperinflammation ver-sus immunosuppression? Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2004; 389:475–84.e1.
Article22. Dagi Glass LR, Freitag SK. Orbital inflammation: Corticosteroids first. Surv Ophthalmol. 2016; 61:670–3.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Orbital Apex Syndrome Caused by Paranasal Sinusitis
- A Case of Deep Neck Infecton Followed by Orbital Cellulitis
- A Case of Orbital Subperiosteal Abscess Associated with Acute Paranasal Sinusitis after Trauma
- A Case of Septic Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis Complicated by Sepsis
- Orbital Apex Syndrome Related to Isolated Sphenoid Fungal Sinusitis