Yonsei Med J.
2014 Mar;55(2):401-409.
Long-Term Clinical and Angiographic Outcomes of Wrap-Clipping Strategies for Unclippable Cerebral Aneurysms
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sk522@yuhs.ac
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the efficacy and stability of the wrap-clipping methods as a reconstructive strategy in the treatment of unclippable cerebral aneurysms.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty four patients who had undergone wrap-clipping microsurgery were retrospectively reviewed. Type and morphology of the treated aneurysm, utilized technique for wrap-clip procedure, and clinical outcome with angiographic results at their last follow-up were evaluated.
RESULTS
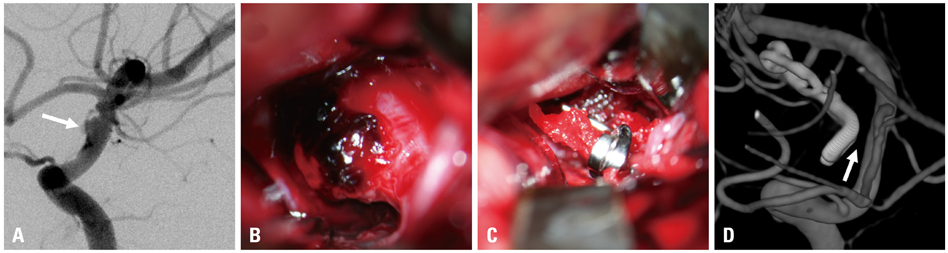
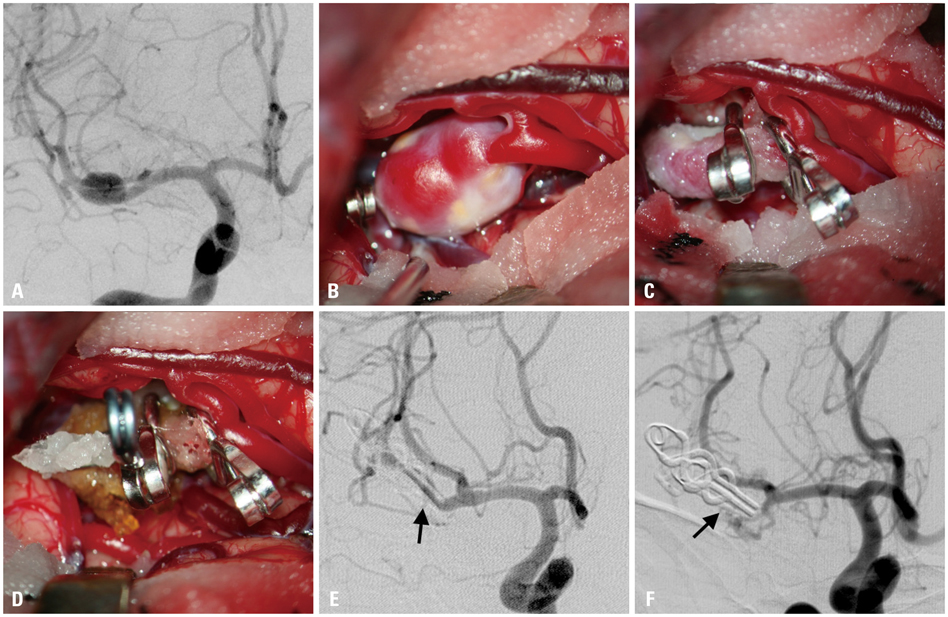
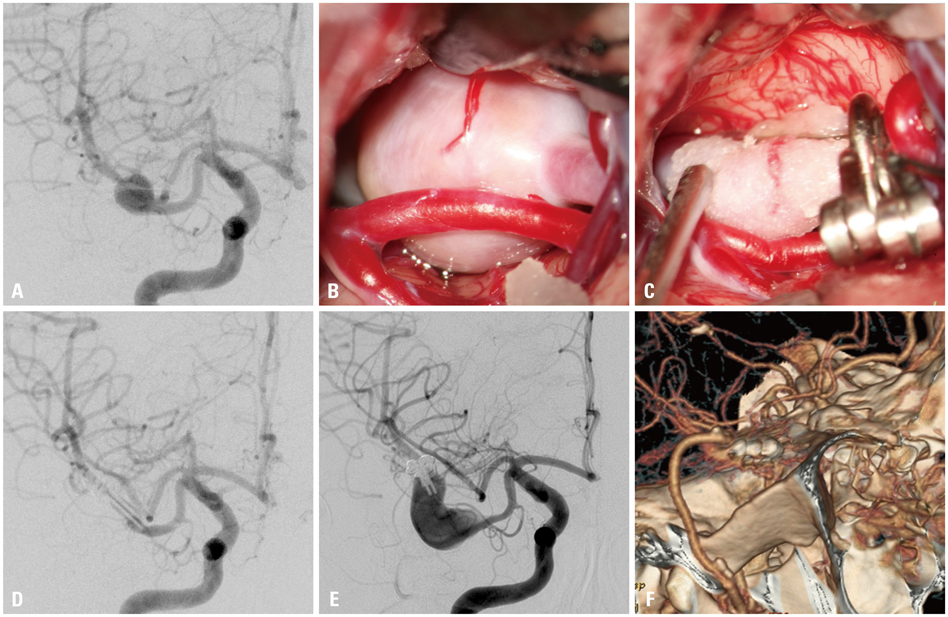
Of 24 patients, eleven patients had internal carotid artery (ICA) blister-like aneurysms, three had dissecting type aneurysms, and ten had fusiform aneurysms. The follow-up period for the late clinical and angiographic results ranged from 10 to 75 months (mean 35 months). Wrap-clipping was performed in eleven, wrap-holding clipping was in ten, and combination of wrap-clip and wrap-holding clip was in three cases. At the last angiographic follow-up study, twelve aneurysms (50%) were found to have completely healed, and nine aneurysms (38%) were at least stable. However, wrap-holding clip for the elongated blister type of ICA aneurysm was found failed, leading to fatal rebleeding in one case, and two cases of combination of wrap-clip-wrap-holding clip revealed delayed branch occlusion and marked regrowing, respectively.
CONCLUSION
Wrap-clipping strategy could be an easy and safe alternative for unclippable aneurysms. The wrapped aneurysm mostly disappeared, or at least remained stationary, after a long-term period. However, surgeons should be aware of that the wrapped aneurysm might become worse. Therefore, follow-up surveillance for an extended period should be mandatory.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cossu M, Pau A, Turtas S, Viola C, Viale GL. Subsequent bleeding from ruptured intracranial aneurysms treated by wrapping or coating: a review of the long-term results in 47 cases. Neurosurgery. 1993; 32:344–346.2. Deshmukh VR, Kakarla UK, Figueiredo EG, Zabramski JM, Spetzler RF. Long-term clinical and angiographic follow-up of unclippable wrapped intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 2006; 58:434–442.
Article3. McLaughlin N, Laroche M, Bojanowski MW. Surgical management of blood blister-like aneurysms of the internal carotid artery. World Neurosurg. 2010; 74:483–493.
Article4. Ogawa A, Suzuki M, Ogasawara K. Aneurysms at nonbranching sites in the surpaclinoid portion of the internal carotid artery: internal carotid artery trunk aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 2000; 47:578–583.
Article5. Ohkuma H, Nakano T, Manabe H, Suzuki S. Subarachnoid hemorrhage caused by a dissecting aneurysm of the internal carotid artery. J Neurosurg. 2002; 97:576–583.
Article6. Todd NV, Tocher JL, Jones PA, Miller JD. Outcome following aneurysm wrapping: a 10-year follow-up review of clipped and wrapped aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 1989; 70:841–846.
Article7. Kamijo K, Matsui T. Acute extracranial-intracranial bypass using a radial artery graft along with trapping of a ruptured blood blister-like aneurysm of the internal carotid artery. Clinical article. J Neurosurg. 2010; 113:781–785.
Article8. Meling TR, Sorteberg A, Bakke SJ, Slettebø H, Hernesniemi J, Sorteberg W. Blood blister-like aneurysms of the internal carotid artery trunk causing subarachnoid hemorrhage: treatment and outcome. J Neurosurg. 2008; 108:662–671.
Article9. Turowski B, Macht S, Kulcsár Z, Hänggi D, Stummer W. Early fatal hemorrhage after endovascular cerebral aneurysm treatment with a flow diverter (SILK-Stent): do we need to rethink our concepts? Neuroradiology. 2011; 53:37–41.
Article10. Cebral JR, Mut F, Raschi M, Scrivano E, Ceratto R, Lylyk P, et al. Aneurysm rupture following treatment with flow-diverting stents: computational hemodynamics analysis of treatment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011; 32:27–33.
Article11. Lubicz B, Collignon L, Raphaeli G, Pruvo JP, Bruneau M, De Witte O, et al. Flow-diverter stent for the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms: a prospective study in 29 patients with 34 aneurysms. Stroke. 2010; 41:2247–2253.
Article12. Kim DJ, Suh SH, Kim BM, Kim DI, Huh SK, Lee JW. Hemorrhagic complications related to the stent-remodeled coil embolization of intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 2010; 67:73–78.
Article13. Drake CG, Vanderlinden RG. The late consequences of incomplete surgical treatment of cerebral aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 1967; 27:226–238.
Article14. Mount LA, Antunes JL. Results of treatment of intracranial aneurysms by wrapping and coating. J Neurosurg. 1975; 42:189–193.
Article15. Abe M, Tabuchi K, Yokoyama H, Uchino A. Blood blisterlike aneurysms of the internal carotid artery. J Neurosurg. 1998; 89:419–424.
Article16. Nakagawa F, Kobayashi S, Takemae T, Sugita K. Aneurysms protruding from the dorsal wall of the internal carotid artery. J Neurosurg. 1986; 65:303–308.
Article17. Lee JW, Choi HG, Jung JY, Huh SK, Lee KC. Surgical strategies for ruptured blister-like aneurysms arising from the internal carotid artery: a clinical analysis of 18 consecutive patients. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2009; 151:125–130.
Article18. Kim LJ, Klopfenstein JD, Spetzler RF. Clip reconstruction and sling wrapping of a fusiform aneurysm: technical note. Neurosurgery. 2007; 61:3 Suppl. 79–80.
Article19. Day AL, Gaposchkin CG, Yu CJ, Rivet DJ, Dacey RG Jr. Spontaneous fusiform middle cerebral artery aneurysms: characteristics and a proposed mechanism of formation. J Neurosurg. 2003; 99:228–240.
Article20. Park SH, Yim MB, Lee CY, Kim E, Son EI. Intracranial Fusiform Aneurysms: It's Pathogenesis, Clinical Characteristics and Managements. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2008; 44:116–123.
Article21. Lanzino G, Kaptain G, Kallmes DF, Dix JE, Kassell NF. Intracranial dissecting aneurysm causing subarachnoid hemorrhage: the role of computerized tomographic angiography and magnetic resonance angiography. Surg Neurol. 1997; 48:477–481.
Article22. Herrera O, Kawamura S, Yasui N, Yoshida Y. Histological changes in the rat common carotid artery induced by aneurysmal wrapping and coating materials. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 1999; 39:134–139.
Article23. Juan GM, Kawamura S, Yasui N, Yoshida Y. Histological changes in the rat common carotid artery following simultaneous topical application of cotton sheet and cyanoacrylate glue. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 1999; 39:908–911.
Article24. Chambi I, Tasker RR, Gentili F, Lougheed WM, Smyth HS, Marshall J, et al. Gauze-induced granuloma ("gauzoma"): an uncommon complication of gauze reinforcement of berry aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 1990; 72:163–170.
Article25. Kubo Y, Ogasawara K, Tomitsuka N, Otawara Y, Watanabe M, Ogawa A. Wrap-clipping with polytetrafluoroethylene for ruptured blisterlike aneurysms of the internal carotid artery. Technical note. J Neurosurg. 2006; 105:785–787.
Article26. Yasuda H, Kuroda S, Nanba R, Ishikawa T, Shinya N, Terasaka S, et al. A novel coating biomaterial for intracranial aneurysms: effects and safety in extra- and intracranial carotid artery. Neuropathology. 2005; 25:66–76.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cerebral Bypass Surgery for Treating Unclippable and Uncoilable Aneurysms
- Surgical Treatment of Unruptured Intracranial Middle Cerebral Artery Aneurysms: Angiographic and Clinical Outcomes in 143 Aneurysms
- Circumferential Wrapping and Clipping with Temporalis Fascia for Treatment of Unclippable Intracranial Aneurysms
- Recent Trends in the Treatment of Cerebral Aneurysms: Comparison between Endovascular Coil Embolization and Surgical Clipping
- Microsurgical management of previously embolized intracranial aneurysms: A single center experience and literature review