J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2017 Jun;43(3):204-211. 10.5125/jkaoms.2017.43.3.204.
Use of elevator instruments when luxating and extracting teeth in dentistry: clinical techniques
- Affiliations
-
- 1Private Practice, Manalapan, NJ, USA. mamounjo@gmail.com
- KMID: 2386368
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2017.43.3.204
Abstract
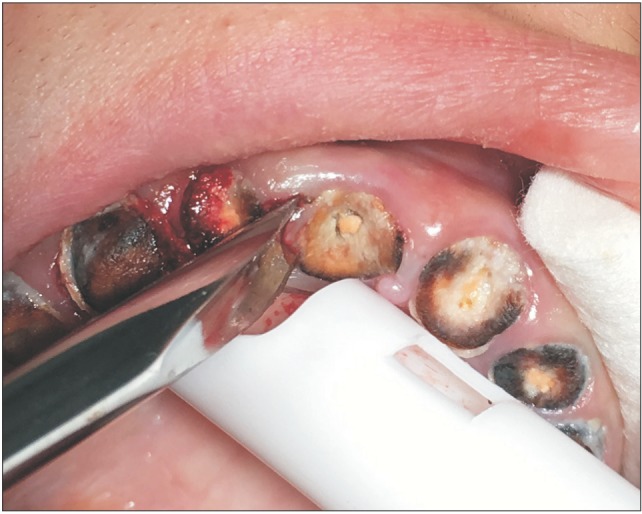
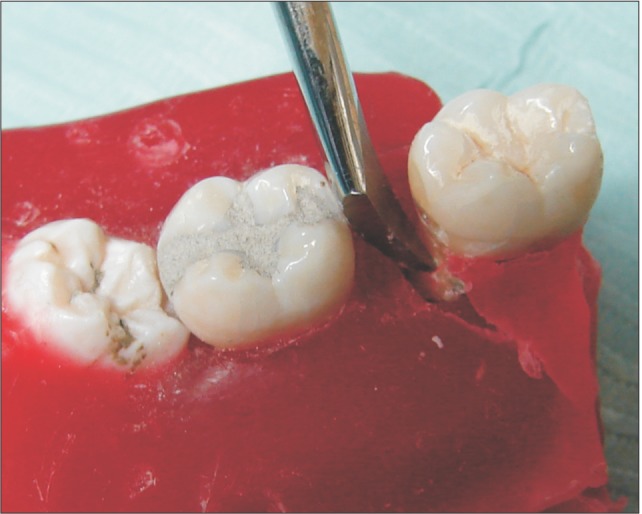
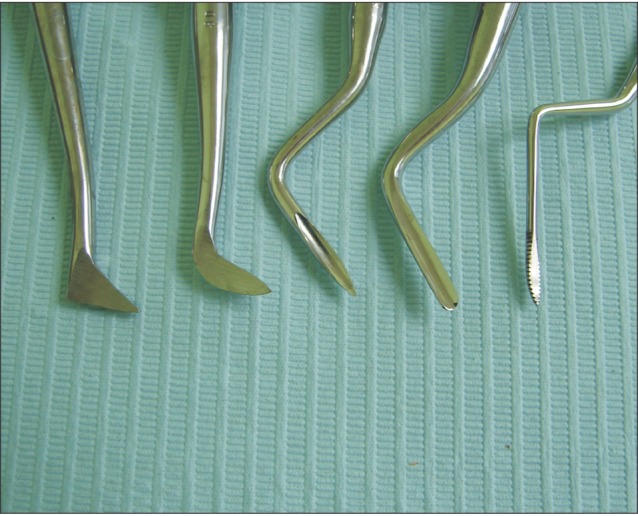
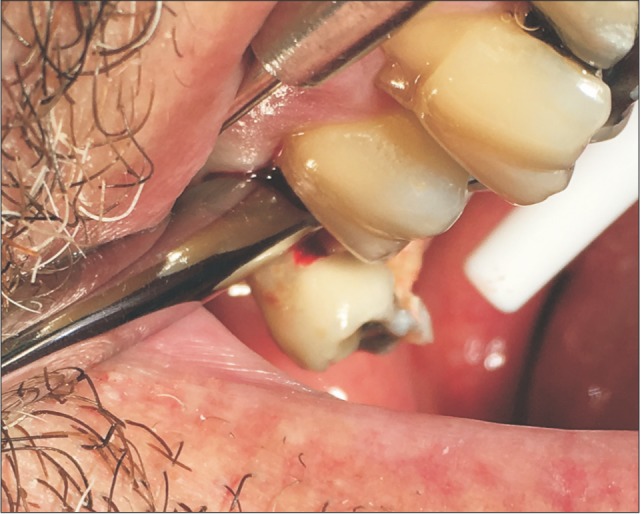
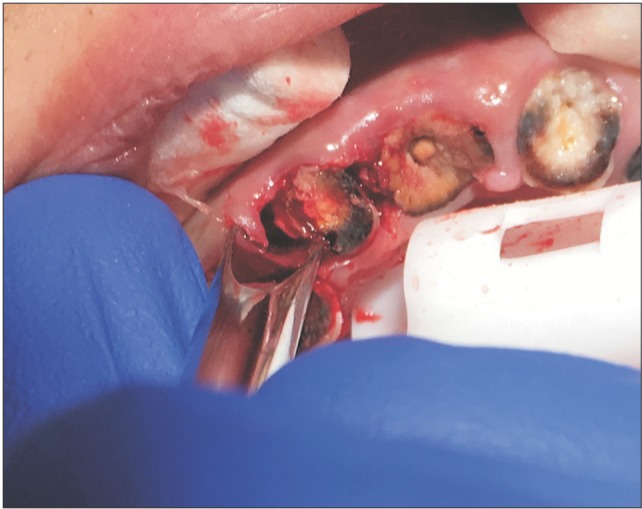
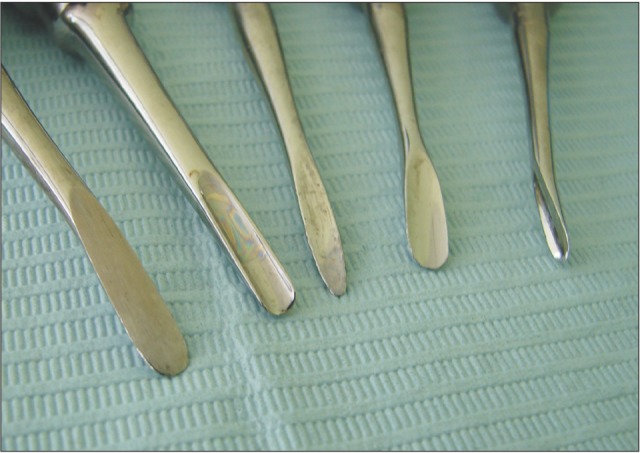
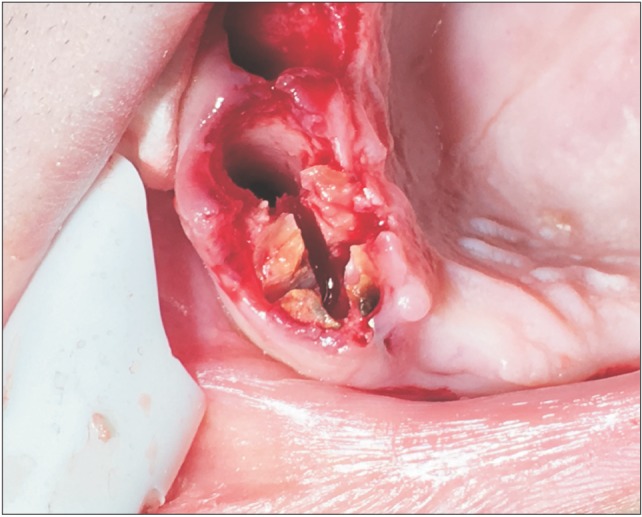
- In dentistry, elevator instruments are used to luxate teeth, and this technique imparts forces to tooth particles that sever the periodontal ligament around tooth roots inside the socket and expand alveolar bone around tooth particles. These effects can result in extraction of the tooth particles or facilitate systematic forceps extraction of the tooth particles. This article presents basic oral surgery techniques for applying elevators to luxate teeth. Determination of the optimal luxation technique requires understanding of the functions of the straight elevator and the Cryer elevator, the concept of purchase points, how the design elements of elevator working ends and tips influence the functionality of an elevator, application of forces to tooth particles, sectioning teeth at furcations, and bone removal to facilitate luxation. The effectiveness of tooth particle luxation is influenced by elevator tip shape and size, the magnitude and the vectors of forces applied to the tooth particle by the tip, and sectioning and bone removal within the operating field. Controlled extraction procedures are facilitated by a dental operating microscope or the magnification of binocular surgical loupes telescopes, combined with co-axial illumination.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fragiskos FD. Oral surgery. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer-Verlag;2007.2. Hupp JR, Ellis E, Tucker MR. Contemporary oral and maxillofacial surgery. 5th ed. St. Louis: Mosby-Elsevier;2008.3. Koerner KR, Tilt LV, Johnson KR. Color atlas of minor oral surgery. London: Mosby-Wolfe;1994.4. Goga Y, Chiba M, Shimizu Y, Mitani H. Compressive force induces osteoblast apoptosis via caspase-8. J Dent Res. 2006; 85:240–244. PMID: 16498071.
Article5. Matsui H, Fukuno N, Kanda Y, Kantoh Y, Chida T, Nagaura Y, et al. The expression of Fn14 via mechanical stress-activated JNK contributes to apoptosis induction in osteoblasts. J Biol Chem. 2014; 289:6438–6450. PMID: 24446436.
Article6. Nettelhoff L, Grimm S, Jacobs C, Walter C, Pabst AM, Goldschmitt J, et al. Influence of mechanical compression on human periodontal ligament fibroblasts and osteoblasts. Clin Oral Investig. 2016; 20:621–629.
Article7. Asanami S, Kasazaki Y. Expert third molar extractions. Tokyo: Quintessence Publishing;1990.8. Kaminishi RM, Davis WH, Nelson NE. Surgical removal of impacted mandibular third molars. Dent Clin North Am. 1979; 23:413–425. PMID: 288669.9. Mamoun J. Use of high-magnification loupes or surgical operating microscope when performing dental extractions. N Y State Dent J. 2013; 79:28–33.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- What Happened to Him Using the Freight Elevator: Fall from Height or Caught Between?
- The clinical usefulness of closed reduction of nasal bone using only a periosteal elevator with a rubber band
- Comparative evaluation of the effectiveness of ultrasonic tips versus the Terauchi file retrieval kit for the removal of separated endodontic instruments
- Dental students' perceptions of undergraduate clinical training in oral and maxillofacial surgery in an integrated curriculum in Saudi Arabia
- Investigation of fracture prevalence of instruments used in root canal treatments at a faculty of dentistry: a prospective study