J Cardiovasc Ultrasound.
2013 Jun;21(2):81-89.
Automated Quantification of Mitral Regurgitation by Three Dimensional Real Time Full Volume Color Doppler Transthoracic Echocardiography: A Validation with Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Comparison with Two Dimensional Quantitative Methods
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 2Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hjchang@yuhs.ac
- 3Department of Radiology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Severance Biomedical Science Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Siemens Medical Solutions, Mountain View, CA, USA.
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Accurate assessment of mitral regurgitation (MR) severity is crucial for clinical decision-making and optimizing patient outcomes. Recent advances in real-time three dimensional (3D) echocardiography provide the option of real-time full volume color Doppler echocardiography (FVCD) measurements. This makes it practical to quantify MR by subtracting aortic stroke volume from the volume of mitral inflow in an automated manner.
METHODS
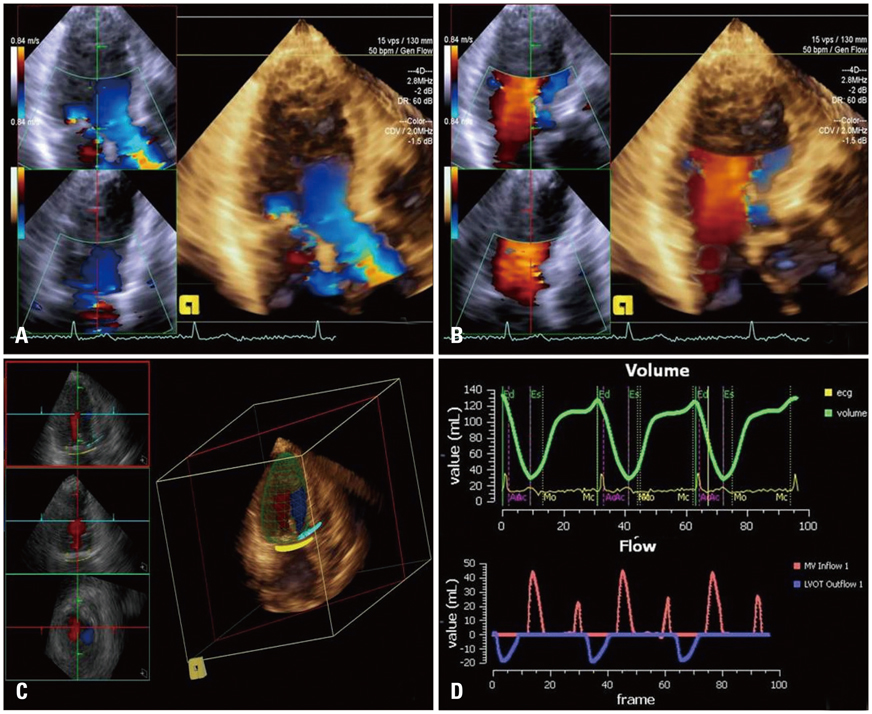
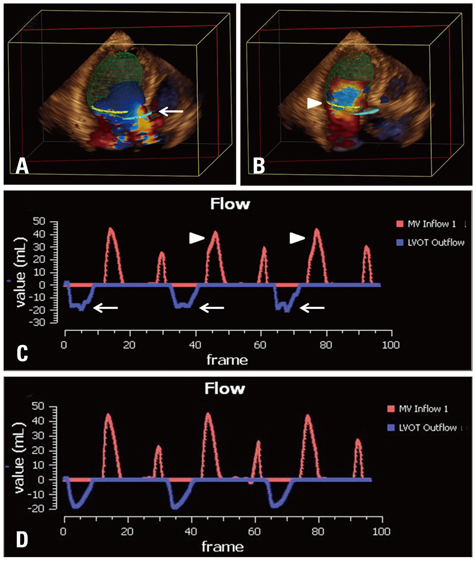
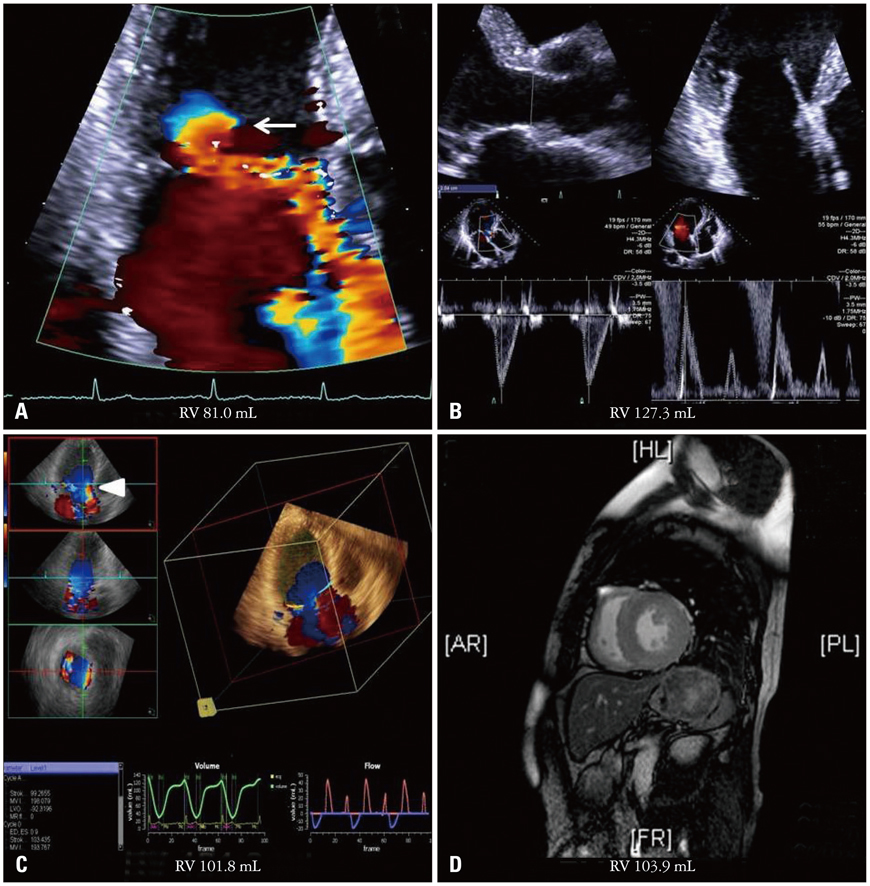
Thirty-two patients with more than a moderate degree of MR assessed by transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) were consecutively enrolled during this study. MR volume was measured by 1) two dimensional (2D) Doppler TTE, using the proximal isovelocity surface area (PISA) and the volumetric quantification methods (VM). Then, 2) real time 3D-FVCD was subsequently obtained, and dedicated software was used to quantify the MR volume. MR volume was also measured using 3) phase contrast cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (PC-CMR). In each patient, all these measurements were obtained within the same day. Automated MR quantification was feasible in 30 of 32 patients.
RESULTS
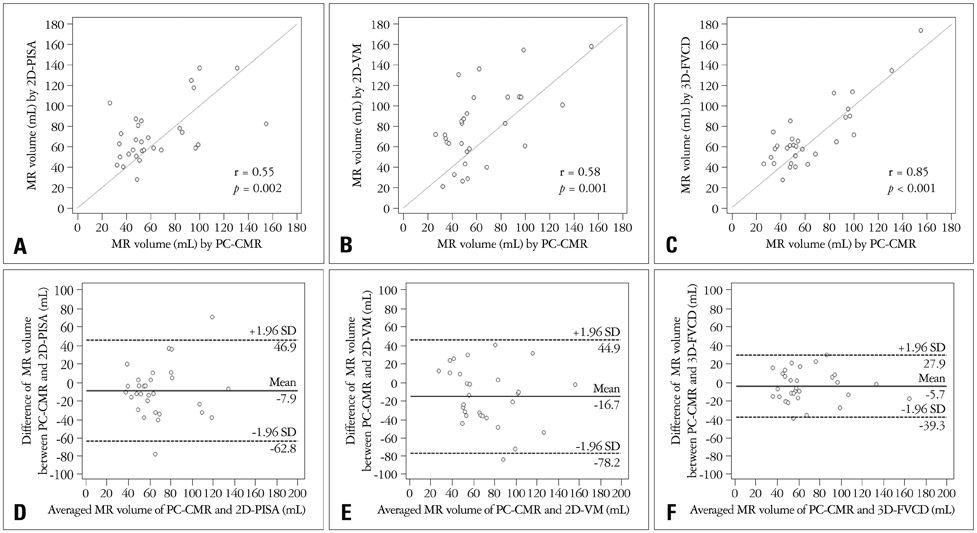
The mean regurgitant volume quantified by 2D-PISA, 2D-VM, 3D-FVCD, and PC-CMR was 72.1 +/- 27.7, 79.9 +/- 36.9, 69.9 +/- 31.5, and 64.2 +/- 30.7 mL, respectively (p = 0.304). There was an excellent correlation between the MR volume measured by PC-CMR and 3D-FVCD (r = 0.85, 95% CI 0.70-0.93, p < 0.001). Compared with PC-CMR, Bland-Altman analysis for 3D-FVCD showed a good agreement (2 standard deviations: 34.3 mL) than did 2D-PISA or 2D-VM (60.0 and 62.8 mL, respectively).
CONCLUSION
Automated quantification of MR with 3D-FVCD is feasible and accurate. It is a promising tool for the real-time 3D echocardiographic assessment of patients with MR.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Enriquez-Sarano M, Akins CW, Vahanian A. Mitral regurgitation. Lancet. 2009; 373:1382–1394.
Article2. Zoghbi WA, Enriquez-Sarano M, Foster E, Grayburn PA, Kraft CD, Levine RA, Nihoyannopoulos P, Otto CM, Quinones MA, Rakowski H, Stewart WJ, Waggoner A, Weissman NJ. American Society of Echocardiography. Recommendations for evaluation of the severity of native valvular regurgitation with two-dimensional and Doppler echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2003; 16:777–802.
Article3. Enriquez-Sarano M, Avierinos JF, Messika-Zeitoun D, Detaint D, Capps M, Nkomo V, Scott C, Schaff HV, Tajik AJ. Quantitative determinants of the outcome of asymptomatic mitral regurgitation. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:875–883.
Article4. Enriquez-Sarano M, Schaff HV, Orszulak TA, Tajik AJ, Bailey KR, Frye RL. Valve repair improves the outcome of surgery for mitral regurgitation. A multivariate analysis. Circulation. 1995; 91:1022–1028.
Article5. Enriquez-Sarano M, Tribouilloy C. Quantitation of mitral regurgitation: rationale, approach, and interpretation in clinical practice. Heart. 2002; 88:Suppl 4. iv1–iv3.
Article6. American College of Cardiology. American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to revise the 1998 guidelines for the management of patients with valvular heart disease). Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists. Bonow RO, Carabello BA, Chatterjee K, de Leon AC Jr, Faxon DP, Freed MD, Gaasch WH, Lytle BW, Nishimura RA, O'Gara PT, O'Rourke RA, Otto CM, Shah PM, Shanewise JS, Smith SC Jr, Jacobs AK, Adams CD, Anderson JL, Antman EM, Fuster V, Halperin JL, Hiratzka LF, Hunt SA, Lytle BW, Nishimura R, Page RL, Riegel B. ACC/AHA 2006 guidelines for the management of patients with valvular heart disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (writing Committee to Revise the 1998 guidelines for the management of patients with valvular heart disease) developed in collaboration with the Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists endorsed by the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006; 48:e1–e148.7. Buck T, Plicht B, Kahlert P, Schenk IM, Hunold P, Erbel R. Effect of dynamic flow rate and orifice area on mitral regurgitant stroke volume quantification using the proximal isovelocity surface area method. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008; 52:767–778.
Article8. Yosefy C, Levine RA, Solis J, Vaturi M, Handschumacher MD, Hung J. Proximal flow convergence region as assessed by real-time 3-dimensional echocardiography: challenging the hemispheric assumption. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2007; 20:389–396.
Article9. Ge S, Bu L, Zhang H, Schelbert E, Disterhoft M, Li X, Li X, Sahn D, Stolpen A, Sonka M. A real-time 3-dimensional digital Doppler method for measurement of flow rate and volume through mitral valve in children: a validation study compared with magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2005; 18:1–7.
Article10. Lodato JA, Weinert L, Baumann R, Coon P, Anderson A, Kim A, Fedson S, Sugeng L, Lang RM. Use of 3-dimensional color Doppler echocardiography to measure stroke volume in human beings: comparison with thermodilution. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2007; 20:103–112.
Article11. Pemberton J, Li X, Karamlou T, Sandquist CA, Thiele K, Shen I, Ungerleider RM, Kenny A, Sahn DJ. The use of live three-dimensional Doppler echocardiography in the measurement of cardiac output: an in vivo animal study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005; 45:433–438.
Article12. Thavendiranathan P, Liu S, Datta S, Walls M, Nitinunu A, Van Houten T, Tomson NA, Vidmar L, Georgescu B, Wang Y, Srinivasan S, De Michelis N, Raman SV, Ryan T, Vannan MA. Automated quantification of mitral inflow and aortic outflow stroke volumes by three-dimensional real-time volume color-flow Doppler transthoracic echocardiography: comparison with pulsed-wave Doppler and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2012; 25:56–65.
Article13. Shanks M, Siebelink HM, Delgado V, van de Veire NR, Ng AC, Sieders A, Schuijf JD, Lamb HJ, Ajmone Marsan N, Westenberg JJ, Kroft LJ, de Roos A, Bax JJ. Quantitative assessment of mitral regurgitation: comparison between three-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography and magnetic resonance imaging. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2010; 3:694–700.14. Lang RM, Bierig M, Devereux RB, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Pellikka PA, Picard MH, Roman MJ, Seward J, Shanewise JS, Solomon SD, Spencer KT, Sutton MS, Stewart WJ. Chamber Quantification Writing Group. American Society of Echocardiography's Guidelines and Standards Committee. European Association of Echocardiography. Recommendations for chamber quantification: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography's Guidelines and Standards Committee and the Chamber Quantification Writing Group, developed in conjunction with the European Association of Echocardiography, a branch of the European Society of Cardiology. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2005; 18:1440–1463.
Article15. Rokey R, Sterling LL, Zoghbi WA, Sartori MP, Limacher MC, Kuo LC, Quinones MA. Determination of regurgitant fraction in isolated mitral or aortic regurgitation by pulsed Doppler two-dimensional echocardiography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1986; 7:1273–1278.
Article16. Enriquez-Sarano M, Bailey KR, Seward JB, Tajik AJ, Krohn MJ, Mays JM. Quantitative Doppler assessment of valvular regurgitation. Circulation. 1993; 87:841–848.
Article17. Wang Y, Georgescu B, Datta S, Liu S, Vannan MA, Comaniciu D. Automatic cardiac flow quantification on 3D volume color Doppler data. In : 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro; Piscataway, NJ: IEEE;2011.18. Zheng Y, Barbu A, Georgescu B, Scheuering M, Comaniciu D. Four-chamber heart modeling and automatic segmentation for 3-D cardiac CT volumes using marginal space learning and steerable features. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2008; 27:1668–1681.
Article19. Matthews F, Largiadèr T, Rhomberg P, van der Loo B, Schmid ER, Jenni R. A novel operator-independent algorithm for cardiac output measurements based on three-dimensional transoesophageal colour Doppler echocardiography. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2010; 11:432–437.
Article20. Pu M, Prior DL, Fan X, Asher CR, Vasquez C, Griffin BP, Thomas JD. Calculation of mitral regurgitant orifice area with use of a simplified proximal convergence method: initial clinical application. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2001; 14:180–185.
Article21. Enriquez-Sarano M, Miller FA Jr, Hayes SN, Bailey KR, Tajik AJ, Seward JB. Effective mitral regurgitant orifice area: clinical use and pitfalls of the proximal isovelocity surface area method. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1995; 25:703–709.
Article22. de Agustín JA, Marcos-Alberca P, Fernandez-Golfin C, Gonçalves A, Feltes G, Nuñez-Gil IJ, Almeria C, Rodrigo JL, Perez de, Macaya C, Zamorano J. Direct measurement of proximal isovelocity surface area by single-beat three-dimensional color Doppler echocardiography in mitral regurgitation: a validation study. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2012; 25:815–823.
Article23. Kizilbash AM, Hundley WG, Willett DL, Franco F, Peshock RM, Grayburn PA. Comparison of quantitative Doppler with magnetic resonance imaging for assessment of the severity of mitral regurgitation. Am J Cardiol. 1998; 81:792–795.
Article24. Hundley WG, Li HF, Willard JE, Landau C, Lange RA, Meshack BM, Hillis LD, Peshock RM. Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of the severity of mitral regurgitation. Comparison with invasive techniques. Circulation. 1995; 92:1151–1158.
Article25. Myerson SG, Francis JM, Neubauer S. Direct and indirect quantification of mitral regurgitation with cardiovascular magnetic resonance, and the effect of heart rate variability. MAGMA. 2010; 23:243–249.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Echocardiographic evaluation of flail mitral valve: Comparison of transthoracic and transesophageal two dimensional and color doppler echocardiography
- Usefulness of Pressure Half Time by Pulse Doppler Ultrasound in Evaluation of the Severity of Mitral Stenosis
- Advances in the Evaluation of Mitral Complex Geometry:Insights from Transthoracic Real-time Three-dimensional Echocardiography
- Assessment of Mitral Stenosis by Doppler Echocardiography: Influence of Regurgitation on Doppler Pressure Half-Time
- Quantitative Evaluation of Regurgitant Volume in the Patients with Mitral Regurgitation Using Color Doppler Proximal Isovelocity Surface Area Method