J Korean Med Sci.
2017 Sep;32(9):1508-1515. 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.9.1508.
Effect of Individual and District-level Socioeconomic Disparities on Cognitive Decline in Community-dwelling Elderly in Seoul
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jjeong@ewha.ac.kr
- 2Gangseo Dementia Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Ewha Brain Institute, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Preventive Medicine, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Psychiatry, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Seoul Metropolitan Center for Dementia, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Molecular Medicine, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Department of Neurology, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 9Yangcheon Dementia Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 10Healthcare Review and Assessment Committee, Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service, Wonju, Korea.
- KMID: 2385959
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2017.32.9.1508
Abstract
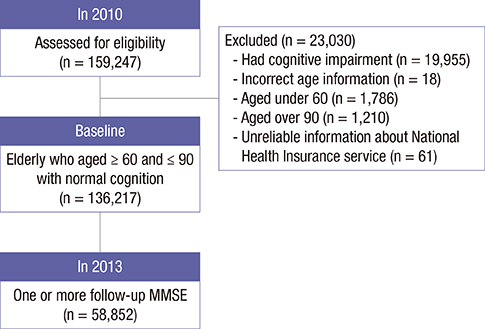
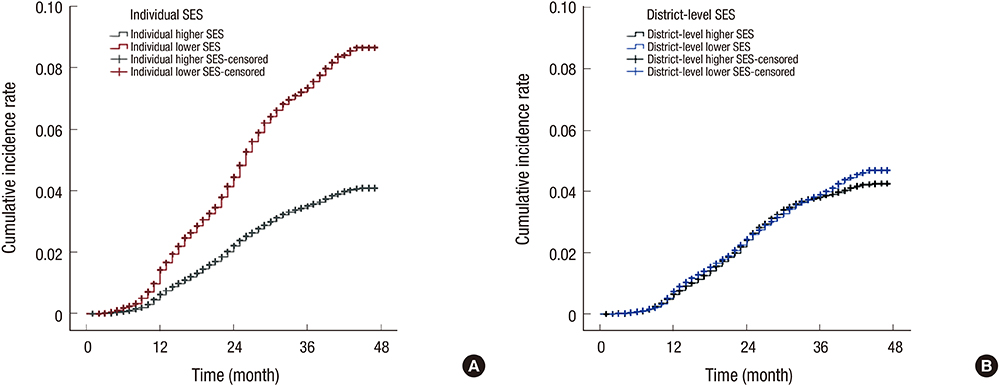
- This study was to investigate the effects of individual and district-level socioeconomic status (SES) on the development of cognitive impairment among the elderly. A 3-year retrospective observational analysis (2010-2013) was conducted which included 136,217 community-dwelling healthy elderly who participated in the Seoul Dementia Management Project. Cognitive impairment was defined as 1.5 standard deviations below the norms on the Mini-mental status examination. In the individual lower SES group, the cumulative incidence rate (CIR) of cognitive impairment was 8.7% (95% confidence interval [CI], 8.64-8.70), whereas the CIR in the individual higher SES group was 4.1% (95% CI, 4.08-4.10). The CIR for lower district-level SES was 4.7% (95% CI, 4.52-4.86), while that in the higher district-level SES was 4.3% (95% CI, 4.06-4.44). There were no additive or synergistic effects between individual and district-level SES. From this study, the individual SES contributed 1.9 times greater to the development of cognitive impairment than the district-level SES, which suggests that individual SES disparities could be considered as one of the important factors in public health related to cognitive impairment in the elderly.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee Y, Back JH, Kim J, Byeon H. Multiple socioeconomic risks and cognitive impairment in older adults. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2010; 29:523–529.2. Koster A, Penninx BW, Bosma H, Kempen GI, Newman AB, Rubin SM, Satterfield S, Atkinson HH, Ayonayon HN, Rosano C. Socioeconomic differences in cognitive decline and the role of biomedical factors. Ann Epidemiol. 2005; 15:564–571.3. Wee LE, Yeo WX, Yang GR, Hannan N, Lim K, Chua C, Tan MY, Fong N, Yeap A, Chen L, et al. Individual and area level socioeconomic status and its association with cognitive function and cognitive impairment (low MMSE) among community-dwelling elderly in Singapore. Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis Extra. 2012; 2:529–542.4. Marengoni A, Fratiglioni L, Bandinelli S, Ferrucci L. Socioeconomic status during lifetime and cognitive impairment no-dementia in late life: the population-based aging in the Chianti Area (InCHIANTI) Study. J Alzheimers Dis. 2011; 24:559–568.5. Yaffe K, Falvey C, Harris TB, Newman A, Satterfield S, Koster A, Ayonayon H, Simonsick E, Health AB. Health ABC Study. Effect of socioeconomic disparities on incidence of dementia among biracial older adults: prospective study. BMJ. 2013; 347:f7051.6. Atti AR, Forlani C, De Ronchi D, Palmer K, Casadio P, Dalmonte E, Fratiglioni L. Cognitive impairment after age 60: clinical and social correlates in the Faenza Project. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010; 21:1325–1334.7. Moretti F, De Ronchi D, Palmer K, Forlani C, Morini V, Ferrari B, Dalmonte E, Atti AR. Prevalence and characteristics of mild cognitive impairment in the general population. Data from an Italian population-based study: the Faenza Project. Aging Ment Health. 2013; 17:267–275.8. Karp A, Kåreholt I, Qiu C, Bellander T, Winblad B, Fratiglioni L. Relation of education and occupation-based socioeconomic status to incident Alzheimer's disease. Am J Epidemiol. 2004; 159:175–183.9. Noble KG, McCandliss BD, Farah MJ. Socioeconomic gradients predict individual differences in neurocognitive abilities. Dev Sci. 2007; 10:464–480.10. Zhang M, Gale SD, Erickson LD, Brown BL, Woody P, Hedges DW. Cognitive function in older adults according to current socioeconomic status. Neuropsychol Dev Cogn B Aging Neuropsychol Cogn. 2015; 22:534–543.11. Wu YT, Prina AM, Brayne C. The association between community environment and cognitive function: a systematic review. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2015; 50:351–362.12. Lang IA, Llewellyn DJ, Langa KM, Wallace RB, Huppert FA, Melzer D. Neighborhood deprivation, individual socioeconomic status, and cognitive function in older people: analyses from the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008; 56:191–198.13. Kim DS. Introduction: health of the health care system in Korea. Soc Work Public Health. 2010; 25:127–141.14. Kim DS. Special issue on the national health care system of South Korea. Soc Work Public Health. 2010; 25:125–126.15. Peter J, Scheef L, Abdulkadir A, Boecker H, Heneka M, Wagner M, Koppara A, Klöppel S, Jessen F. Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Gray matter atrophy pattern in elderly with subjective memory impairment. Alzheimers Dement. 2014; 10:99–108.16. Han C, Jo SA, Jo I, Kim E, Park MH, Kang Y. An adaptation of the Korean mini-mental state examination (K-MMSE) in elderly Koreans: demographic influence and population-based norms (the AGE study). Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2008; 47:302–310.17. Lee JH, Lee KU, Lee DY, Kim KW, Jhoo JH, Kim JH, Lee KH, Kim SY, Han SH, Woo JI. Development of the Korean version of the Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Packet (CERAD-K): clinical and neuropsychological assessment batteries. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. 2002; 57:47–53.18. Cox AM, McKevitt C, Rudd AG, Wolfe CD. Socioeconomic status and stroke. Lancet Neurol. 2006; 5:181–188.19. Diez Roux AV, Borrell LN, Haan M, Jackson SA, Schultz R. Neighbourhood environments and mortality in an elderly cohort: results from the cardiovascular health study. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2004; 58:917–923.20. Wight RG, Aneshensel CS, Miller-Martinez D, Botticello AL, Cummings JR, Karlamangla AS, Seeman TE. Urban neighborhood context, educational attainment, and cognitive function among older adults. Am J Epidemiol. 2006; 163:1071–1078.21. Zeki Al Hazzouri A, Haan MN, Osypuk T, Abdou C, Hinton L, Aiello AE. Neighborhood socioeconomic context and cognitive decline among older Mexican Americans: results from the Sacramento Area Latino Study on Aging. Am J Epidemiol. 2011; 174:423–431.22. Clarke PJ, Weuve J, Barnes L, Evans DA, Mendes de Leon CF. Cognitive decline and the neighborhood environment. Ann Epidemiol. 2015; 25:849–854.23. Barnes DE, Yaffe K. The projected effect of risk factor reduction on Alzheimer’s disease prevalence. Lancet Neurol. 2011; 10:819–828.24. Thorpe RJ Jr, Koster A, Kritchevsky SB, Newman AB, Harris T, Ayonayon HN, Perry S, Rooks RN, Simonsick EM. Health, Aging, and Body Composition Study. Race, socioeconomic resources, and late-life mobility and decline: findings from the Health, Aging, and Body Composition study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2011; 66:1114–1123.25. Wang HX, Jin Y, Hendrie HC, Liang C, Yang L, Cheng Y, Unverzagt FW, Ma F, Hall KS, Murrell JR, et al. Late life leisure activities and risk of cognitive decline. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2013; 68:205–213.26. James BD, Wilson RS, Barnes LL, Bennett DA. Late-life social activity and cognitive decline in old age. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2011; 17:998–1005.27. McEwen BS, Gianaros PJ. Central role of the brain in stress and adaptation: links to socioeconomic status, health, and disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010; 1186:190–222.28. Grundy E, Holt G. The socioeconomic status of older adults: how should we measure it in studies of health inequalities? J Epidemiol Community Health. 2001; 55:895–904.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Group-Based Cognitive Training on Cognitive Performance, Depression, and Quality of Life in Community-Dwelling Elderly
- A 6 Months Follow-Up of Cognitive Function in Urban Community Elderly
- Effect of Cognitive Function, Social Activity Participation and Social Support on Quality of Life of Community-Dwelling Elderly
- Cognitive Function and Survival among the Elderly in a Rural Korean Community
- Effectiveness of Cognitive Training to Instrumental Activities of Daily Living in Community-Dwelling Elderly