Korean J Ophthalmol.
2017 Aug;31(4):336-342. 10.3341/kjo.2016.0114.
Vascular Displacement in Idiopathic Macular Hole after Single-layered Inverted Internal Limiting Membrane Flap Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea. jlee@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Ophthalmology, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 4Research Institute for Convergence of Biomedical Science and Technology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2385583
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2016.0114
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare vascular displacement in the macula after surgical closure of idiopathic macular hole (MH) after single-layered inverted internal limiting membrane (ILM) flap technique and conventional ILM removal.
METHODS
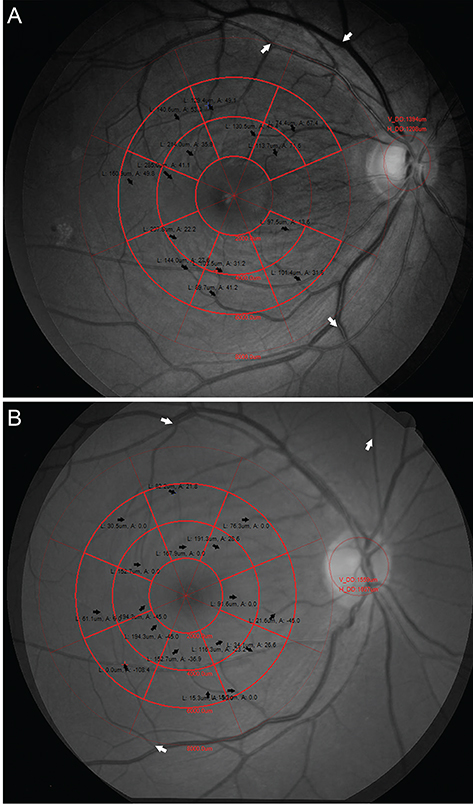
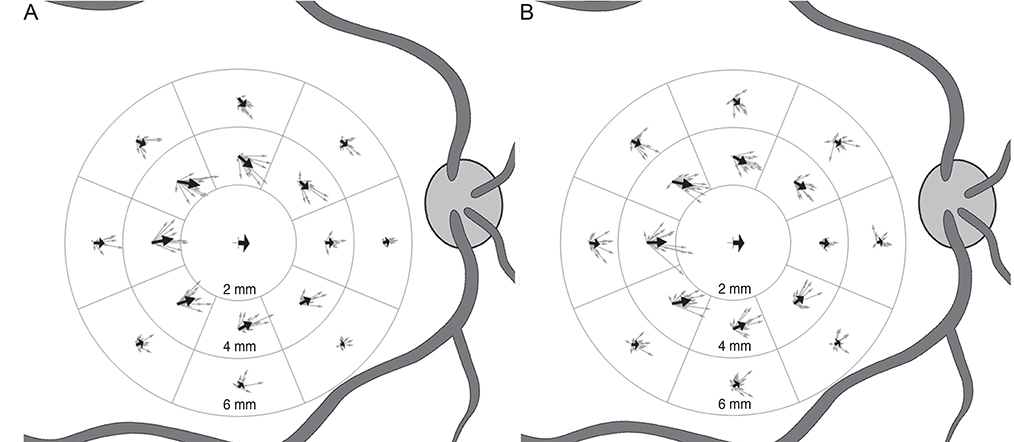
This retrospective study included patients who underwent either vitrectomy and ILM removal only or vitrectomy with single-layered inverted ILM flap for idiopathic MH larger than 400 µm from 2012 to 2015. A customized program compared the positions of the retinal vessels in the macula between preoperative and postoperative photographs. En face images of 6 × 6 mm optical coherence tomography volume scans were registered to calculate the scale. Retinal vessel displacement was measured as a vector value by comparing its location in 16 sectors of a grid partitioned into eight sectors in two rings (inner, 2 to 4 mm; outer, 4 to 6 mm). The distance and angle of displacement were calculated as an average vector and were compared between the two groups for whole sectors, inner ring, outer ring, and for each sector.
RESULTS
Twenty patients were included in the ILM flap group and 22 in the ILM removal group. There were no statistical differences between the groups for baseline characteristics. The average displacement in the ILM flap group and the ILM removal group was 56.6 µm at −3.4° and 64.9 µm at −2.7°, respectively, for the whole sectors (p = 0.900), 76.1 µm at −1.1° and 87.3 µm at −0.9° for the inner ring (p = 0.980), and 37.4 µm at −8.2° and 42.7 µm at −6.3° for the outer ring (p = 0.314). There was no statistical difference in the displacement of each of the sectors.
CONCLUSIONS
Postoperative topographic changes showed no significant differences between the ILM flap and the ILM removal group for idiopathic MH. The single-layered ILM flap technique did not appear to cause additional displacement of the retinal vessels in the macula.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. la Cour M, Friis J. Macular holes: classification, epidemiology, natural history and treatment. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2002; 80:579–587.2. Mester V, Kuhn F. Internal limiting membrane removal in the management of full-thickness macular holes. Am J Ophthalmol. 2000; 129:769–777.3. Tognetto D, Grandin R, Sanguinetti G, et al. Internal limiting membrane removal during macular hole surgery: results of a multicenter retrospective study. Ophthalmology. 2006; 113:1401–1410.4. Haritoglou C, Gass CA, Schaumberger M, et al. Macular changes after peeling of the internal limiting membrane in macular hole surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001; 132:363–368.5. Ito Y, Terasaki H, Takahashi A, et al. Dissociated optic nerve fiber layer appearance after internal limiting membrane peeling for idiopathic macular holes. Ophthalmology. 2005; 112:1415–1420.6. Ishida M, Ichikawa Y, Higashida R, et al. Retinal displacement toward optic disc after internal limiting membrane peeling for idiopathic macular hole. Am J Ophthalmol. 2014; 157:971–977.7. Kawano K, Ito Y, Kondo M, et al. Displacement of foveal area toward optic disc after macular hole surgery with internal limiting membrane peeling. Eye (Lond). 2013; 27:871–877.8. Kim JH, Kang SW, Park DY, et al. Asymmetric elongation of foveal tissue after macular hole surgery and its impact on metamorphopsia. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:2133–2140.9. Fukuda S, Okamoto F, Yuasa M, et al. Vision-related quality of life and visual function in patients undergoing vitrectomy, gas tamponade and cataract surgery for macular hole. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009; 93:1595–1599.10. Konstantinidis A, Hero M, Nanos P, Panos GD. Efficacy of autologous platelets in macular hole surgery. Clin Ophthalmol. 2013; 7:745–750.11. Michalewska Z, Michalewski J, Adelman RA, Nawrocki J. Inverted internal limiting membrane flap technique for large macular holes. Ophthalmology. 2010; 117:2018–2025.12. Michalewska Z, Michalewski J, Dulczewska-Cichecka K, et al. Temporal inverted internal limiting membrane flap technique versus classic inverted internal limiting membrane flap technique: a comparative study. Retina. 2015; 35:1844–1850.13. Shin MK, Park KH, Park SW, et al. Perfluoro-n-octane-assisted single-layered inverted internal limiting membrane flap technique for macular hole surgery. Retina. 2014; 34:1905–1910.14. Michalewska Z, Michalewski J, Dulczewska-Cichecka K, Nawrocki J. Inverted internal limiting membrane flap technique for surgical repair of myopic macular holes. Retina. 2014; 34:664–669.15. Pak KY, Park KH, Kim KH, et al. Topographic changes of the macula after closure of idiopathic macular hole. Retina. 2017; 37:667–672.16. Chung CY, Wong DS, Li KK. Is it necessary to cover the macular hole with the inverted internal limiting membrane flap in macular hole surgery? A case report. BMC Ophthalmol. 2015; 15:115.17. Okuda T, Higashide T, Kobayashi K, et al. Macular hole closure over residual subretinal fluid by an inverted internal limiting membrane flap technique in patients with macular hole retinal detachment in high myopia. Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2016; 10:140–144.18. Yoshikawa M, Murakami T, Nishijima K, et al. Macular migration toward the optic disc after inner limiting membrane peeling for diabetic macular edema. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013; 54:629–635.19. Rodrigues IA, Lee EJ, Williamson TH. Measurement of retinal displacement and metamorphopsia after epiretinal membrane or macular hole surgery. Retina. 2016; 36:695–702.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Treatment of Large Macular Holes Using a Multi-layered Inverted Internal Limiting Membrane Flap Technique
- Exhibiting Residual Subretinal Fluid after High Myopic Macular Hole Retinal Detachment Surgery
- Delayed Closure of Macular Hole with an Internal Limiting Membrane Flap After Intravitreal Triamcinolone Acetonide Injection: Case Report
- Long-term Clinical Outcomes of Macular Hole Surgery Using Internal Limiting Membrane Flap or Insertion
- Perfluoro-n-octane-assisted Superior Inverted ILM Flap without Using the Peeling-off Technique for Large Macular Holes