Kosin Med J.
2017 Jun;32(1):99-104. 10.7180/kmj.2017.32.1.99.
Bronchial Varices in a Patient with Behçet's diasese: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Incheon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Incheon, Korea. kimjusang@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2384838
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2017.32.1.99
Abstract
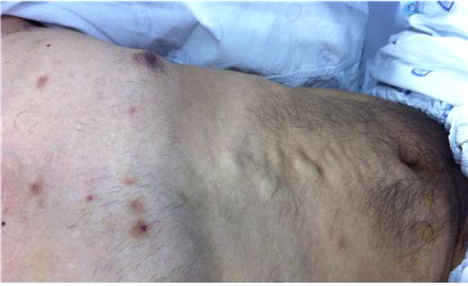
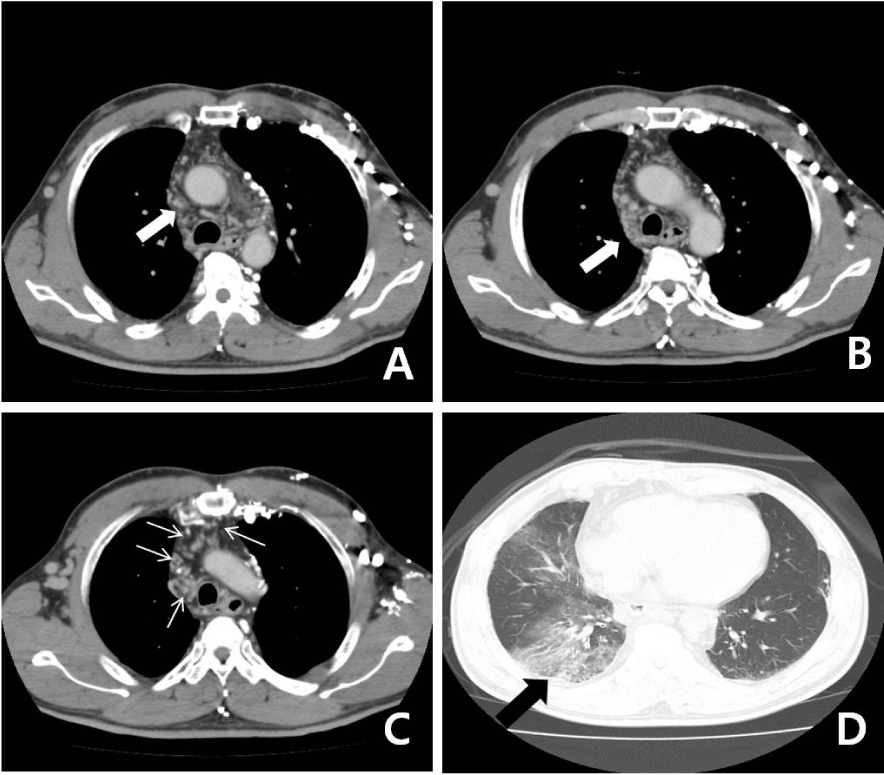
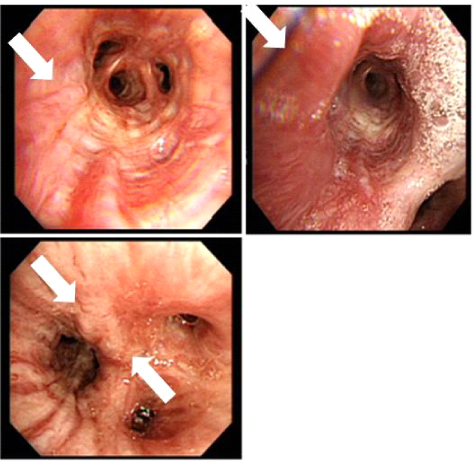
- We report a case of a 65-year-old man with Behcet's disease who presented with massive hemoptysis caused by bronchial varices. A computed tomography (CT) scan and bronchoscopy were performed to identify the bleeding site. The CT scan revealed pneumonia and a combined hemorrhage in the right-middle and lower lobes. Massive bleeding was detected during the bronchoscopy and emergency embolization was attempted but angiographic findings were normal. An anteriojugulo-right femoral bypass operation was performed to relieve the tortuous and hypertrophied jugular venous obstruction. However, thrombectomy and thrombolysis followed because of graft thrombosis six days post-surgery. The patient was treated with steroid and high-dose cyclophosphamide therapy for his Behçet's disease, which caused the venous obstructions; the saccular bronchial varices in the right-middle and right lower lobes on bronchoscopy regressed slightly after four cycles of cyclophosphamide therapy
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chajek T, Fainaru M. Behçet's disease. Report of 41 cases and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 1975; 54:179–196.
Article2. Düzgün N, Ateş A, Aydintuğ OT, Demir O, Olmez U. Characteristics of vascular involvement in Behcet's disease. Scand J Rheumatol. 2006; 35:65–68.3. Moon SY, Kim SY, Cheon WS, Eom KS, Jang SH, Bahn JW, et al. A Case of Bronchial Varices in a Patient with Severe Mitral Stenosis. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2005; 58:174–178.
Article4. Wiebe S, Masclusky I, Manson D, Holowka S, Yoo SJ. Hemoptysis: a rare cause can be related to a bronchial varix due to pulmonary venous obstruction. Pediatr Radiol. 2003; 33:884–886.
Article5. Tavakkoli H, Asadi M, Haghigh M, Esmaeili A. Therapeutic approach to “downhill” esophageal varices bleeding due to superior vena cava syndrome in Behcet's disease: a case report. BMC Gastroenterol. 2006; 6:43.
Article6. Yu M, Shi A, Jin B, Jiang X, Liang H, Ouyang C. Superior vena cava occlusion caused by Behçet disease. J Vasc Surg. 2012; 55:1488–1491.
Article7. Nagahiro I, Toda D, Andou A, Shimizu N. A Case of bronchial varices due to extrahepatic portal hypertension. Respiration. 2007; 74:460–461.
Article8. Seyahi E, Yurdakul S. Behçet's Syndrome and Thrombosis. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2011; 3:e2011026.
Article9. Mansilla AV, Ball D, Putman SG, Cohen GS, Krachman S, Black M. Massive hemoptysis secondary to bronchial collaterals: treatment with use of TIPS and embolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 1999; 10:372–374.
Article10. Roberts LR, Kamath PS. Pathophysiology and treatment of variceal hemorrhage. Mayo Clin Proc. 1996; 71:973–983.
Article11. Ahn JK, Lee YS, Jeon CH, Koh EM, Cha HS. Treatment of venous thrombosis associated with Behcet's disease: immunosuppressive therapy alone versus immunosuppressive therapy plus anticoagulation. Clin Rheumatol. 2008; 27:201–205.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Bronchial Varices in a Patient with Severe Mitral Stenosis
- Multiple Intracranial Aneurysms Associated with Behçet's Disease
- Rupture of Renal Artery in a Patient with Behçet's Disease
- Blepharoptosis in Behçet's Disease
- Successfully treated isolated renal artery pseudoaneurysm in a patient with Behçet's disease