Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2017 Jun;20(2):134-137. 10.5223/pghn.2017.20.2.134.
Gastric Hemangioma Treated with Argon Plasma Coagulation in a Newborn Infant
- Affiliations
-
- 1Good Gang-An Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Pusan National University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. jhongpark@pusan.ac.kr
- 3Department of Radiology, Pusan National University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2384828
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2017.20.2.134
Abstract
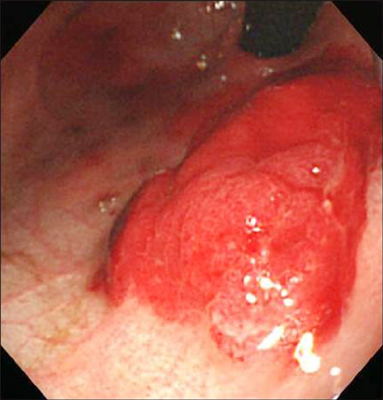
- Gastric hemangioma in the neonatal period is a very rare cause of upper gastrointestinal bleeding. We present a case of hemangioma limited to the gastric cavity in a 10-day-old infant. A huge, erythematous mass with bleeding was observed on the lesser curvature side of the upper part of the stomach. Surgical resection was ruled out because the location of the lesion was too close to the gastroesophageal junction. Medical treatment with intravenous Hâ‚‚ blockers, octreotide, packed red blood cell infusions, local epinephrine injection at the lesion site, application of hemoclip, and gel-form embolization of the left gastric artery did not significantly alter the transfusion requirement. Hemostasis was achieved with endoscopic argon plasma coagulation (APC). After two sessions of APC, complete removal of the lesion was achieved. APC was a simple, safe and effective tool for hemostasis and the ablation of gastric hemangioma without significant complications.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Newborn with Gastric Hemangioma Treated Using Propranolol
Huseyin Kaya, Ismail Kursad Gokce, Sukru Gungor, Hatice Turgut, Ramazan Ozdemir
Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2018;21(4):341-346. doi: 10.5223/pghn.2018.21.4.341.
Reference
-
1. Menon P, Rao KL, Bhasin S, Vanitha V, Thapa BR, Lal A, et al. Giant isolated cavernous hemangioma of the stomach. J Pediatr Surg. 2007; 42:747–749.
Article2. Bamanikar AA, Diwan AG, Benoj D. Gastric hemangioma: an unusual cause of upper gastrointestinal bleed. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2004; 23:113–114.3. Fishman SJ, Burrows PE, Leichtner AM, Mulliken JB. Gastrointestinal manifestations of vascular anomalies in childhood: varied etiologies require multiple therapeutic modalities. J Pediatr Surg. 1998; 33:1163–1167.
Article4. López-Gutiérrez JC. Hemangiomas and vascular malformations of the stomach. J Pediatr Surg. 2007; 42:1634–1635.
Article5. Nagaya M, Kato J, Niimi N, Tanaka S, Akiyoshi K, Tanaka T. Isolated cavernous hemangioma of the stomach in a neonate. J Pediatr Surg. 1998; 33:653–654.
Article6. Stillman AE, Hansen RC, Hallinan V, Strobel C. Diffuse neonatal hemangiomatosis with severe gastrointestinal involvement. Favorable response to steroid therapy. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1983; 22:589–591.
Article7. Bak YT, Oh CH, Kim JH, Lee CH. Blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome: endoscopic removal of the gastrointestinal hemangiomas. Gastrointest Endosc. 1997; 45:90–92.
Article8. Dieckmann K, Maurage C, Faure N, Margulies A, Lorette G, Rudler J, et al. Combined laser-steroid therapy in blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome: case report and review of the literature. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 1994; 4:372–374.
Article9. Khan K, Weisdorf-Schindele S. Gastric hemangiomas in an infant managed with argon plasma coagulation. Pediatr Endosurgery Innov Tech. 2003; 7:185–188.
Article10. Khan K, Schwarzenberg SJ, Sharp H, Weisdorf-Schindele S. Argon plasma coagulation: clinical experience in pediatric patients. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 57:110–112.
Article11. Grund KE. Argon plasma coagulation (APC): ballyhoo or breakthrough? Endoscopy. 1997; 29:196–198.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of gastric antral vascular ectasia treated with argon plasma coagulation
- A Case of Huge Gastric Angiodysplasia Treated with Argon Plasma Coagulation
- Trial of Argon Plasma Coagulation in Patients with Heterotopic Gastric Mucosa Presenting with Laryngopharyngeal Symptoms
- Two Cases of Asymptomatic Pneumoperitoneum after Argon Plasma Coagulation Treatment
- A Case of Argon Plasma Coagulation Therapy for Hemorrhagic Radiation-induced Gastritis