J Korean Assoc Pediatr Surg.
2017 Jun;23(1):5-8. 10.13029/jkaps.2017.23.1.5.
Esophageal Atresia with Bronchogenic Cyst
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatric Surgery, Seoul National University Children's Hospital, Seoul, Korea. spkhy02@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2384423
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13029/jkaps.2017.23.1.5
Abstract
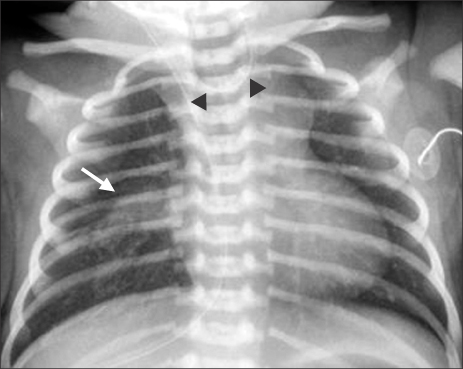
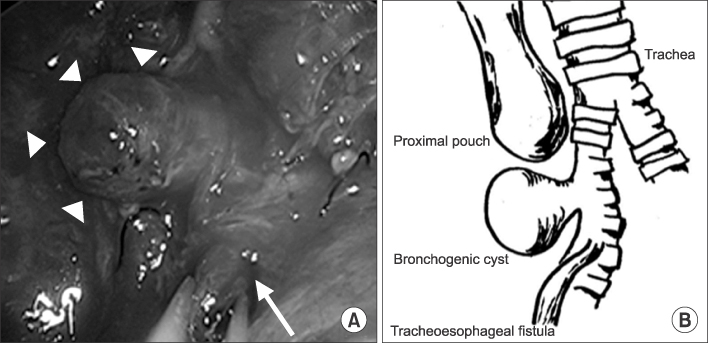
- A baby was diagnosed with esophageal atresia (EA) with tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) on the next day after birth, and end-to-end anastomosis of esophagus with TEF ligation was performed. The distance between proximal and distal esophageal pouch was checked as 3 vertebral body lengths and a 1 cm-sized bronchogenic cyst (BC) was identified near carina on the right side, just below the proximal esophageal pouch. This case report described the baby who have a BC was located between the both esophageal pouch and a longer esophageal gap than usual EA with distal TEF.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Goyal A, Jones MO, Couriel JM, Losty PD. Oesophageal atresia and tracheo-oesophageal fistula. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2006; 91:F381–F384.2. Spitz L. Esophageal atresia: past, present, and future. J Pediatr Surg. 1996; 31:19–25.3. Maier HC. Bronchiogenic cysts of the mediastinum. Ann Surg. 1948; 127:476–502.4. Heithoff KB, Sane SM, Williams HJ, Jarvis CJ, Carter J, Kane P, et al. Bronchopulmonary foregut malformations. A unifying etiological concept. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1976; 126:46–55.5. Newman B. Congenital bronchopulmonary foregut malformations: concepts and controversies. Pediatr Radiol. 2006; 36:773–791.6. Chang EY, Chang HK, Han SJ, Choi SH, Hwang EH, Oh JT. Clinical characteristics and treatment of esophageal atresia: a single institutional experience. J Korean Surg Soc. 2012; 83:43–49.7. Smith N. Oesophageal atresia and tracheo-oesophageal fistula. Early Hum Dev. 2014; 90:947–950.8. Shamji FM, Sachs HJ, Perkins DG. Cystic disease of the lungs. Surg Clin North Am. 1988; 68:581–620.9. Spitz L, Ruangtrakool R. Esophageal substitution. Semin Pediatr Surg. 1998; 7:130–133.10. Nobuhara KK, Gorski YC, La Quaglia MP, Shamberger RC. Bronchogenic cysts and esophageal duplications: common origins and treatment. J Pediatr Surg. 1997; 32:1408–1413.11. Foker JE, Linden BC, Boyle EM Jr, Marquardt C. Development of a true primary repair for the full spectrum of esophageal atresia. Ann Surg. 1997; 226:533–541. discussion 541-3.12. Engum SA, Grosfeld JL, West KW, Rescorla FJ, Scherer LR 3rd. Analysis of morbidity and mortality in 227 cases of esophageal atresia and/or tracheoesophageal fistula over two decades. Arch Surg. 1995; 130:502–508. discussion 508-9.13. Dessanti A, Caccia G, Iannuccelli M, Dettori G. Use of “Gore-Tex surgical membrane” to minimize surgical adhesions in multistaged extrathoracic esophageal elongation for esophageal atresia. J Pediatr Surg. 2000; 35:610–612.14. Holder TM, Ashcraft KW, Sharp RJ, Amoury RA. Care of infants with esophageal atresia, tracheoesophageal fistula, and associated anomalies. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1987; 94:828–835.15. Louhimo I, Lindahl H. Esophageal atresia: primary results of 500 consecutively treated patients. J Pediatr Surg. 1983; 18:217–229.16. Ein SH, Shandling B, Heiss K. Pure esophageal atresia: outlook in the 1990s. J Pediatr Surg. 1993; 28:1147–1150.17. Brown AK, Tam PK. Measurement of gap length in esophageal atresia: a simple predictor of outcome. J Am Coll Surg. 1996; 182:41–45.18. Narasimharao KL, Mitra SK. Esophageal atresia associated with esophageal duplication cyst. J Pediatr Surg. 1987; 22:984–985.19. Hemalatha V, Batcup G, Brereton RJ, Spitz L. Intrathoracic foregut cyst (foregut duplication) associated with esophageal atresia. J Pediatr Surg. 1980; 15:178–180.20. McNally J, Charles AK, Spicer RD, Grier D. Mixed foregut cyst associated with esophageal atresia. J Pediatr Surg. 2001; 36:939–940.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Coexistence of Bronchial Atresia and Bronchogenic Cyst: A Case of Report
- Intramural Bronchogenic Cyst of the Esophagus: A case report
- Extralobar pulmonary sequestration with an associated cyst of mixed bronchogenic and esophageal type--a case report
- Intramural Bronchogenic Cyst of the Esophagus: A case report
- A Case of an Esophageal Bronchogenic Cyst Presenting with Dysphagia