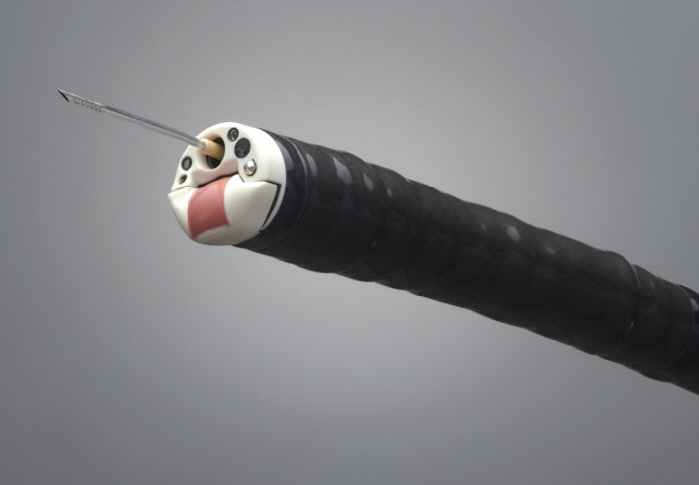
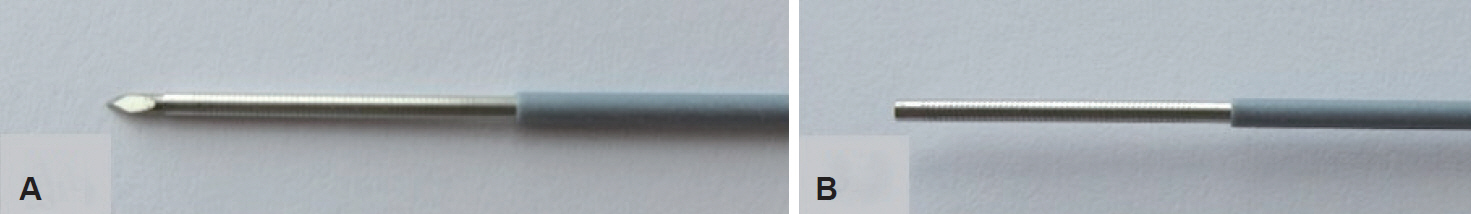
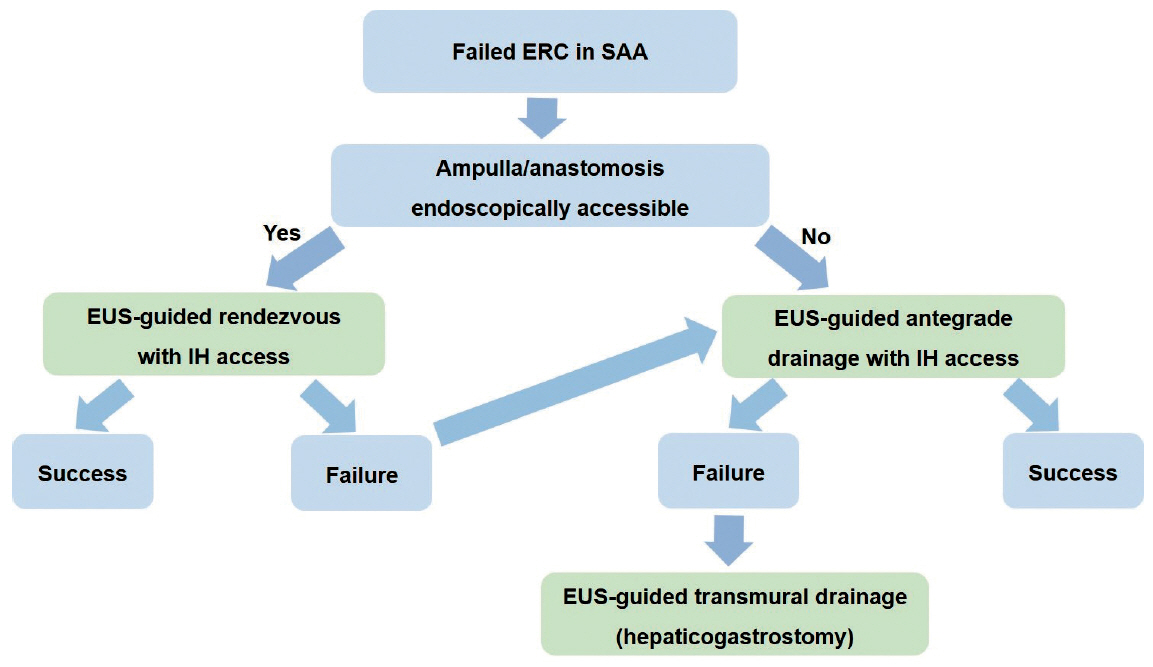
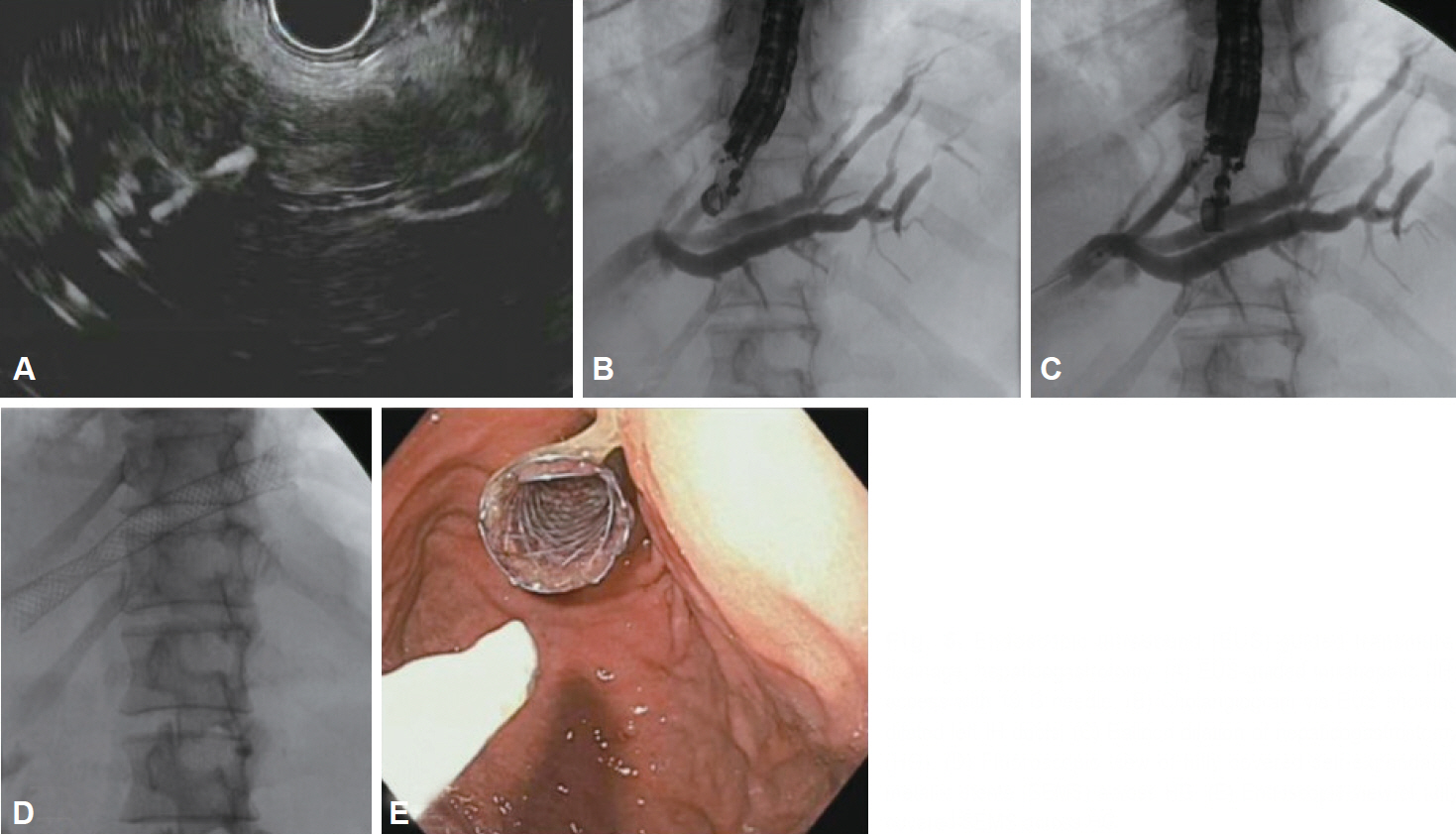
Clin Endosc.
2016 Nov;49(6):515-529. 10.5946/ce.2016.144.
Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Pancreatobiliary Endoscopy in Surgically Altered Anatomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA. lslee@partners.org
- KMID: 2383446
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2016.144
Abstract
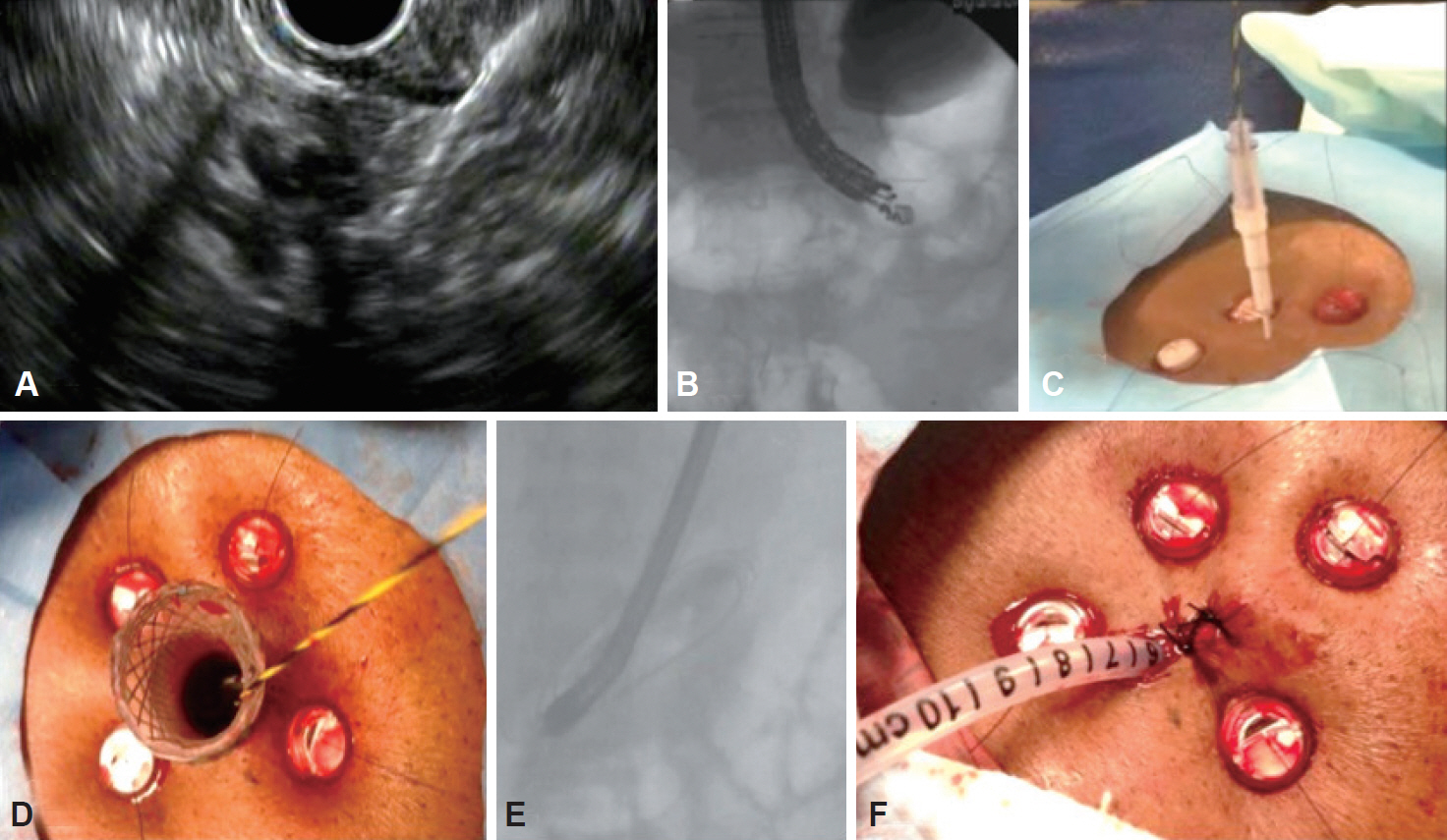
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) has become the mainstay of therapy for pancreatobiliary diseases. While ERCP is safe and highly effective in the general population, the procedure remains challenging or impossible in patients with surgically altered anatomy (SAA). Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) allows transmural access to the bile or pancreatic duct (PD) prior to ductal drainage using ERCP-based techniques. Also known as endosonography-guided cholangiopancreatography (ESCP), the procedure provides multiple advantages over overtube-assisted enteroscopy ERCP or percutaneous or surgical approaches. However, the procedure should only be performed by endoscopists experienced in both EUS and ERCP and with the proper tools. In this review, various EUS-guided diagnostic and therapeutic drainage techniques in patients with SAA are examined. Detailed step-by-step procedural descriptions, technical tips, feasibility, and safety data are also discussed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Biliary Drainage for Benign Biliary Diseases
Yousuke Nakai, Hirofumi Kogure, Hiroyuki Isayama, Kazuhiko Koike
Clin Endosc. 2019;52(3):212-219. doi: 10.5946/ce.2018.188.Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Biliary Access, with Focus on Technique and Practical Tips
Woo Hyun Paik, Do Hyun Park
Clin Endosc. 2017;50(2):104-111. doi: 10.5946/ce.2017.036.
Reference
-
1. Kethu SR, Adler DG, Conway JD, et al. ERCP cannulation and sphincterotomy devices. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:435–445.
Article2. Enestvedt BK, Kothari S, Pannala R, et al. Devices and techniques for ERCP in the surgically altered GI tract. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 83:1061–1075.
Article3. Moreels TG. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in patients with altered anatomy: How to deal with the challenges? World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2014; 6:345–351.
Article4. Al-Lehibi AH, Kumar N, Sayuk GS, et al. Success Rates for Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) in Patients With Altered Anatomy From Prior Surgical Intervention. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:AB228.5. Skinner M, Popa D, Neumann H, Wilcox CM, Mönkemüller K. ERCP with the overtube-assisted enteroscopy technique: a systematic review. Endoscopy. 2014; 46:560–572.
Article6. Feitoza AB, Baron TH. Endoscopy and ERCP in the setting of previous upper GI tract surgery. Part I: reconstruction without alteration of pancreaticobiliary anatomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001; 54:743–749.
Article7. Feitoza AB, Baron TH. Endoscopy and ERCP in the setting of previous upper GI tract surgery. Part II: postsurgical anatomy with alteration of the pancreaticobiliary tree. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 55:75–79.
Article8. Bilroth T. Offenes Schreiben an Herrn Dr. L. Wittelshöfer. Wien Med Wochenschr. 1881; 31:161–165.9. Mason EE, Ito C. Gastric bypass in obesity. Surg Clin North Am. 1967; 47:1345–1351.
Article10. Ponce J, Nguyen NT, Hutter M, Sudan R, Morton JM. American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery estimation of bariatric surgery procedures in the United States, 2011-2014. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2015; 11:1199–1200.
Article11. Cameron JL. Atlas of surgery. vol 2. St. Louis: Mosby;1994.12. Jones DB, Maithel SK, Schneider BE. Atlas of minimally invasive surgery. Woodbury, CT: Cine-Med;2006.13. Sauve L. Des pancréatectomies et spécialement de la pancréatectomie céphalique. Rev chir. 1908; 37:113–385. 113-152, 335-385.14. Whipple AO, Parsons WB, Mullins CR. TREATMENT OF CARCINOMA OF THE AMPULLA OF VATER. Ann Surg. 1935; 102:763–779.15. Fusaroli P, Serrani M, Lisotti A, D’Ercole MC, Ceroni L, Caletti G. Performance of the forward-view echoendoscope for pancreaticobiliary examination in patients with status post-upper gastrointestinal surgery. Endosc Ultrasound. 2015; 4:336–341.
Article16. Lee JH, Topazian M. Pancreatic endosonography after Billroth II gastrectomy. Endoscopy. 2004; 36:972–975.
Article17. Wilson JA, Hoffman B, Hawes RH, Romagnuolo J. EUS in patients with surgically altered upper GI anatomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 72:947–953.
Article18. Sanders M, McGrath K. Endoscopic Ultrasound in the Patient with Difficult Anatomy. Tech Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 9:84–89.
Article19. Kahaleh M, Artifon EL, Perez-Miranda M, et al. Endoscopic ultrasonography guided biliary drainage: summary of consortium meeting, May 7th, 2011, Chicago. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:1372–1379.
Article20. Wiersema MJ, Sandusky D, Carr R, Wiersema LM, Erdel WC, Frederick PK. Endosonography-guided cholangiopancreatography. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996; 43:102–106.
Article21. Giovannini M, Bories E, Tellez F. EUS-Guided Bilio-Pancreatic Drainage. In : Lee LS, editor. ERCP and EUS: A Case-Based Approach. New York (NY): Springer;2015. p. 575–588.22. Kunda R, Pérez-Miranda M, Will U, et al. EUS-guided choledochoduodenostomy for malignant distal biliary obstruction using a lumen- apposing fully covered metal stent after failed ERCP. Surg Endosc. 2016; 30:5002–5008.23. Tyberg A, Desai AP, Kumta NA, et al. EUS-guided biliary drainage after failed ERCP: a novel algorithm individualized based on patient anatomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; May. 26. [Epub]. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2016.05.035.
Article24. Weilert F. Prospective evaluation of simplified algorithm for EUS-guided intra-hepatic biliary access and anterograde interventions for failed ERCP. Surg Endosc. 2014; 28:3193–3199.
Article25. Khashab MA, Valeshabad AK, Modayil R, et al. EUS-guided biliary drainage by using a standardized approach for malignant biliary obstruction: rendezvous versus direct transluminal techniques (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 78:734–741.
Article26. Mallery S, Matlock J, Freeman ML. EUS-guided rendezvous drainage of obstructed biliary and pancreatic ducts: Report of 6 cases. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004; 59:100–107.
Article27. Kahaleh M, Yoshida C, Kane L, Yeaton P. Interventional EUS cholangiography: A report of five cases. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004; 60:138–142.
Article28. Gupta K, Mallery S, Hunter D, Freeman ML. Endoscopic ultrasound and percutaneous access for endoscopic biliary and pancreatic drainage after initially failed ERCP. Rev Gastroenterol Disord. 2007; 7:22–37.29. Kahaleh M, Wang P, Shami VM, Tokar J, Yeaton P. EUS-guided transhepatic cholangiography: report of 6 cases. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 61:307–313.
Article30. Brauer BC, Chen YK, Fukami N, Shah RJ. Single-operator EUS-guided cholangiopancreatography for difficult pancreaticobiliary access (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 70:471–479.
Article31. Tarantino I, Barresi L, Repici A, Traina M. EUS-guided biliary drainage: a case series. Endoscopy. 2008; 40:336–339.
Article32. Maranki J, Hernandez AJ, Arslan B, et al. Interventional endoscopic ultrasound- guided cholangiography: long-term experience of an emerging alternative to percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography. Endoscopy. 2009; 41:532–538.33. Shah JN, Marson F, Weilert F, et al. Single-operator, single-session EUS-guided anterograde cholangiopancreatography in failed ERCP or inaccessible papilla. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 75:56–64.
Article34. Dhir V, Bhandari S, Bapat M, Maydeo A. Comparison of EUS-guided rendezvous and precut papillotomy techniques for biliary access (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 75:354–359.
Article35. Giovannini M, Moutardier V, Pesenti C, Bories E, Lelong B, Delpero JR. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided bilioduodenal anastomosis: a new technique for biliary drainage. Endoscopy. 2001; 33:898–900.
Article36. Weilert F, Binmoeller KF, Marson F, Bhat Y, Shah JN. Endoscopic ultrasound- guided anterograde treatment of biliary stones following gastric bypass. Endoscopy. 2011; 43:1105–1108.
Article37. Park DH, Jang JW, Lee SS, Seo DW, Lee SK, Kim MH. EUS-guided transhepatic antegrade balloon dilation for benign bilioenteric anastomotic strictures in a patient with hepaticojejunostomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 75:692–693.
Article38. Iwashita T, Yasuda I, Doi S, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided antegrade treatments for biliary disorders in patients with surgically altered anatomy. Dig Dis Sci. 2013; 58:2417–2422.
Article39. Nguyen-Tang T, Binmoeller KF, Sanchez-Yague A, Shah JN. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided transhepatic anterograde self-expandable metal stent (SEMS) placement across malignant biliary obstruction. Endoscopy. 2010; 42:232–236.
Article40. Puspok A, Lomoschitz F, Dejaco C, Hejna M, Sautner T, Gangl A. Endoscopic ultrasound guided therapy of benign and malignant biliary obstruction: a case series. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005; 100:1743–1747.
Article41. Iwashita T, Nakai Y, Hara K, Isayama H, Itoi T, Park do H. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided antegrade treatment of bile duct stone in patients with surgically altered anatomy: a multicenter retrospective cohort study. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2016; 23:227–233.
Article42. Itoi T, Sofuni A, Tsuchiya T, Ijima M, Iwashita T. Endoscopic ultrasonography- guided transhepatic antegrade stone removal in patients with surgically altered anatomy: case series and technical review (with videos). J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2014; 21:E86–E93.43. Sansak I, Itoi T, Moriyasu F. Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided transhepatic antegrade stone removal in a patient with Roux-en-Y anastomosis (with video). J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2014; 21:719–720.
Article44. Ogura T, Chiba Y, Masuda D, et al. Comparison of the clinical impact of endoscopic ultrasound-guided choledochoduodenostomy and hepaticogastrostomy for bile duct obstruction with duodenal obstruction. Endoscopy. 2016; 48:156–163.
Article45. Burmester E, Niehaus J, Leineweber T, Huetteroth T. EUS-cholangio- drainage of the bile duct: report of 4 cases. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 57:246–251.46. Giovannini M, Dotti M, Bories E, et al. Hepaticogastrostomy by echo-endoscopy as a palliative treatment in a patient with metastatic biliary obstruction. Endoscopy. 2003; 35:1076–1078.
Article47. Kahaleh M, Hernandez AJ, Tokar J, Adams RB, Shami VM, Yeaton P. Interventional EUS-guided cholangiography: evaluation of a technique in evolution. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 64:52–59.
Article48. Artifon EL, Chaves DM, Ishioka S, Souza TF, Matuguma SE, Sakai P. Echoguided hepatico-gastrostomy: a case report. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2007; 62:799–802.
Article49. Will U, Thieme A, Fueldner F, Gerlach R, Wanzar I, Meyer F. Treatment of biliary obstruction in selected patients by endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS)-guided transluminal biliary drainage. Endoscopy. 2007; 39:292–295.
Article50. Bories E, Pesenti C, Caillol F, Lopes C, Giovannini M. Transgastric endoscopic ultrasonography-guided biliary drainage: results of a pilot study. Endoscopy. 2007; 39:287–291.51. Dhir V, Itoi T, Khashab MA, et al. Multicenter comparative evaluation of endoscopic placement of expandable metal stents for malignant distal common bile duct obstruction by ERCP or EUS-guided approach. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 81:913–923.
Article52. Artifon EL, Loureiro JF, Baron TH, Fernandes K, Kahaleh M, Marson FP. Surgery or EUS-guided choledochoduodenostomy for malignant distal biliary obstruction after ERCP failure. Endosc Ultrasound. 2015; 4:235–243.
Article53. Khashab MA, Valeshabad AK, Afghani E, et al. A comparative evaluation of EUS-guided biliary drainage and percutaneous drainage in patients with distal malignant biliary obstruction and failed ERCP. Dig Dis Sci. 2015; 60:557–565.
Article54. Bapaye A, Dubale N, Aher A. Comparison of endosonography-guided vs. percutaneous biliary stenting when papilla is inaccessible for ERCP. United European Gastroenterol J. 2013; 1:285–293.
Article55. Artifon EL, Aparicio D, Paione JB, et al. Biliary drainage in patients with unresectable, malignant obstruction where ERCP fails: endoscopic ultrasonography- guided choledochoduodenostomy versus percutaneous drainage. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2012; 46:768–774.56. Harada N, Kouzu T, Arima M, Asano T, Kikuchi T, Isono K. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreatography: a case report. Endoscopy. 1995; 27:612–615.
Article57. Fujii-Lau LL, Levy MJ. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreatic duct drainage. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2015; 22:51–57.
Article58. Takano S, Ito Y, Oishi H, et al. A retrospective analysis of 88 patients with pancreaticogastrostomy after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Hepatogastroenterology. 2000; 47:1454–1457.59. Haddad LB, Scatton O, Randone B, et al. Pancreatic fistula after pancreaticoduodenectomy: the conservative treatment of choice. HPB (Oxford). 2009; 11:203–209.
Article60. Tyberg A, Sharaiha RZ, Kedia P, et al. EUS-guided pancreatic drainage for pancreatic strictures after failed ERCP: a multicenter international collaborative study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; Jul. 25. [Epub]. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2016.07.030.
Article61. Chen YI, Levy MJ, Moreels TG, et al. An international multicenter study comparing EUS-guided pancreatic duct drainage with enteroscopy- assisted endoscopic retrograde pancreatography after Whipple surgery. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; Jul. 25. [Epub]. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2016.07.031.62. Barkay O, Sherman S, McHenry L, et al. Therapeutic EUS-assisted endoscopic retrograde pancreatography after failed pancreatic duct cannulation at ERCP. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:1166–1173.
Article63. Will U, Meyer F, Manger T, Wanzar I. Endoscopic ultrasound-assisted rendezvous maneuver to achieve pancreatic duct drainage in obstructive chronic pancreatitis. Endoscopy. 2005; 37:171–173.
Article64. Papachristou GI, Gleeson FC, Petersen BT, Levy MJ. Pancreatic endoscopic ultrasound-assisted rendezvous procedure to facilitate drainage of nondilated pancreatic ducts. Endoscopy. 2007; 39 Suppl 1:E324–E325.
Article65. Itoi T, Kikuyama M, Ishii K, Matsumura K, Sofuni A, Itokawa F. EUS-guided rendezvous with single-balloon enteroscopy for treatment of stenotic pancreaticojejunal anastomosis in post-Whipple patients (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 73:398–401.
Article66. Kikuyama M, Itoi T, Ota Y, et al. Therapeutic endoscopy for stenotic pancreatodigestive tract anastomosis after pancreatoduodenectomy (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 73:376–382.
Article67. Kurihara T, Itoi T, Sofuni A, Itokawa F, Moriyasu F. Endoscopic ultrasonography- guided pancreatic duct drainage after failed endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in patients with malignant and benign pancreatic duct obstructions. Dig Endosc. 2013; 25 Suppl 2:109–116.68. Bataille L, Deprez P. A new application for therapeutic EUS: main pancreatic duct drainage with a “pancreatic rendezvous technique”. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 55:740–743.
Article69. Keenan J, Mallery S, Freeman ML. EUS rendezvous for pancreatic stent placement during endoscopic snare ampullectomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66:850–853.
Article70. Saftoiu A, Dumitrescu D, Stoica M, et al. EUS-assisted rendezvous stenting of the pancreatic duct for chronic calcifying pancreatitis with multiple pseudocysts. Pancreatology. 2007; 7:74–79.
Article71. Cooper ST, Malick J, McGrath K, Slivka A, Sanders MK. EUS-guided rendezvous for the treatment of pancreaticopleural fistula in a patient with chronic pancreatitis and pancreas pseudodivisum. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:652–654.
Article72. Itoi T, Sofuni A, Tsuchiya T, et al. Initial evaluation of a new plastic pancreatic duct stent for endoscopic ultrasonography-guided placement. Endoscopy. 2015; 47:462–465.
Article73. Oh D, Park do H, Cho MK, et al. Feasibility and safety of a fully covered self-expandable metal stent with antimigration properties for EUS-guided pancreatic duct drainage: early and midterm outcomes (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 83:366–373. e2.
Article74. Francois E, Kahaleh M, Giovannini M, Matos C, Deviere J. EUS-guided pancreaticogastrostomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 56:128–133.75. Kahaleh M, Yoshida C, Yeaton P. EUS antegrade pancreatography with gastropancreatic duct stent placement: Review of two cases. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 58:919–923.
Article76. Ryou M, Mullady DK, Dimaio CJ, Swanson RS, Carr-Locke DL, Thompson CC. Pancreatic antegrade needle-knife (PANK) for treatment of symptomatic pancreatic duct obstruction in Whipple patients (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 72:1081–1088.
Article77. Tessier G, Bories E, Arvanitakis M, et al. EUS-guided pancreatogastrostomy and pancreatobulbostomy for the treatment of pain in patients with pancreatic ductal dilatation inaccessible for transpapillary endoscopic therapy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 65:233–241.
Article78. Ergun M, Aouattah T, Gillain C, Gigot JF, Hubert C, Deprez PH. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided transluminal drainage of pancreatic duct obstruction: long-term outcome. Endoscopy. 2011; 43:518–525.
Article79. Baron TH, Vickers SM. Surgical gastrostomy placement as access for diagnostic and therapeutic ERCP. Gastrointest Endosc. 1998; 48:640–641.
Article80. Thompson CC, Ryou MK, Kumar N, Slattery J, Aihara H, Ryan MB. Single-session EUS-guided transgastric ERCP in the gastric bypass patient. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014; 80:517.
Article81. Kedia P, Kumta NA, Widmer J, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-directed transgastric ERCP (EDGE) for Roux-en-Y anatomy: a novel technique. Endoscopy. 2015; 47:159–163.
Article82. Kedia P, Sharaiha RZ, Kumta NA, Kahaleh M. Internal EUS-directed transgastric ERCP (EDGE): game over. Gastroenterology. 2014; 147:566–568.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recent development of endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Biliary Drainage for Benign Biliary Diseases
- Challenges of Endoscopic Management of Pancreaticobiliary Complications in Surgically Altered Gastrointestinal Anatomy
- Technical tips for endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreatic duct access and drainage
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Pancreatic Duct Intervention