Korean J Gastroenterol.
2017 Apr;69(4):248-252. 10.4166/kjg.2017.69.4.248.
A Rare Case of Pancreas Divisum Accompanied by Acute Pancreatitis Following Endoscopic Hemostasis for Duodenal Ulcer Bleeding
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea. smyoon@chungbuk.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea.
- KMID: 2383404
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2017.69.4.248
Abstract
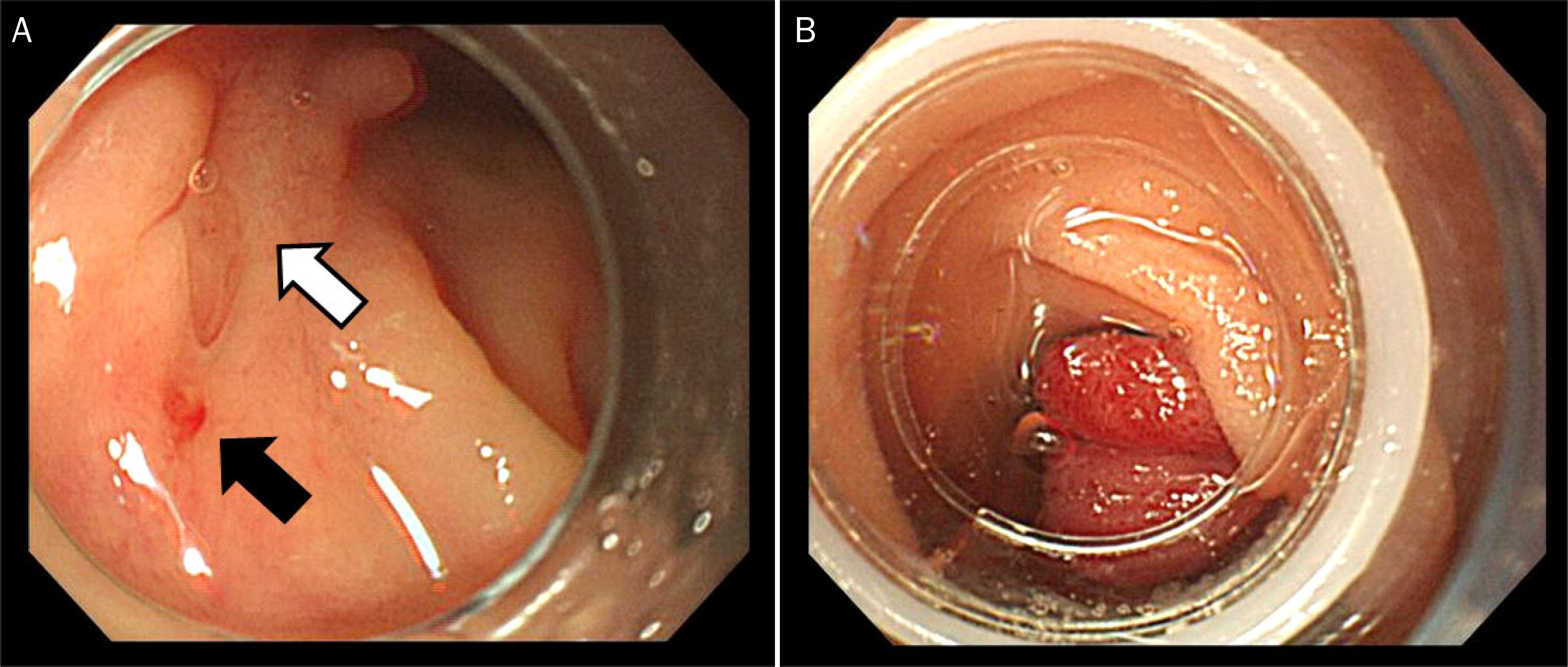
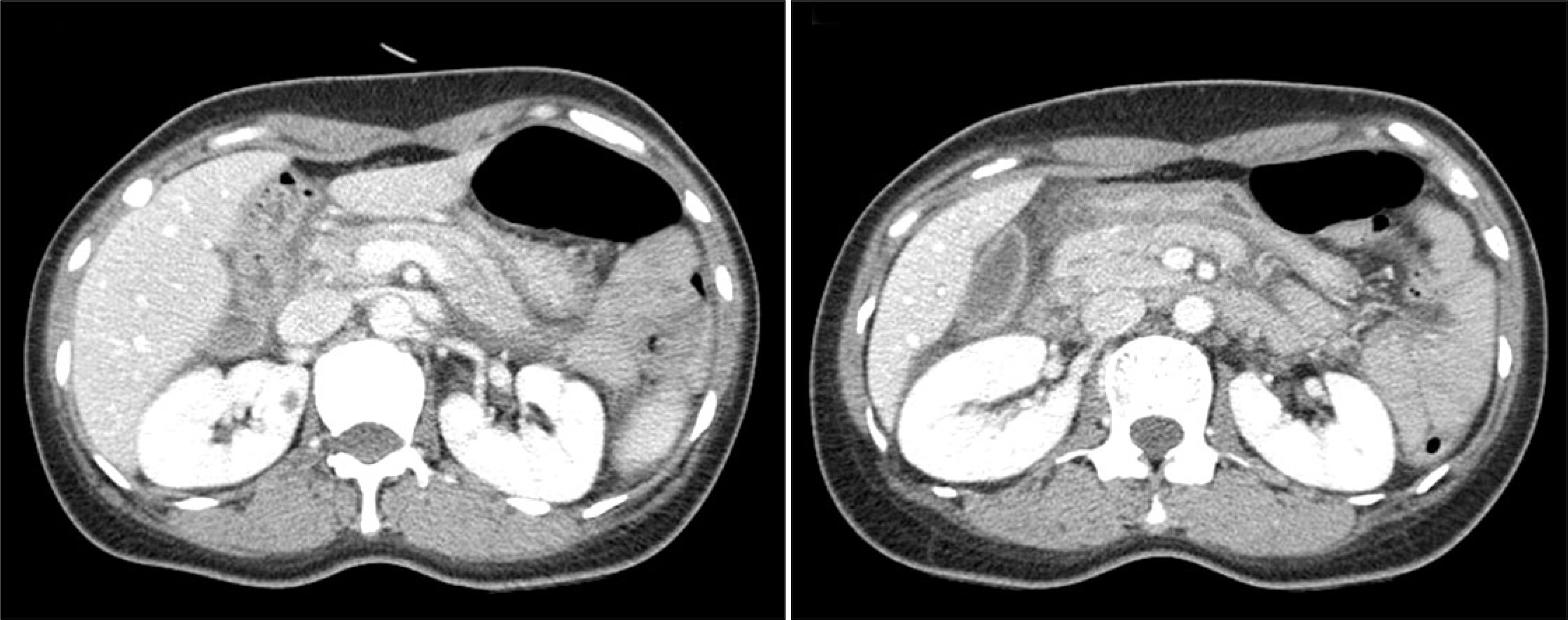
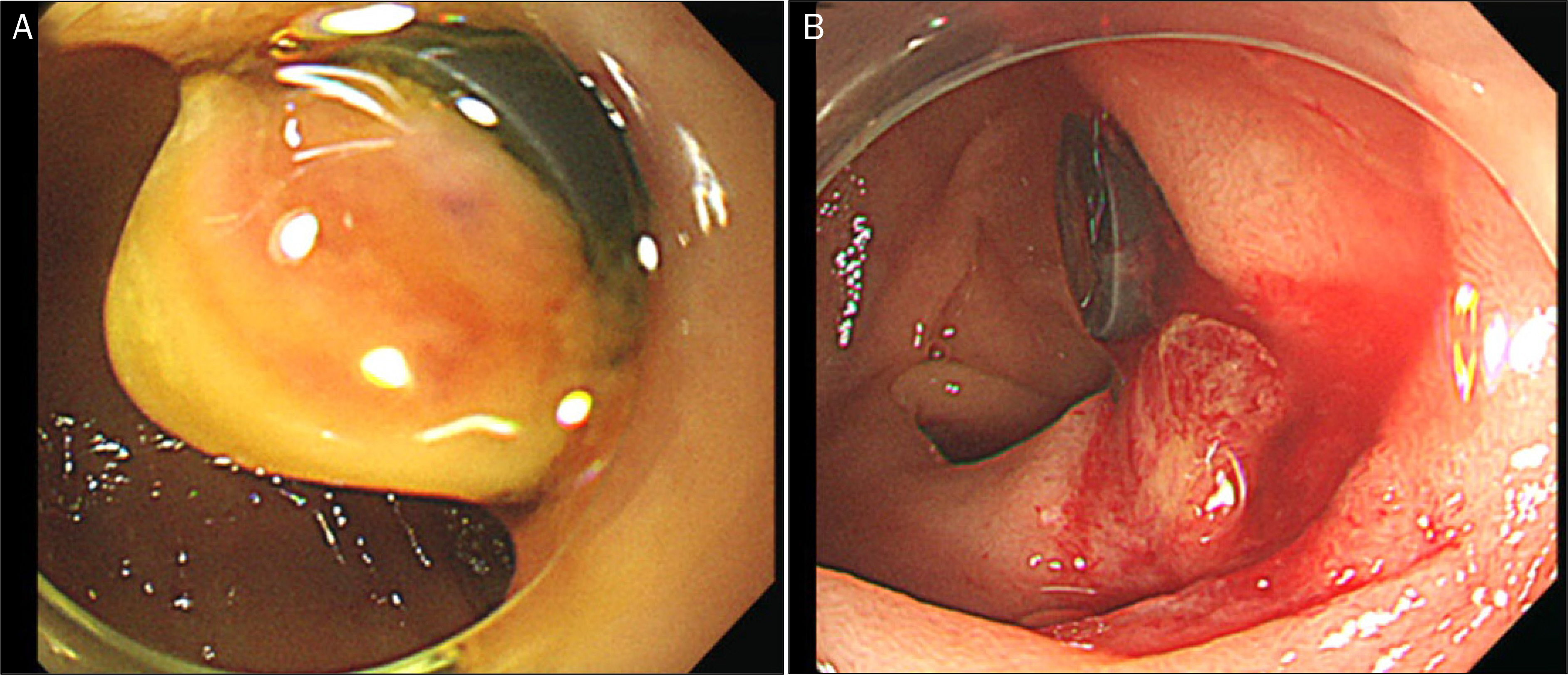
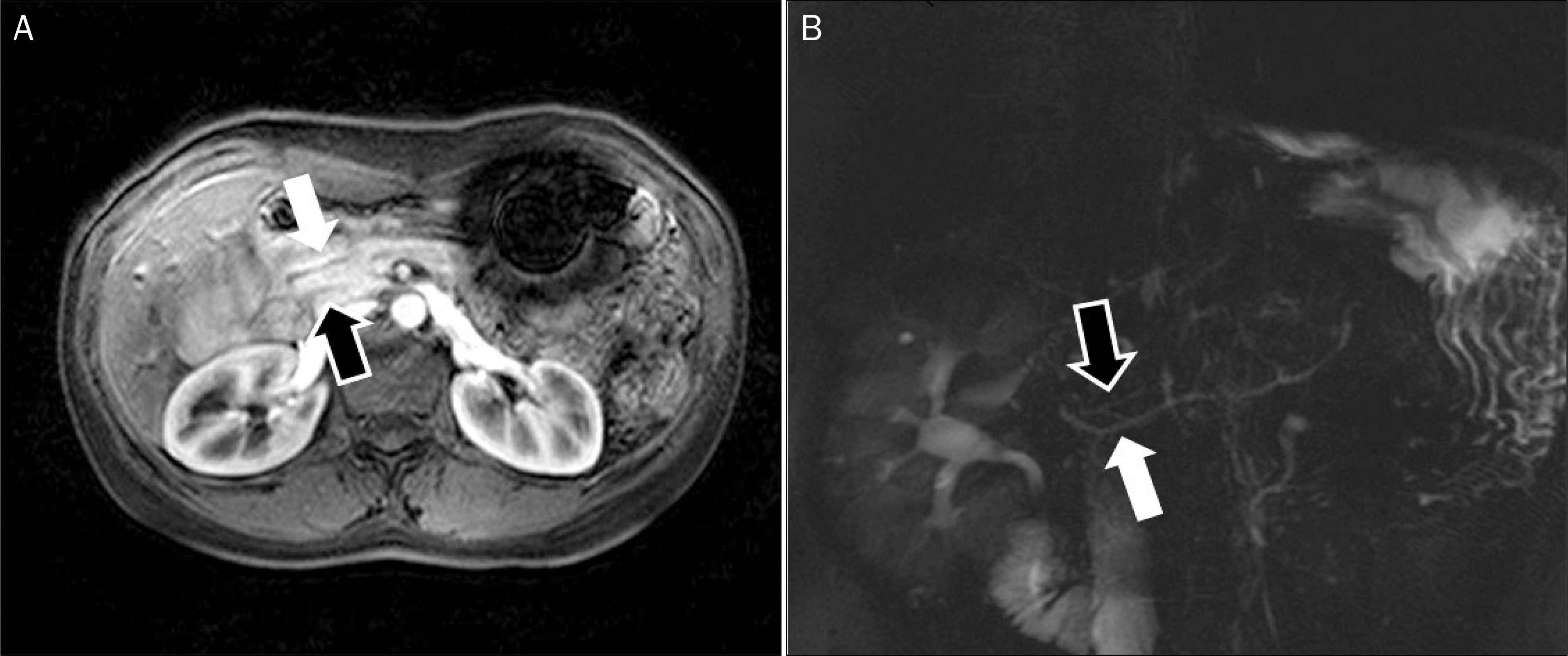
- Peptic ulcer bleeding is treated using endoscopic hemostasis using clips or bands. Pancreas divisum (PD), a congenital anomaly of the pancreas, usually has no clinical symptoms; however, pancreatitis may occur if there are disturbances in the drainage of pancreatic secretions. We report an unusual case of PD accompanied by acute pancreatitis, following endoscopic band ligation for duodenal ulcer bleeding. A 48-year-old woman was admitted to our hospital due to melena. An upper endoscopy revealed a small ulcer with oozing adjacent minor papilla. An endoscopic band ligation was performed on this lesion. Acute pancreatitis developed suddenly 6 hours after the band ligation and improved dramatically after removal of the band. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography was performed, revealing complete PD. Endoscopic band ligation is known as the effective method for peptic ulcer bleeding; however, it should be used carefully in duodenal ulcer bleeding near the minor duodenal papilla due to the possibility of PD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Laine L. Gastrointestinal bleeding. Kasper DL, Fauci AS, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Jameson JL, Loscalzo J, editors. Harrison's principles of internal medicine. Volume 1. 19th ed.New York: Mc Graw Hill Education;2015. p. 276–279.2. Kim YG, Kim TN, Kim KO. Carcinoid tumor of the minor papilla in complete pancreas divisum presenting as recurrent abdominal pain. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010; 10:17.
Article3. Holster IL, Kuipers EJ. Update on the endoscopic management of peptic ulcer bleeding. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2011; 13:525–531.
Article4. Kim KB, Yoon SM, Youn SJ. Endoscopy for nonvariceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Clin Endosc. 2014; 47:315–319.
Article5. Marmo R, Rotondano G, Piscopo R, Bianco MA, D'Angella R, Cipolletta L. Dual therapy versus monotherapy in the endoscopic treatment of high-risk bleeding ulcers: a metaanalysis of controlled trials. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007; 102:279–289. quiz 469.
Article6. Sung JJ, Tsoi KK, Lai LH, Wu JC, Lau JY. Endoscopic clipping versus injection and thermo-coagulation in the treatment of nonvariceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding: a metaanalysis. Gut. 2007; 56:1364–1373.
Article7. Park CH, Lee WS, Joo YE, Choi SK, Rew JS, Kim SJ. Endoscopic band ligation for control of acute peptic ulcer bleeding. Endoscopy. 2004; 36:79–82.
Article8. Misra SP, Dwivedi M, Misra V, Kunwar B, Arora JS, Dharmani S. Endoscopic band ligation as salvage therapy in patients with bleeding peptic ulcers not responding to injection therapy. Endoscopy. 2005; 37:626–629.
Article9. Banerjee B, Trivedi MH, Swied AM. Endoscopic band ligation for gastric ulcer bleeding. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2000; 10:246–248.
Article10. Lu WF. ERCP and CT diagnosis of pancreas divisum and its relation to etiology of chronic pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 1998; 4:150–152.
Article11. Kamisawa T. Clinical significance of the minor duodenal papilla and accessory pancreatic duct. J Gastroenterol. 2004; 39:605–615.
Article12. Warshaw AL, Simeone JF, Schapiro RH, Flavin-Warshaw B. Evaluation and treatment of the dorsal duct syndrome (pancreas divisum redefined). Am J Surg. 1990; 159:59–66. discussion 64–66.13. Jacob L, Geenen JE, Catalano MF, Johnson GK, Geenen DJ, Hogan WJ. Clinical presentation and short-term outcome of endoscopic therapy of patients with symptomatic incomplete pancreas divisum. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999; 49:53–57.
Article14. Kamisawa T, Tabata I, Tajima T, Tsushima K, Yoshida Y. Patency of the human accessory pancreatic duct as determined by dye-injection endoscopic retrograde pancreatography. Digestion. 1997; 58:78–82.
Article15. Lehman GA, Sherman S, Nisi R, Hawes RH. Pancreas divisum: results of minor papilla sphincterotomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1993; 39:1–8.
Article16. Nevins AB, Keeffe EB. Acute pancreatitis after gastrointestinal endoscopy. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2002; 34:94–95.
Article17. Lu Y, Xu B, Chen L, Bie LK, Gong B. Endoscopic intervention through endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in the management of symptomatic pancreas divisum: a long-term follow-up study. Gut Liver. 2016; 10:476–482.
Article18. Mariani A, Di Leo M, Petrone MC, et al. Outcome of endotherapy for pancreas divisum in patients with acute recurrent pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:17468–17475.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Intramural Duodenal Hematoma Accompanied by Acute Pancreatitis Following Endoscopic Hemostasis for Duodenal Ulcer Bleeding
- An Impacted Pancreatic Stone at the Orifice of the Minor Papilla Causing a Bout of Acute Pancreatitis in a Patient with Pancreas Divisum
- A Case of Successful Endoscopic Treatment for Acute Recurrent Pancreatitis Due to Pancreas Divisum with Santorinicele Masquerading as Drug Induced Pancreatitis
- Endoscopic Treatment of a Pediatric Patient with Acute Pancreatitis Caused by Anomalous Union of Pancreaticobiliary Duct Combined with Incomplete Pancreatic Divisum
- Intramural Duodenal Hematoma Complicated with Pancreatitis after Endoscopic Hemostasis in a Chronic Renal Failure Patient with Maintenance Hemodialysis