Immune Netw.
2017 Jun;17(3):186-191. 10.4110/in.2017.17.3.186.
Moderate Exercise Enhances the Production of Interferon-γ and Interleukin-12 in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Immunology, School of Medicine, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan 6517838736, Iran. m.hajibehzad@umsha.ac.ir
- 2Molecular Immunology Research Group, Research Center for Molecular Medicine, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan 6517838736, Iran.
- 3Research Center for Molecular Medicine, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan 6517838736, Iran.
- 4Neurophysiology Research Center, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan 6517838736, Iran.
- KMID: 2383357
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2017.17.3.186
Abstract
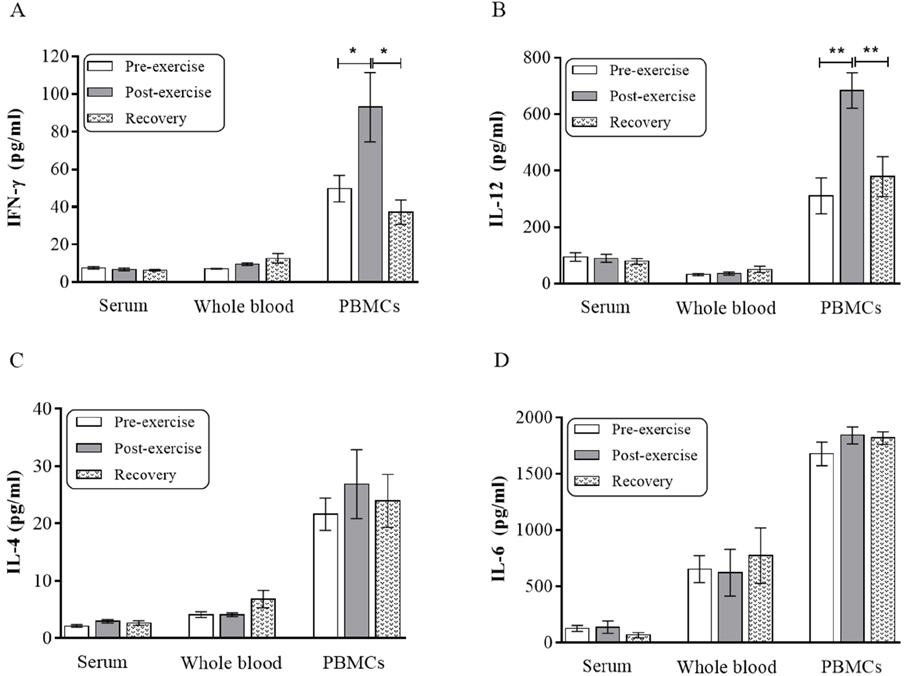
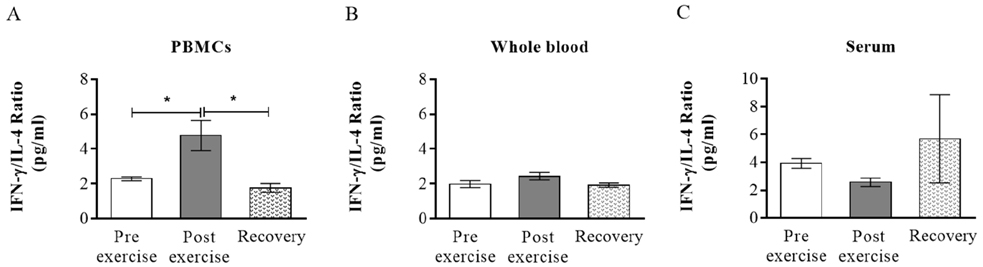
- The purpose of this study was to explore the effect of two months moderate exercise on levels of IFN-γ, IL-12, IL-6 and IL-4 in serum and supernatants of in vitro mitogen-activated (PHA for 48 h) whole blood (WB) and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Sixteen healthy males participated in running program (30 min/day, 5 days/week). Blood samples were collected in three stages; 24 h before to start exercise, 48 h and two months after the last session of the exercise. The samples were analyzed for the cytokines by ELISA. The levels of IFN-γ and IL-12 were increased significantly in activated PBMCs culture after exercise and were back to normal level after two months rest. A significant elevation of IFN-γ/IL-4 ratio was observed in activated PBMCs culture by acting possibly on IFN-γ. The results suggest that short moderate intensity exercise enhances Th1 immune inflammatory and anti-allergic conditions in response to mitogen.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Alterations in Spontaneous Movement, Corticosterone, and Cytokines in Mice Exposed to 835 MHz Radiofrequency Radiation
Min Sun Lee, Chang Seok Oh, Ji Ho Ryu, Jin-Koo Lee, Myeung Ju Kim
Korean J Phys Anthropol. 2018;31(1):19-26. doi: 10.11637/kjpa.2018.31.1.19.
Reference
-
1. Zhu J, Paul WE. Peripheral CD4+ T-cell differentiation regulated by networks of cytokines and transcription factors. Immunol Rev. 2010; 238:247–262.
Article2. Schroder K, Hertzog PJ, Ravasi T, Hume DA. Interferon-gamma: an overview of signals, mechanisms and functions. J Leukoc Biol. 2004; 75:163–189.3. Alahgholi-Hajibehzad M, Kasapoglu P, Jafari R, Rezaei N. The role of T regulatory cells in immunopathogenesis of myasthenia gravis: implications for therapeutics. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2015; 11:859–870.
Article4. Jager A, Kuchroo VK. Effector and regulatory T-cell subsets in autoimmunity and tissue inflammation. Scand J Immunol. 2010; 72:173–184.
Article5. Garcia-Aymerich J, Varraso R, Danaei G, Camargo CA Jr, Hernan MA. Incidence of adult-onset asthma after hypothetical interventions on body mass index and physical activity: an application of the parametric g-formula. Am J Epidemiol. 2014; 179:20–26.
Article6. Matthews CE, Ockene IS, Freedson PS, Rosal MC, Merriam PA, Hebert JR. Moderate to vigorous physical activity and risk of upper-respiratory tract infection. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2002; 34:1242–1248.
Article7. Robson-Ansley P, Howatson G, Tallent J, Mitcheson K, Walshe I, Toms C, DU Toit G, Smith M, Ansley L. Prevalence of allergy and upper respiratory tract symptoms in runners of the London marathon. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2012; 44:999–1004.
Article8. Pedersen L, Elers J, Backer V. Asthma in elite athletes: pathogenesis, diagnosis, differential diagnoses, and treatment. Phys Sportsmed. 2011; 39:163–171.
Article9. Zhao G, Zhou S, Davie A, Su Q. Effects of moderate and high intensity exercise on T1/T2 balance. Exerc Immunol Rev. 2012; 18:98–114.10. Kruger K, Mooren FC, Pilat C. The Immunomodulatory effects of physical activity. Curr Pharm Des. 2016; 22:3730–3748.
Article11. Suzuki K, Nakaji S, Yamada M, Totsuka M, Sato K, Sugawara K. Systemic inflammatory response to exhaustive exercise. Cytokine kinetics. Exerc Immunol Rev. 2002; 8:6–48.12. Visser M, Pahor M, Taaffe DR, Goodpaster BH, Simonsick EM, Newman AB, Nevitt M, Harris TB. Relationship of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha with muscle mass and muscle strength in elderly men and women: the Health ABC Study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2002; 57:M326–M332.13. Ibfelt T, Petersen EW, Bruunsgaard H, Sandmand M, Pedersen BK. Exercise-induced change in type 1 cytokine-producing CD8+ T cells is related to a decrease in memory T cells. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2002; 93:645–648.
Article14. Shimizu K, Kimura F, Akimoto T, Akama T, Tanabe K, Nishijima T, Kuno S, Kono I. Effect of moderate exercise training on T-helper cell subpopulations in elderly people. Exerc Immunol Rev. 2008; 14:24–37.15. Malm C. Exercise immunology: the current state of man and mouse. Sports Med. 2004; 34:555–566.16. Lancaster GI, Khan Q, Drysdale PT, Wallace F, Jeukendrup AE, Drayson MT, Gleeson M. Effect of prolonged exercise and carbohydrate ingestion on type 1 and type 2 T lymphocyte distribution and intracellular cytokine production in humans. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2005; 98:565–571.
Article17. Rehm K, Sunesara I, Marshall GD. Increased Circulating Anti-inflammatory Cells in Marathon-trained Runners. Int J Sports Med. 2015; 36:832–836.
Article18. Alahgholi-Hajibehzad M, Oflazer P, Aysal F, Durmus H, Gulsen-Parman Y, Marx A, Deymeer F, Saruhan-Direskeneli G. Regulatory function of CD4+CD25++ T cells in patients with myasthenia gravis is associated with phenotypic changes and STAT5 signaling: 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 modulates the suppressor activity. J Neuroimmunol. 2015; 281:51–60.
Article19. Zamani A, Omidi M, Hemmatfar A, Salehi I, Bazmamoun H. Wrestlers' immune cells produce higher interleukin-6 and lower interleukin-12 and interleukin-13 in response to in vitro mitogen activation. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2014; 17:917–912.20. Deenadayalan A, Maddineni P, Raja A. Comparison of whole blood and PBMC assays for T-cell functional analysis. BMC Res Notes. 2013; 6:120.
Article21. Baum M, Muller-Steinhardt M, Liesen H, Kirchner H. Moderate and exhaustive endurance exercise influences the interferon-gamma levels in whole-blood culture supernatants. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1997; 76:165–169.
Article22. Wagner B, Burton A, Ainsworth D. Interferongamma, interleukin-4 and interleukin-10 production by T helper cells reveals intact Th1 and regulatory TR1 cell activation and a delay of the Th2 cell response in equine neonates and foals. Vet Res. 2010; 41:47.
Article23. Nguyen TH, Stokes JR, Casale TB. Future forms of immunotherapy and immunomodulators in allergic disease. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2011; 31:343–365. x–xi.
Article24. Jutel M, Van de Veen W, Agache I, Azkur KA, Akdis M, Akdis CA. Mechanisms of allergen-specific immunotherapy and novel ways for vaccine development. Allergol Int. 2013; 62:425–433.
Article25. Ogawa K, Oka J, Yamakawa J, Higuchi M. Habitual exercise did not affect the balance of type 1 and type 2 cytokines in elderly people. Mech Ageing Dev. 2003; 124:951–956.
Article26. Steensberg A, Toft AD, Bruunsgaard H, Sandmand M, Halkjaer-Kristensen J, Pedersen BK. Strenuous exercise decreases the percentage of type 1 T cells in the circulation. J Appl Physiol. 2001; 91:1708–1712.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Functional Changes of Interleukin-4 and Interferon-gamma of Peripheral Blood and Nasal Mucosa after Immunotherapy in Patients with Perennial Allergic Rhinitis
- Comparison of Manuka, Kanuka, and Black Locust Honey on the Production of Chemical Mediators by Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Cytokine Pattern is Affected by Training Intensity in Women Futsal Players
- The Expression of IL-4 and Interferon-gamma Genes in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Patients with Severe Atopic Dermatitis:Evaluation in Proportion to Serum IgE Levels
- Effect of Staphylococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1 on Secretion of Interleukins and Interferon-gamma by Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells from Atopic Donors