Obstet Gynecol Sci.
2017 Jan;60(1):32-38. 10.5468/ogs.2017.60.1.32.
Single port access laparoscopic surgery for large adnexal tumors: Initial 51 cases of a single institute
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Konyang University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea. kcj0307@kyuh.ac.kr
- KMID: 2383205
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5468/ogs.2017.60.1.32
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Investigation of initial 51 cases of single port access (SPA) laparoscopic surgery for large adnexal tumors and evaluation of safety and feasibility of the surgical technique.
METHODS
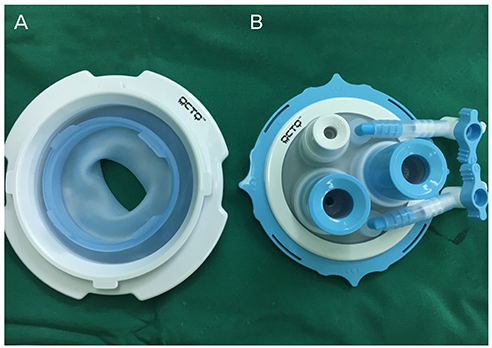
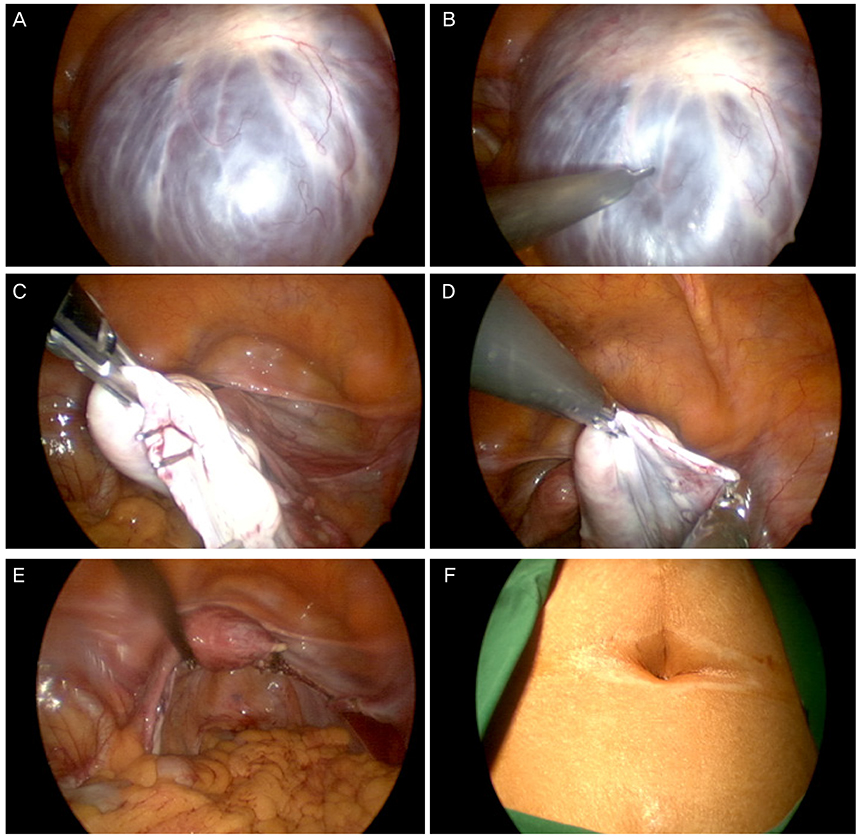
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of the first 51 patients who received SPA laparoscopic surgery for large adnexal tumors greater than 10 cm, from July 2010 to February 2015.
RESULTS
SPA adnexal surgeries were successfully completed in 51 patients (100%). The mean age, body mass index of the patients were 43.1 years and 22.83 kg/m², respectively. The median operative time, median blood loss were 73.5 (range, 20 to 185) minutes, 54 (range, 5 to 500) mL, and the median tumor diameter was 13.6 (range, 10 to 30) cm. The procedures included bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (n=18, 36.0%), unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (n=14, 27.45%), and paratubal cystectomy (n=1, 1.96%). There were no cases of malignancy and none were insertion of additional ports or conversion to laparotomy. The cases with intraoperative spillage were 3 (5.88%) and benign cystic tumors. No other intraoperative and postoperative complications were observed during hospital days and 6-weeks follow-up period after discharge.
CONCLUSION
Our results suggest that SPA laparoscopic surgery for large adnexal tumors may be a safe and feasible alternative to conventional laparoscopic surgery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Escobar PF, Starks D, Fader AN, Catenacci M, Falcone T. Laparoendoscopic single-site and natural orifice surgery in gynecology. Fertil Steril. 2010; 94:2497–2502.2. Canis M, Rabischong B, Houlle C, Botchorishvili R, Jardon K, Safi A, et al. Laparoscopic management of adnexal masses: a gold standard? Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2002; 14:423–428.3. Lee LC, Sheu BC, Chou LY, Huang SC, Chang DY, Chang WC. An easy new approach to the laparoscopic treatment of large adnexal cysts. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2011; 20:150–154.4. Eltabbakh GH, Charboneau AM, Eltabbakh NG. Laparoscopic surgery for large benign ovarian cysts. Gynecol Oncol. 2008; 108:72–76.5. Chapron C, Dubuisson JB, Kadoch O, Capella-Allouc S, Vacher-Lavenu MC. Laparoscopic management of organic ovarian cysts: is there a place for frozen section diagnosis? Hum Reprod. 1998; 13:324–329.6. Maiman M, Seltzer V, Boyce J. Laparoscopic excision of ovarian neopla subsequently found to be malignant. Obstet Gynecol. 1991; 77:563–565.7. Kim TJ, Lee YY, Kim MJ, Kim CJ, Kang H, Choi CH, et al. Single port access laparoscopic adnexal surgery. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2009; 16:612–615.8. Lee YY, Kim TJ, Kim CJ, Park HS, Choi CH, Lee JW, et al. Single port access laparoscopic adnexal surgery versus conventional laparoscopic adnexal surgery: a comparison of peri-operative outcomes. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2010; 151:181–184.9. Kim WC, Im KS, Kwon YS. Single-port transumbilical laparoscopic-assisted adnexal surgery. JSLS. 2011; 15:222–227.10. Kim WC, Lee JE, Kwon YS, Koo YJ, Lee IH, Lim KT. Laparoendoscopic single-site surgery (LESS) for adnexal tumors: one surgeon's initial experience over a one-year period. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2011; 158:265–268.11. Ghezzi F, Cromi A, Bergamini V, Uccella S, Siesto G, Franchi M, et al. Should adnexal mass size influence surgical approach? A series of 186 laparoscopically managed large adnexal masses. BJOG. 2008; 115:1020–1027.12. Ou CS, Liu YH, Zabriskie V, Rowbotham R. Alternate methods for laparoscopic management of adnexal masses greater than 10 cm in diameter. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2001; 11:125–132.13. Salem HA. Laparoscopic excision of large ovarian cysts. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2002; 28:290–294.14. Sagiv R, Golan A, Glezerman M. Laparoscopic management of extremely large ovarian cysts. Obstet Gynecol. 2005; 105:1319–1322.15. Goh SM, Yam J, Loh SF, Wong A. Minimal access approach to the management of large ovarian cysts. Surg Endosc. 2007; 21:80–83.16. Vergote I, De Brabanter J, Fyles A, Bertelsen K, Einhorn N, Sevelda P, et al. Prognostic importance of degree of differentiation and cyst rupture in stage I invasive epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Lancet. 2001; 357:176–182.17. Dembo AJ, Davy M, Stenwig AE, Berle EJ, Bush RS, Kjorstad K. Prognostic factors in patients with stage I epithelial ovarian cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 1990; 75:263–273.18. Timmerman D, Testa AC, Bourne T, Ferrazzi E, Ameye L, Konstantinovic ML, et al. Logistic regression model to distinguish between the benign and malignant adnexal mass before surgery: a multicenter study by the International Ovarian Tumor Analysis Group. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:8794–8801.19. Ekerhovd E, Wienerroith H, Staudach A, Granberg S. Preoperative assessment of unilocular adnexal cysts by transvaginal ultrasonography: a comparison between ultrasonographic morphologic imaging and histopathologic diagnosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2001; 184:48–54.20. Childers JM, Nasseri A, Surwit EA. Laparoscopic management of suspicious adnexal masses. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1996; 175:1451–1457.21. Chong GO, Hong DG, Lee YS. Single-port (OctoPort) assisted extracorporeal ovarian cystectomy for the treatment of large ovarian cysts: compare to conventional laparoscopy and laparotomy. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2015; 22:45–49.22. Yuen PM, Yu KM, Yip SK, Lau WC, Rogers MS, Chang A. A randomized prospective study of laparoscopy and laparotomy in the management of benign ovarian masses. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1997; 177:109–114.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Techniques of gynecologic single-port access laparoscopic surgery
- Single port laparoscopic surgery
- Single port transumbilical total laparoscopic hysterectomy (TLH): initial experience in Korea
- Single-Port Laparoscopic Appendectomy
- Single-port Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: Comparative Study of Consecutive Initial 206 Cases