Ann Rehabil Med.
2016 Oct;40(5):835-844. 10.5535/arm.2016.40.5.835.
Effect of Intra-articular Hyaluronic Acid Injection on Hemiplegic Shoulder Pain After Stroke
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. zmh1048@naver.com
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2382915
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2016.40.5.835
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the efficacy of intra-articular hyaluronic acid (IAHA) injection for hemiplegic shoulder pain (HSP) after stroke.
METHODS
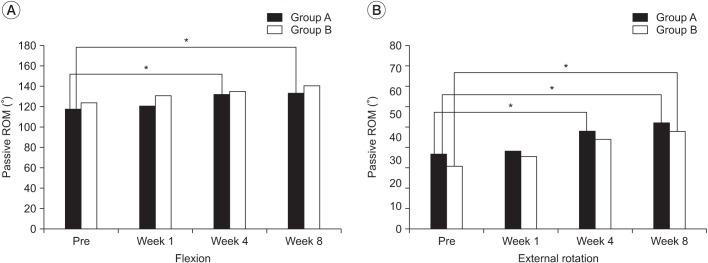
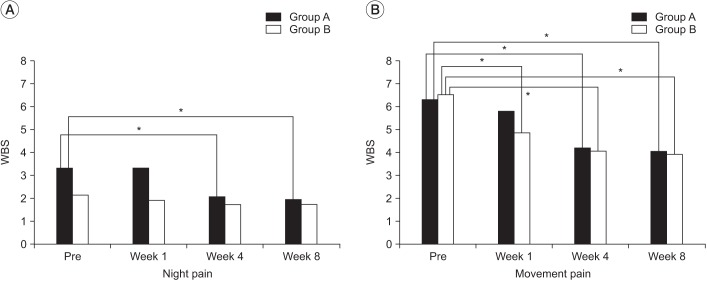
Thirty-one patients with HSP and limited range of motion (ROM) without spasticity of upper extremity were recruited. All subjects were randomly allocated to group A (n=15) for three weekly IAHA injection or group B (n=16) for a single intra-articular steroid (IAS) injection. All injections were administered by an expert physician until the 8th week using a posterior ultrasonography-guided approach. Shoulder joint pain was measured using the Wong-Baker Scale (WBS), while passive ROM was measured in the supine position by an expert physician.
RESULTS
There were no significant intergroup differences in WBS or ROM at the 8th week. Improvements in forward flexion and external rotation were observed from the 4th week in the IAHA group and the 8th week in the IAS group. Subjects experienced a statistically significant improvement in pain from the 1st week in the IAS and from the 8th week in IAHA group, respectively.
CONCLUSION
IAHA seems to have a less potent ability to reduce movement pain compared to steroid in the early period. However, there was no statistically significant intergroup difference in WBS and ROM improvements at the 8th week. IAHA might be a good alternative to steroid for managing HSP when the use of steroid is limited.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
2. Jensen EM. The hemiplegic shoulder. Scand J Rehabil Med Suppl. 1980; 7:113–119. PMID: 6932719.3. Zhu Y, Su B, Li N, Jin H. Pain management of hemiplegic shoulder pain post stroke in patients from Nanjing, China. Neural Regen Res. 2013; 8:2389–2398. PMID: 25206549.4. Vuagnat H, Chantraine A. Shoulder pain in hemiplegia revisited: contribution of functional electrical stimulation and other therapies. J Rehabil Med. 2003; 35:49–54. PMID: 12691333.
Article5. Pong YP, Wang LY, Wang L, Leong CP, Huang YC, Chen YK. Sonography of the shoulder in hemiplegic patients undergoing rehabilitation after a recent stroke. J Clin Ultrasound. 2009; 37:199–205. PMID: 19253350.
Article6. Snels IA, Beckerman H, Twisk JW, Dekker JH, De Koning P, Koppe PA, et al. Effect of triamcinolone acetonide injections on hemiplegic shoulder pain: a randomized clinical trial. Stroke. 2000; 31:2396–2401. PMID: 11022070.7. Gamble GE, Barberan E, Laasch HU, Bowsher D, Tyrrell PJ, Jones AK. Poststroke shoulder pain: a prospective study of the association and risk factors in 152 patients from a consecutive cohort of 205 patients presenting with stroke. Eur J Pain. 2002; 6:467–474. PMID: 12413435.
Article8. Andersen LT. Shoulder pain in hemiplegia. Am J Occup Ther. 1985; 39:11–19. PMID: 2579561.
Article9. Gaffney K, Ledingham J, Perry JD. Intra-articular triamcinolone hexacetonide in knee osteoarthritis: factors influencing the clinical response. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995; 54:379–381. PMID: 7794044.
Article10. Gottlieb NL, Riskin WG. Complications of local corticosteroid injections. JAMA. 1980; 243:1547–1548. PMID: 6965736.
Article11. Pelletier JP, Martel-Pelletier J. Protective effects of corticosteroids on cartilage lesions and osteophyte formation in the Pond-Nuki dog model of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1989; 32:181–193. PMID: 2920053.
Article12. Steinberg JJ, Sledge CB. Synovial factors and chondrocyte-mediated breakdown of cartilage: inhibition by hydrocortisone. J Orthop Res. 1983; 1:13–21. PMID: 6679571.13. Nakazawa F, Matsuno H, Yudoh K, Watanabe Y, Katayama R, Kimura T. Corticosteroid treatment induces chondrocyte apoptosis in an experimental arthritis model and in chondrocyte cultures. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2002; 20:773–781. PMID: 12508768.14. Hulmes DJ, Marsden ME, Strachan RK, Harvey RE, McInnes N, Gardner DL. Intra-articular hyaluronate in experimental rabbit osteoarthritis can prevent changes in cartilage proteoglycan content. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2004; 12:232–238. PMID: 14972340.15. Kitoh Y, Katsuramaki T, Tanaka H, Tanaka M, Kitabayashi N, Kataoka M, et al. Effect of SL-1010 (sodium hyaluronate with high molecular weight) on experimental osteoarthritis induced by intra-articularly applied papain in rabbits. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1992; 100:67–76. PMID: 1644371.
Article16. Kim HW, Kim HS, Ahn KH. The effect of intraarticular injection of hyaluronic acid and steroid in adhesive capsulitis of shoulder. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 1999; 23:117–123.17. Peng PW, Cheng P. Ultrasound-guided interventional procedures in pain medicine: a review of anatomy, sonoanatomy, and procedures. Part III: shoulder. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2011; 36:592–605. PMID: 22005657.18. Dogan SK, Ay S, Oztuna D, Aytur YK, Evcik D. The utility of the Faces Pain Scale in the assessment of shoulder pain in Turkish stroke patients: its relation with quality of life and psychologic status. Int J Rehabil Res. 2010; 33:363–367. PMID: 20651601.
Article19. Bender L, McKenna K. Hemiplegic shoulder pain: defining the problem and its management. Disabil Rehabil. 2001; 23:698–705. PMID: 11732559.20. Bruckner FE, Nye CJ. A prospective study of adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder ("frozen shoulder') in a high risk population. Q J Med. 1981; 50:191–204. PMID: 7302118.21. Murie-Fernandez M, Carmona Iragui M, Gnanakumar V, Meyer M, Foley N, Teasell R. Painful hemiplegic shoulder in stroke patients: causes and management. Neurologia. 2012; 27:234–244. PMID: 21514698.22. Rizk TE, Christopher RP, Pinals RS, Salazar JE, Higgins C. Arthrographic studies in painful hemiplegic shoulders. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1984; 65:254–256. PMID: 6712451.23. Joynt RL. The source of shoulder pain in hemiplegia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1992; 73:409–413. PMID: 1580765.24. Neviser JS. Adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder: a study of the pathological findings in periarthritis of the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1945; 27:211–222.25. Recommendations for the medical management of osteoarthritis of the hip and knee: 2000 update. American College of Rheumatology Subcommittee on Osteoarthritis Guidelines. Arthritis Rheum. 2000; 43:1905–1915. PMID: 11014340.26. Singh G. Recent considerations in nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug gastropathy. Am J Med. 1998; 105:31S–38S. PMID: 9715832.
Article27. Harris JD, Griesser MJ, Copelan A, Jones GL. Treatment of adhesive capsulitis with intra-articular hyaluronate: a systematic review. Int J Shoulder Surg. 2011; 5:31–37. PMID: 21897581.
Article28. Blaine T, Moskowitz R, Udell J, Skyhar M, Levin R, Friedlander J, et al. Treatment of persistent shoulder pain with sodium hyaluronate: a randomized, controlled trial. A multicenter study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008; 90:970–979. PMID: 18451387.29. Calis M, Demir H, Ulker S, Kirnap M, Duygulu F, Calis HT. Is intraarticular sodium hyaluronate injection an alternative treatment in patients with adhesive capsulitis? Rheumatol Int. 2006; 26:536–540. PMID: 16091920.
Article30. Hsieh LF, Hsu WC, Lin YJ, Chang HL, Chen CC, Huang V. Addition of intra-articular hyaluronate injection to physical therapy program produces no extra benefits in patients with adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2012; 93:957–964. PMID: 22502793.
Article31. Yamakado K. The targeting accuracy of subacromial injection to the shoulder: an arthrographic evaluation. Arthroscopy. 2002; 18:887–891. PMID: 12368787.
Article32. Mulcahy KA, Baxter AD, Oni OO, Finlay D. The value of shoulder distension arthrography with intraarticular injection of steroid and local anaesthetic: a followup study. Br J Radiol. 1994; 67:263–266. PMID: 8130999.
Article33. Sharma RK, Bajekal RA, Bhan S. Frozen shoulder syndrome. A comparison of hydraulic distension and manipulation. Int Orthop. 1993; 17:275–278. PMID: 8125660.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Suprascapular Nerve Block versus Intra-articular Hyaluronic Acid Injection in Hemiplegic Shoulder Pain
- Intra-Articular Hyaluronic Acid Injection in Ankle Osteoarthritis
- The Effect of Intra-articular Hyaluronic Acid and Steroid Injection in Osteoarthritis of the Knee
- Effects of Intra-Articular Injection and Subscapularis Motor Point Block on Painful Hemiplegic Shoulder
- The Comparison of Effects of Suprascapular Nerve Block, Intra-articular Steroid Injection, and a Combination Therapy on Hemiplegic Shoulder Pain: Pilot Study