Analysis of Mutations in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene in Korean Patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Summary of a Nationwide Survey
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. wskim@kuh.ac.kr
- 2Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 3Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 6Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 7National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea.
- 8Busan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 9Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- 10Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 11Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 12Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 13Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 14Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 15Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 16Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
- 17Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2381407
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.09.14
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Analysis of mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor gene (EGFR) is important for predicting response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. The overall rate of EGFR mutations in Korean patients is variable. To obtain comprehensive data on the status of EGFR mutations in Korean patients with lung cancer, the Cardiopulmonary Pathology Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists initiated a nationwide survey.
METHODS
We obtained 1,753 reports on EGFR mutations in patients with lung cancer from 15 hospitals between January and December 2009. We compared EGFR mutations with patient age, sex, history of smoking, histologic diagnosis, specimen type, procurement site, tumor cell dissection, and laboratory status.
RESULTS
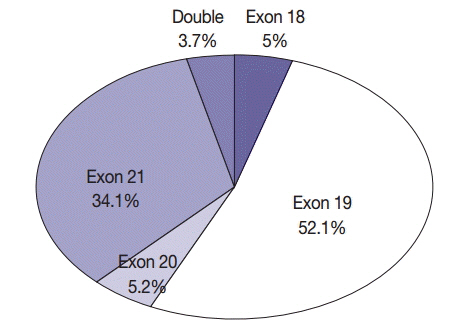
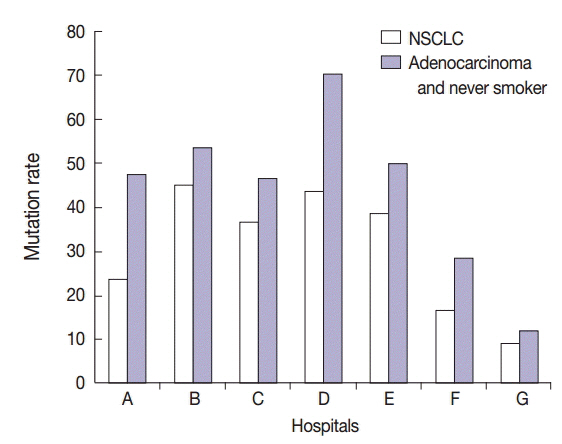
The overall EGFR mutation rate was 34.3% in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and 43.3% in patients with adenocarcinoma. EGFR mutation rate was significantly higher in women, never smokers, patients with adenocarcinoma, and patients who had undergone excisional biopsy. EGFR mutation rates did not differ with respect to patient age or procurement site among patients with NSCLC.
CONCLUSIONS
EGFR mutation rates and statuses were similar to those in published data from other East Asian countries.
MeSH Terms
-
Adenocarcinoma
Asian Continental Ancestry Group
Biopsy
Carcinoma, Non-Small-Cell Lung*
Diagnosis
Epidermal Growth Factor*
Female
Humans
Lung Neoplasms
Mutation Rate
Pathology
Protein-Tyrosine Kinases
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor*
Smoke
Smoking
Epidermal Growth Factor
Protein-Tyrosine Kinases
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor
Smoke
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Prognostic Role of S100A8 and S100A9 Protein Expressions in Non-small Cell Carcinoma of the Lung
Hyun Min Koh, Hyo Jung An, Gyung Hyuck Ko, Jeong Hee Lee, Jong Sil Lee, Dong Chul Kim, Jung Wook Yang, Min Hye Kim, Sung Hwan Kim, Kyung Nyeo Jeon, Gyeong-Won Lee, Se Min Jang, Dae Hyun Song
J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(1):13-22. doi: 10.4132/jptm.2018.11.12.Molecular biomarker testing for non–small cell lung cancer: consensus statement of the Korean Cardiopulmonary Pathology Study Group
Sunhee Chang, Hyo Sup Shim, Tae Jung Kim, Yoon-La Choi, Wan Seop Kim, Dong Hoon Shin, Lucia Kim, Heae Surng Park, Geon Kook Lee, Chang Hun Lee
J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(3):181-191. doi: 10.4132/jptm.2021.03.23.Osimertinib in Patients with T790M-Positive Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Korean Subgroup Analysis from Phase II Studies
Myung-Ju Ahn, Ji-Youn Han, Dong-Wan Kim, Byoung Chul Cho, Jin-Hyoung Kang, Sang-We Kim, James Chih-Hsin Yang, Tetsuya Mitsudomi, Jong Seok Lee
Cancer Res Treat. 2020;52(1):284-291. doi: 10.4143/crt.2019.200.Landscape of
EGFR mutations in lung adenocarcinoma: a single institute experience with comparison of PANAMutyper testing and targeted next-generation sequencing
Jeonghyo Lee, Yeon Bi Han, Hyun Jung Kwon, Song Kook Lee, Hyojin Kim, Jin-Haeng Chung
J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(5):249-259. doi: 10.4132/jptm.2022.06.11.
Reference
-
1. Jung KW, Won YJ, Kong HJ, et al. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2012. Cancer Res Treat. 2015; 47:127–41.
Article2. Owonikoko TK, Ragin CC, Belani CP, et al. Lung cancer in elderly patients: an analysis of the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results database. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:5570–7.
Article3. Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:947–57.
Article4. Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012; 13:239–46.5. Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011; 12:735–42.6. Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362:2380–8.
Article7. Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010; 11:121–8.
Article8. Fukuoka M, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, et al. Biomarker analyses and final overall survival results from a phase III, randomized, open-label, first-line study of gefitinib versus carboplatin/paclitaxel in clinically selected patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer in Asia (IPASS). J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29:2866–74.
Article9. Yang JC, Wu YL, Schuler M, et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin-based chemotherapy for EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma (LUX-Lung 3 and LUX-Lung 6): analysis of overall survival data from two randomised, phase 3 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2015; 16:141–51.10. Yatabe Y, Kerr KM, Utomo A, et al. EGFR mutation testing practices within the Asia Pacific region: results of a multicenter diagnostic survey. J Thorac Oncol. 2015; 10:438–45.11. Yang CH. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of NSCLC in East Asia: present and future. Lung Cancer. 2008; 60 Suppl 2:S23–30.
Article12. Shigematsu H, Lin L, Takahashi T, et al. Clinical and biological features associated with epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations in lung cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005; 97:339–46.
Article13. Skov BG, Høgdall E, Clementsen P, et al. The prevalence of EGFR mutations in non-small cell lung cancer in an unselected Caucasian population. APMIS. 2015; 123:108–15.14. Gahr S, Stoehr R, Geissinger E, et al. EGFR mutational status in a large series of Caucasian European NSCLC patients: data from daily practice. Br J Cancer. 2013; 109:1821–8.15. Soung YH, Lee JW, Kim SY, et al. Mutational analysis of EGFR and K-RAS genes in lung adenocarcinomas. Virchows Arch. 2005; 446:483–8.16. Bae NC, Chae MH, Lee MH, et al. EGFR, ERBB2, and KRAS mutations in Korean non-small cell lung cancer patients. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2007; 173:107–13.17. Park S, Holmes-Tisch AJ, Cho EY, et al. Discordance of molecular biomarkers associated with epidermal growth factor receptor pathway between primary tumors and lymph node metastasis in nonsmall cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2009; 4:809–15.
Article18. Lee YJ, Park IK, Park MS, et al. Activating mutations within the EGFR kinase domain: a molecular predictor of disease-free survival in resected pulmonary adenocarcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2009; 135:1647–54.
Article19. Ahn MJ, Park BB, Ahn JS, et al. Are there any ethnic differences in molecular predictors of erlotinib efficacy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer? Clin Cancer Res. 2008; 14:3860–6.
Article20. Sun PL, Seol H, Lee HJ, et al. High incidence of EGFR mutations in Korean men smokers with no intratumoral heterogeneity of lung adenocarcinomas: correlation with histologic subtypes, EGFR/TTF-1 expressions, and clinical features. J Thorac Oncol. 2012; 7:323–30.21. Kim YT, Seong YW, Jung YJ, et al. The presence of mutations in epidermal growth factor receptor gene is not a prognostic factor for long-term outcome after surgical resection of non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2013; 8:171–8.
Article22. Choi YL, Sun JM, Cho J, et al. EGFR mutation testing in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a comprehensive evaluation of real-world practice in an East Asian tertiary hospital. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e56011.23. Ma BB, Hui EP, Mok TS. Population-based differences in treatment outcome following anticancer drug therapies. Lancet Oncol. 2010; 11:75–84.
Article24. Chan SK, Gullick WJ, Hill ME. Mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small cell lung cancer: search and destroy. Eur J Cancer. 2006; 42:17–23.25. Shi Y, Au JS, Thongprasert S, et al. A prospective, molecular epidemiology study of EGFR mutations in Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology (PIONEER). J Thorac Oncol. 2014; 9:154–62.
Article26. Liu J, Zhao R, Zhang J, Zhang J. ARMS for EGFR mutation analysis of cytologic and corresponding lung adenocarcinoma histologic specimens. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015; 141:221–7.27. Heymann JJ, Bulman WA, Maxfield RA, et al. Molecular testing guidelines for lung adenocarcinoma: utility of cell blocks and concordance between fine-needle aspiration cytology and histology samples. Cytojournal. 2014; 11:12.
Article28. Khode R, Larsen DA, Culbreath BC, et al. Comparative study of epidermal growth factor receptor mutation analysis on cytology smears and surgical pathology specimens from primary and metastatic lung carcinomas. Cancer Cytopathol. 2013; 121:361–9.
Article29. Sun PL, Jin Y, Kim H, Lee CT, Jheon S, Chung JH. High concordance of EGFR mutation status between histologic and corresponding cytologic specimens of lung adenocarcinomas. Cancer Cytopathol. 2013; 121:311–9.30. Pirker R, Herth FJ, Kerr KM, et al. Consensus for EGFR mutation testing in non-small cell lung cancer: results from a European workshop. J Thorac Oncol. 2010; 5:1706–13.31. Pao W, Ladanyi M. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation testing in lung cancer: searching for the ideal method. Clin Cancer Res. 2007; 13:4954–5.32. Kim SK, Kim DL, Han HS, et al. Pyrosequencing analysis for detection of a BRAFV600E mutation in an FNAB specimen of thyroid nodules. Diagn Mol Pathol. 2008; 17:118–25.33. Dufort S, Richard MJ, Lantuejoul S, de Fraipont F. Pyrosequencing, a method approved to detect the two major EGFR mutations for anti EGFR therapy in NSCLC. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2011; 30:57.
Article34. Choi JJ, Cho M, Oh M, Kim H, Kil MS, Park H. PNA-mediated real-time PCR clamping for detection of EGFR mutations. Bull Korean Chem Soc. 2010; 31:3525–9.35. Lee HJ, Xu X, Kim H, et al. Comparison of direct sequencing, PNA clamping-real time polymerase chain reaction, and pyrosequencing methods for the detection of EGFR mutations in non-small cell lung carcinoma and the correlation with clinical responses to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment. Korean J Pathol. 2013; 47:52–60.36. Kim HJ, Lee KY, Kim YC, et al. Detection and comparison of peptide nucleic acid-mediated real-time polymerase chain reaction clamping and direct gene sequencing for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2012; 75:321–5.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinicopathologic Analysis of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Status in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Protein Expression, Gene Amplification and Survival Analysis
- Molecular Basis of Drug Resistance: Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Inhibitors
- Carcinoembryonic antigen and epidermal growth factor receptor expression in non-small cell lung cancer definited by immunohistoc- hemical stain
- Intron 1 Polymorphism, Mutation and the Protein Expression of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Relation to the Gefitinib Sensitivity of Korean Lung Cancer Patients
- Overview of ALK and ROS1 Rearranged Lung Cancer