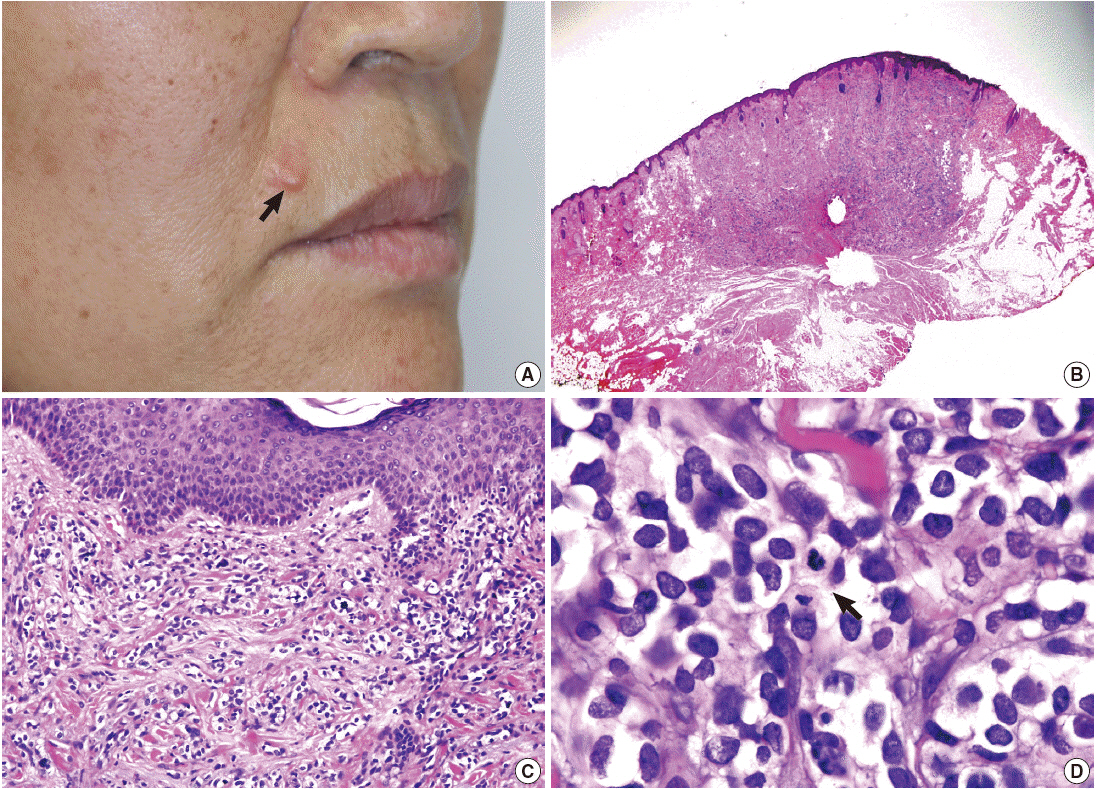
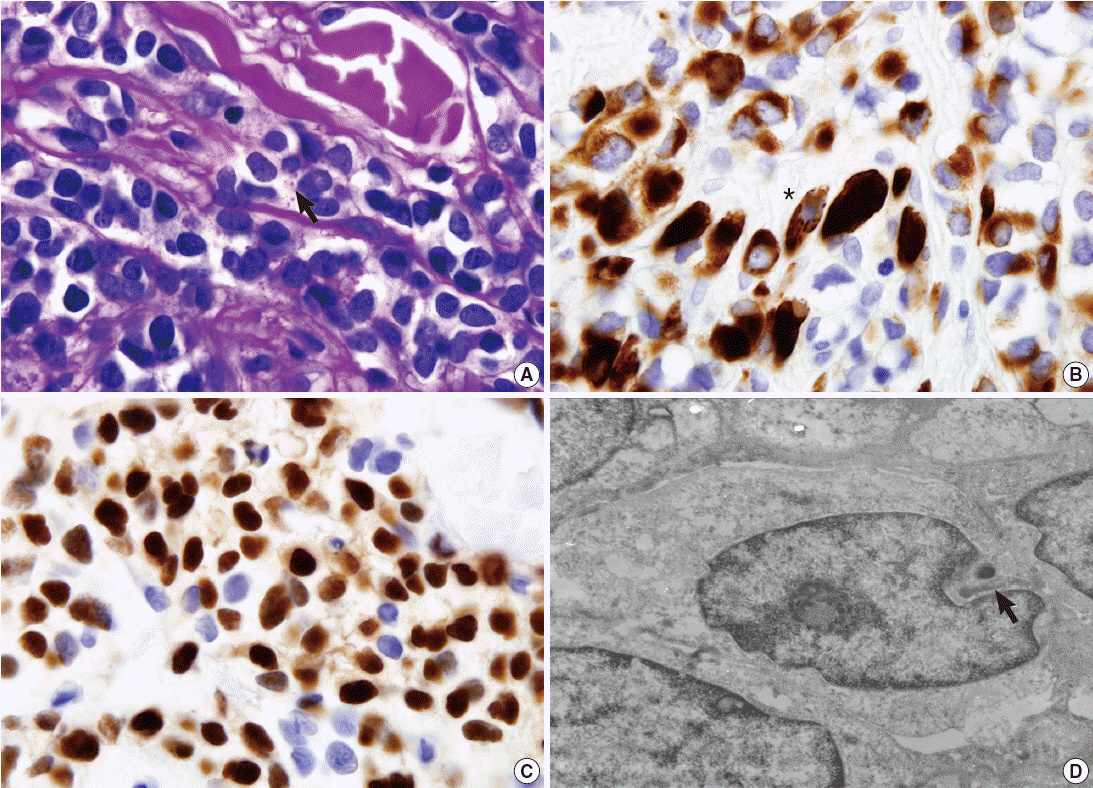
J Pathol Transl Med.
2015 Jan;49(1):81-84. 10.4132/jptm.2014.06.03.
Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma of the Lip in an Adult with Clear Cell Features
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea. dhchung@gilhospital.com
- 2Department of Plastic Surgery, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2381359
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2014.06.03
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Weiss SW, Goldblum JR, Enzinger FM. Enzinger and Weiss’s soft tissue tumors. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Mosby Elsevier;2008.2. Jung WH, Kim YJ, Jung SH, Yim H, Yoo CJ. Rhabdomyosarcoma in children: histologic subtypes and prognosis. Korean J Pathol. 1992; 26:573–81.3. Smith JF. Rhabdomyosarcoma of the lower lip. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1962; 15:454–7.
Article4. Piattelli A. Pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma of the upper lip in an adult patient: report of a case and review of the literature. Acta Stomatol Belg. 1991; 88:57–64.5. D’Amico AV, Goldwein J, Womer R. Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma of the lip in an infant. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1996; 26:409–13.6. Brecher AR, Reyes-Mugica M, Kamino H, Chang MW. Congenital primary cutaneous rhabdomyosarcoma in a neonate. Pediatr Dermatol. 2003; 20:335–8.
Article7. Seth T, Kempert P. Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma of lower lip. Ind Pediatr. 2004; 41:858–9.8. Marburger TB, Gardner JM, Prieto VG, Billings SD. Primary cutaneous rhabdomyosarcoma: a clinicopathologic review of 11 cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2012; 39:987–95.
Article9. Dhull AK. Primary alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma: a horrendous presentation with miraculous remission. BMJ Case Rep. 2012; 2012:bcr2012007657.10. Singh GB, Arora R, Kumar D, Jain M, Puri V. A rare case of congenital rhabdomyosarcoma with review of the literature. Case Rep Otolaryngol. 2013; 2013:518952.
Article11. Parham DM, Barr FG. Classification of rhabdomyosarcoma and its molecular basis. Adv Anat Pathol. 2013; 20:387–97.
Article12. Bégin LR, Schürch W, Lacoste J, Hiscott J, Melnychuk DA. Glycogen-rich clear cell rhabdomyosarcoma of the mediastinum: potential diagnostic pitfall. Am J Surg Pathol. 1994; 18:302–8.13. Ahmed AA, Tsokos M. Sinonasal rhabdomyosarcoma in children and young adults. Int J Surg Pathol. 2007; 15:160–5.
Article14. Lázaro-Santander R, Andrés-Gozalbo C, Rodríguez-Pereira C, Vera-Román JM. Clear cell atypical fibroxanthoma. Histopathology. 1999; 35:484–5.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma of vulva
- A Case of Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma Originating from the Chest Wall
- A case of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma of the uterine cervix
- Cytologic Diagnosis of Metastatic Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma in Cerebrospinal Fluid: A Case Report
- Rhabdomyosarcoma(Report of two cases)