Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2017 Jun;10(2):153-157. 10.21053/ceo.2016.00318.
Update on Clinical Strategies in Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia from an ENT Point of View
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, University of Regensburg, Regensburg, Germany. Kornelia.Wirsching@ukr.de
- KMID: 2380433
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2016.00318
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) is characterized by the presence of vascular malformations with an absence of capillaries between arteries and veins. One major manifestation site is the nasal mucous membrane where recurrent nosebleeds occur. Our clinical strategy to treat patients with HHT has the aim to reduce nasal bleeding long-term with minimal local and general side effects.
METHODS
We describe staged diagnosis and therapy including individual medical treatments of 97 patients with HHT. The success of treatment is monitored with a systematic questionnaire.
RESULTS
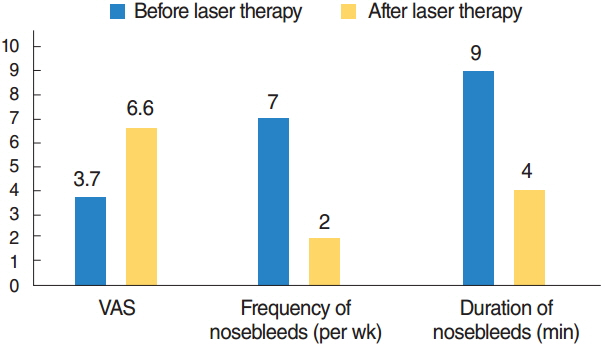
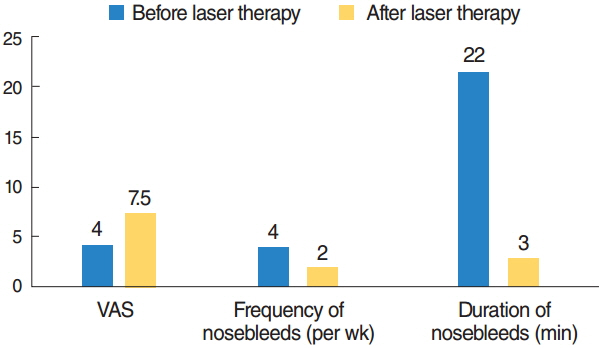
The neodymium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet (Nd:YAG) laser therapy remains standard treatment of choice with no major side effects despite the need for repeated treatment. In addition new treatment strategies like nasal occlusion, local drug therapy, and nasal septal splinting show initial success.
CONCLUSION
Improvement of the quality of life of HHT patients can be achieved by a multimodal concept. Several new treatment strategies like nasal septal splinting and nasal occlusion successfully expand the range of established methods. Further studies have to prove the safety and long-term effectiveness of the described individual medical treatments.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Braverman IM, Keh A, Jacobson BS. Ultrastructure and three-dimensional organization of the telangiectases of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. J Invest Dermatol. 1990; Oct. 95(4):422–7.
Article2. Faughnan ME, Palda VA, Garcia-Tsao G, Geisthoff UW, McDonald J, Proctor DD, et al. International guidelines for the diagnosis and management of hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. J Med Genet. 2011; Feb. 48(2):73–87.
Article3. Byahatti SV, Rebeiz EE, Shapshay SM. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: what the otolaryngologist should know. Am J Rhinol. 1997; Jan-Feb. 11(1):55–62.
Article4. Geisthoff UW, Schneider G, Fischinger J, Plinkert PK. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler’s disease): an interdisciplinary challenge. HNO. 2002; Feb. 50(2):114–28.5. Guttmacher AE, Marchuk DA, White RI Jr. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. N Engl J Med. 1995; Oct. 333(14):918–24.
Article6. Porteous ME, Burn J, Proctor SJ. Hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia: a clinical analysis. J Med Genet. 1992; Aug. 29(8):527–30.
Article7. van Gent MW, Velthuis S, Post MC, Snijder RJ, Westermann CJ, Letteboer TG, et al. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: how accurate are the clinical criteria? Am J Med Genet A. 2013; Mar. 161(3):461–6.
Article8. Kuhnel TS, Wagner BH, Schurr CP, Strutz J. Clinical strategy in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Am J Rhinol. 2005; Sep-Oct. 19(5):508–13.9. Rohrmeier C, Sachs HG, Kuehnel TS. A retrospective analysis of low dose, intranasal injected bevacizumab (Avastin) in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2012; Feb. 269(2):531–6.
Article10. Golding-Wood PH. The role of arterial ligation in intractable epistaxis. J Laryngol Otol Suppl. 1983; 8:120–2.11. Werner JA, Geisthoff UW, Lippert BM, Rudert H. Treatment of recurrent epistaxis in Rendu-Osler-Weber disease. HNO. 1997; Sep. 45(9):673–81.12. Parkin JL, Dixon JA. Laser photocoagulation in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1981; Mar-Apr. 89(2):204–8.
Article13. Shapshay SM, Oliver P. Treatment of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia by Nd-YAG laser photocoagulation. Laryngoscope. 1984; Dec. 94(12 Pt 1):1554–6.
Article14. Kluger PB, Shapshay SM, Hybels RL, Bohigian RK. NeodymiumYAG laser intranasal photocoagulation in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: an update report. Laryngoscope. 1987; Dec. 97(12):1397–401.15. Folz BJ, Tennie J, Lippert BM, Werner JA. Natural history and control of epistaxis in a group of German patients with Rendu-OslerWeber disease. Rhinology. 2005; Mar. 43(1):40–6.16. Mahoney EJ, Shapshay SM. New classification of nasal vasculature patterns in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Am J Rhinol. 2006; Jan-Feb. 20(1):87–90.
Article17. Gluckman JL, Portugal LG. Modified Young’s procedure for refractory epistaxis due to hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Laryngoscope. 1994; Sep. 104(9):1174–7.
Article18. Al Kadah B, Papaspyrou G, Schneider M, Schick B. First experiences with an individual nasal olive in patients with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT). Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2015; Jan. 272(1):117–22.19. Sadick H, Riedel F, Naim R, Goessler U, Hormann K, Hafner M, et al. Patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia have increased plasma levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and transforming growth factor-beta1 as well as high ALK1 tissue expression. Haematologica. 2005; Jun. 90(6):818–28.20. Fischer M, Dietrich U, Labisch C, Zanella FE, Jahnke K. Critical evaluation of vascular embolization in patients with Rendu-Osler disease. Laryngorhinootologie. 1997; Aug. 76(8):490–4.21. Elden L, Montanera W, Terbrugge K, Willinsky R, Lasjaunias P, Charles D. Angiographic embolization for the treatment of epistaxis: a review of 108 cases. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1994; Jul. 111(1):44–50.
Article22. Dubel GJ, Ahn SH, Soares GM. Transcatheter embolization in the management of epistaxis. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2013; Sep. 30(3):249–62.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia in a Family
- Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia Combined with Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformation Treated with Transcatheter Embolotherapy
- A Case of Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia
- Genetic Mutation Analysis Can Supplement Clinically Confirmed Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia Populations
- Hepatic Involvement in Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia