Cancer Res Treat.
2014 Oct;46(4):403-410. 10.4143/crt.2013.168.
Analysis of Biologically Equivalent Dose of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Primary and Metastatic Lung Tumors
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Inje University Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. oncodoc@inje.ac.kr
- 2Department of Preventive Medicine, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2380378
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2013.168
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to determine the optimal biologically equivalent dose (BED) for stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) by comparing local control rates in proportion to various total doses and fractionation schedules.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty-four patients with early non-small-cell lung cancer and a single metastatic lung tumor were included in this study. Differences in local control rates were evaluated according to gender, primary tumor site, response, tumor size, and BED. For comparison of BEDs, the prescribed dose for SBRT was stratified according to three groups: high (BED > 146 Gy), medium to high (BED, 106 to 146 Gy), and low to medium (BED < 106 Gy).
RESULTS
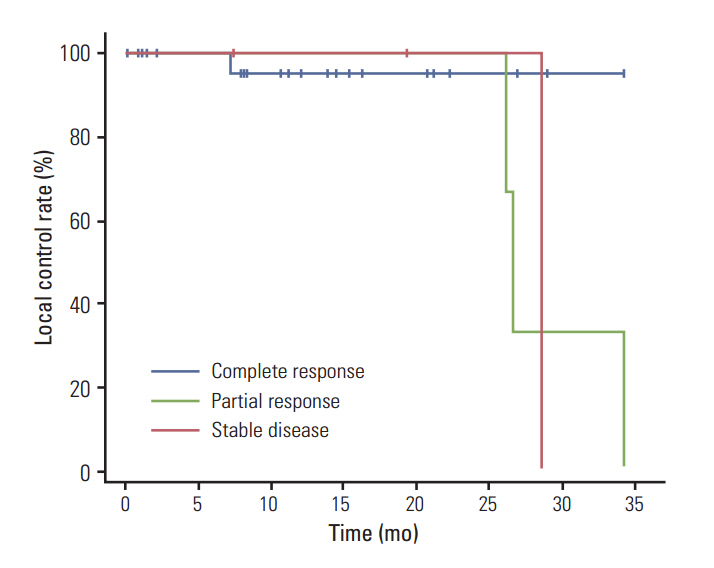
For all patients, the overall local control rate was 85.3% at two years after treatment. Five local recurrences were observed, and, notably, all of them were observed in the low to medium BED group. Significantly higher local control rates were observed for patients with a complete response than for those with a partial response or stable disease (p < 0.001). Twenty-six patients with a tumor size of < 3 cm showed no dose-response relationship in the low to medium, medium to high, and high BED groups, whereas eight patients with a tumor size of > or = 3 cm showed a significant dose-response relationship. The observed 2-year local recurrence-free survival rates in patients with a tumor size of < 3 cm and in those with a tumor size of > or = 3 cm were 96.2% and 50.0%, respectively, which were significantly different (p=0.007).
CONCLUSION
BED > 100 Gy is required in order to achieve a > 85% local control rate regardless of tumor size. The optimal dose for small tumors of < 3 cm appears to be within a range below 150 Gy BED. Escalation of BED to high levels (> 150 Gy) may be required for patients with a tumor size larger than 3 cm.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Radiation Therapy Alone in cT1-3N0 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Who Are Unfit for Surgical Resection or Stereotactic Radiation Therapy: Comparison of Risk-Adaptive Dose Schedules
Won Kyung Cho, Jae Myoung Noh, Yong Chan Ahn, Dongryul Oh, Hongryull Pyo
Cancer Res Treat. 2016;48(4):1187-1195. doi: 10.4143/crt.2015.391.
Reference
-
References
1. Norihisa Y, Nagata Y, Takayama K, Matsuo Y, Sakamoto T, Sakamoto M, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for oligometastatic lung tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008; 72:398–403.
Article2. Wulf J, Haedinger U, Oppitz U, Thiele W, Mueller G, Flentje M. Stereotactic radiotherapy for primary lung cancer and pulmonary metastases: a noninvasive treatment approach in medically inoperable patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004; 60:186–96.
Article3. Chi A, Liao Z, Nguyen NP, Xu J, Stea B, Komaki R. Systemic review of the patterns of failure following stereotactic body radiation therapy in early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer: clinical implications. Radiother Oncol. 2010; 94:1–11.
Article4. Underberg RW, Lagerwaard FJ, Cuijpers JP, Slotman BJ, van Sornsen de Koste JR, Senan S. Four-dimensional CT scans for treatment planning in stereotactic radiotherapy for stage I lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004; 60:1283–90.
Article5. Van Baardwijk A, Tome WA, van Elmpt W, Bentzen SM, Reymen B, Wanders R, et al. Is high-dose stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for stage I non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) overkill? A systematic review. Radiother Oncol. 2012; 105:145–9.
Article6. Olsen JR, Robinson CG, El Naqa I, Creach KM, Drzymala RE, Bloch C, et al. Dose-response for stereotactic body radiotherapy in early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011; 81:e299–303.
Article7. Kestin LL, Grills IS, Guckenberger M, Belderbos J, Hope AJ, Werner-Wasik M, et al. Substantial dose-response relationship with clinical outcome for lung stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) delivered via online image guidance. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010; 78 Suppl:S14.
Article8. Onishi H, Shirato H, Nagata Y, Hiraoka M, Fujino M, Gomi K, et al. Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (Hypo-FXSRT) for stage I non-small cell lung cancer: updated results of 257 patients in a Japanese multi-institutional study. J Thorac Oncol. 2007; 2(7 Suppl 3):S94–100.
Article9. Timmerman R, Paulus R, Galvin J, Michalski J, Straube W, Bradley J, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable early stage lung cancer. JAMA. 2010; 303:1070–6.
Article10. Zhang J, Yang F, Li B, Li H, Liu J, Huang W, et al. Which is the optimal biologically effective dose of stereotactic body radiotherapy for Stage I non-small-cell lung cancer? A meta-analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011; 81:e305–16.
Article11. Aoki T, Nagata Y, Negoro Y, Takayama K, Mizowaki T, Kokubo M, et al. Evaluation of lung injury after threedimensional conformal stereotactic radiation therapy for solitary lung tumors: CT appearance. Radiology. 2004; 230:101–8.
Article12. Park C, Papiez L, Zhang S, Story M, Timmerman RD. Universal survival curve and single fraction equivalent dose: useful tools in understanding potency of ablative radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008; 70:847–52.
Article13. Baumann P, Nyman J, Lax I, Friesland S, Hoyer M, Rehn Ericsson S, et al. Factors important for efficacy of stereotactic body radiotherapy of medically inoperable stage I lung cancer: a retrospective analysis of patients treated in the Nordic countries. Acta Oncol. 2006; 45:787–95.
Article14. Onimaru R, Fujino M, Yamazaki K, Onodera Y, Taguchi H, Katoh N, et al. Steep dose-response relationship for stage I non-small-cell lung cancer using hypofractionated high-dose irradiation by real-time tumor-tracking radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008; 70:374–81.
Article15. Mehta N, King CR, Agazaryan N, Steinberg M, Hua A, Lee P. Stereotactic body radiation therapy and 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer: a pooled analysis of biological equivalent dose and local control. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2012; 2:288–95.
Article16. Guckenberger M, Wulf J, Mueller G, Krieger T, Baier K, Gabor M, et al. Dose-response relationship for image-guided stereotactic body radiotherapy of pulmonary tumors: relevance of 4D dose calculation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009; 74:47–54.
Article17. Dunlap NE, Larner JM, Read PW, Kozower BD, Lau CL, Sheng K, et al. Size matters: a comparison of T1 and T2 peripheral non-small-cell lung cancers treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT). J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010; 140:583–9.
Article18. Ohri N, Werner-Wasik M, Grills IS, Belderbos J, Hope A, Yan D, et al. Modeling local control after hypofractionated stereotactic body radiation therapy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer: a report from the elekta collaborative lung research group. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012; 84:e379–84.
Article19. Baumann P, Nyman J, Hoyer M, Wennberg B, Gagliardi G, Lax I, et al. Outcome in a prospective phase II trial of medically inoperable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:3290–6.
Article20. Matsuo Y, Shibuya K, Nagata Y, Takayama K, Norihisa Y, Mizowaki T, et al. Prognostic factors in stereotactic body radiotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011; 79:1104–11.
Article21. Koto M, Takai Y, Ogawa Y, Matsushita H, Takeda K, Takahashi C, et al. A phase II study on stereotactic body radiotherapy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2007; 85:429–34.
Article22. Baba F, Shibamoto Y, Ogino H, Murata R, Sugie C, Iwata H, et al. Clinical outcomes of stereotactic body radiotherapy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer using different doses depending on tumor size. Radiat Oncol. 2010; 5:81.
Article23. Takeda A, Kunieda E, Ohashi T, Aoki Y, Koike N, Takeda T. Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for oligometastatic lung tumors from colorectal cancer and other primary cancers in comparison with primary lung cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2011; 101:255–9.
Article24. Kim MS, Yoo SY, Cho CK, Yoo HJ, Choi CW, Seo YS, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy using three fractions for isolated lung recurrence from colorectal cancer. Oncology. 2009; 76:212–9.
Article25. Matsuo Y, Shibuya K, Nagata Y, Norihisa Y, Narabayashi M, Sakanaka K, et al. Preliminary report of late recurrences, at 5 years or more, after stereotactic body radiation therapy for non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2012; 7:453–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Early Stage Lung Cancer
- Predictive factors of symptomatic radiation pneumonitis in primary and metastatic lung tumors treated with stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy
- Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases
- Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
- Treatment Outcome of Brain Metastasis after the Cranial Radiotherapy Followed by Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy and Its Prognostic Factors