Korean J Leg Med.
2017 May;41(2):32-40. 10.7580/kjlm.2017.41.2.32.
Asian Ethnic Group Classification Model Using Data Mining
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Applied Statistics, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Forensic Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Institute of Forensic Science, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Information and Statistics, Yonsei University, Wonju, Korea. ahn2615@yonsei.ac.kr
- KMID: 2379670
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7580/kjlm.2017.41.2.32
Abstract
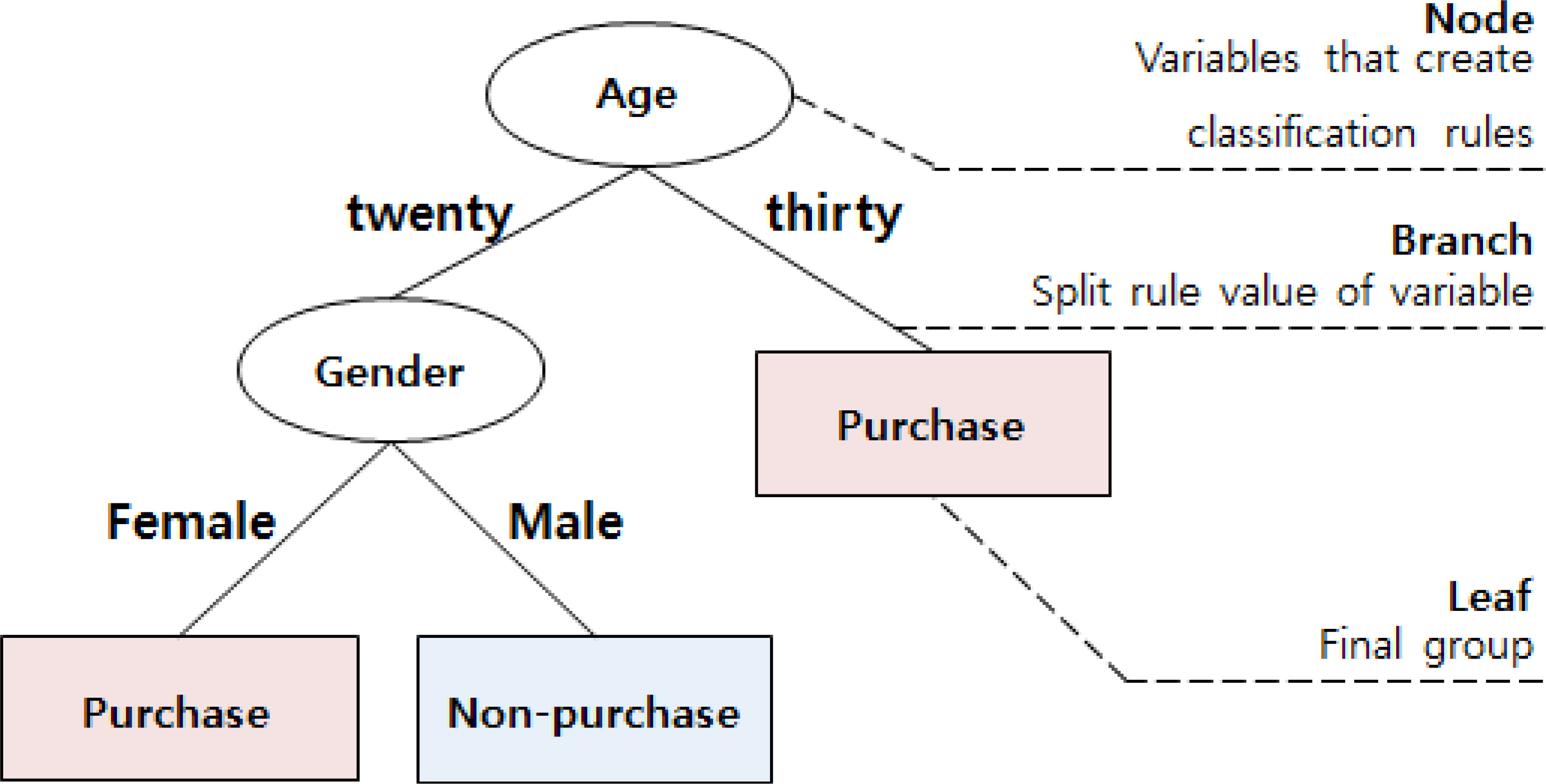
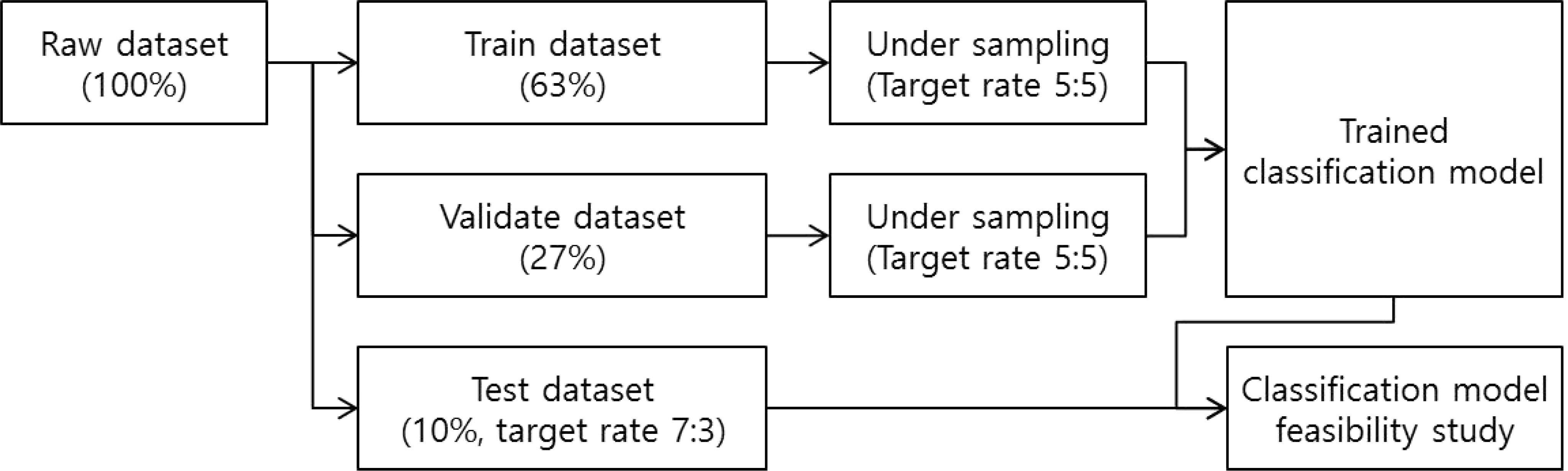
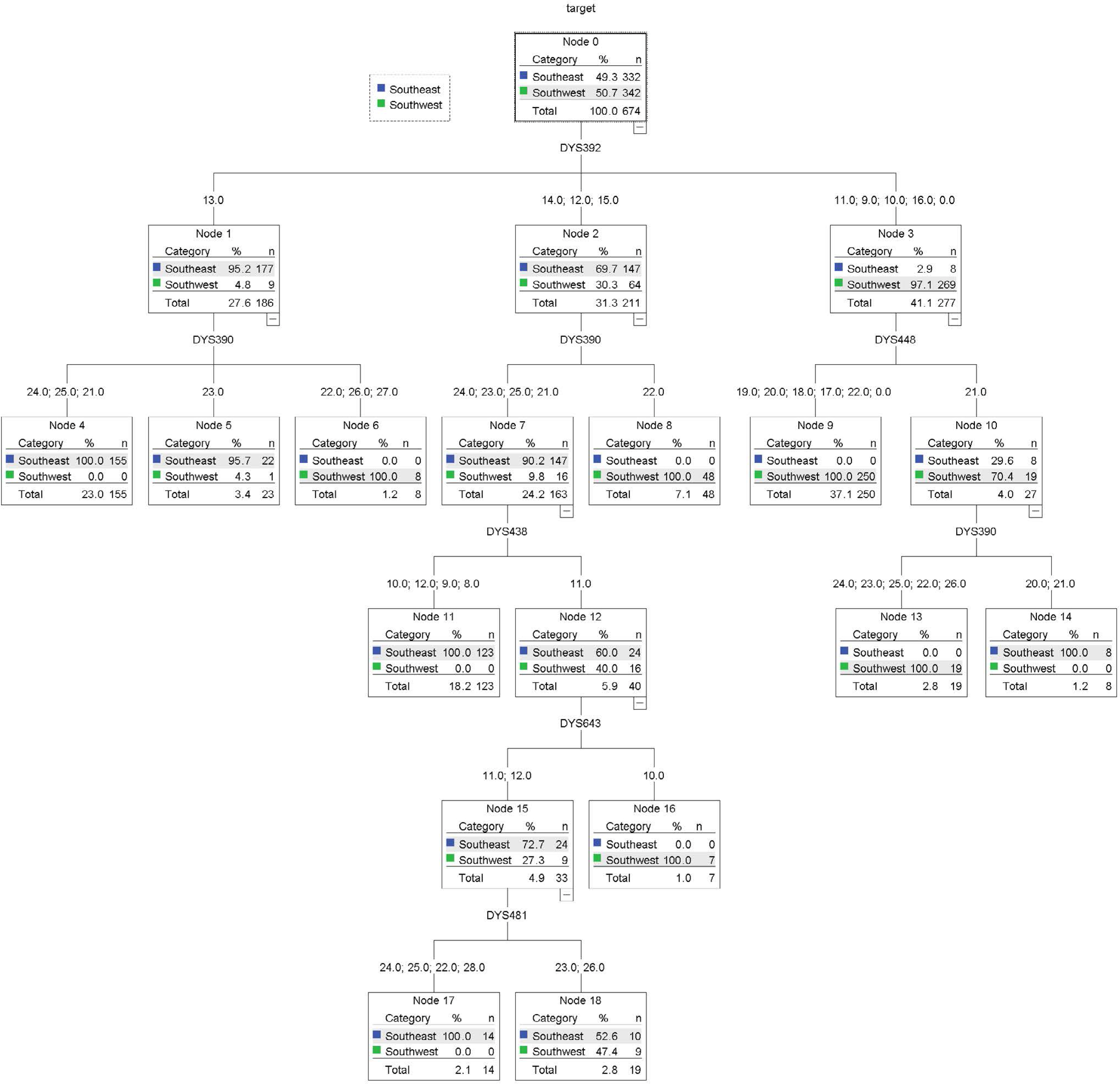
- In addition to identifying genetic differences between target populations, it is also important to determine the impact of genetic differences with regard to the respective target populations. In recent years, there has been an increasing number of cases where this approach is needed, and thus various statistical methods must be considered. In this study, genetic data from populations of Southeast and Southwest Asia were collected, and several statistical approaches were evaluated on the Y-chromosome short tandem repeat data. In order to develop a more accurate and practical classification model, we applied gradient boosting and ensemble techniques. To infer between the Southeast and Southwest Asian populations, the overall performance of the classification models was better than that of the decision trees and regression models used in the past. In conclusion, this study suggests that additional statistical approaches, such as data mining techniques, could provide more useful interpretations for forensic analyses. These trials are expected to be the basis for further studies extending from target regions to the entire continent of Asia as well as the use of additional genes such as mitochondrial genes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Butler JM. Advanced topics in forensic DNA typing: methodology. San Diego, CA: Academic Press;2011.2.Enoch MA., Shen PH., Xu K, et al. Using ancestry-informative markers to define populations and detect population stratification. J Psychopharmacol. 2006. 20:(4 Suppl):. 19–26.
Article3.Li JZ., Absher DM., Tang H, et al. Worldwide human relationships inferred from genome-wide patterns of variation. Science. 2008. 319:1100–4.
Article4.Rosenberg NA., Pritchard JK., Weber JL, et al. Genetic structure of human populations. Science. 2002. 298:2381–5.
Article5.Pritchard JK., Stephens M., Donnelly P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics. 2000. 155:945–59.
Article6.Quinlan JR. Induction of decision trees. Mach Learn. 1986. 1:81–106.
Article7.Opitz D., Maclin R. Popular ensemble methods: an empirical study. J Artif Intell Res. 1999. 11:169–98.
Article8.Rokach L. Ensemble-based classifiers. Artif Intell Rev. 2010. 33:1–39.
Article9.Quinlan JR. Bagging, boosting, and C4.5. AAAI/IAAI '96 Proceedings of the Thirteenth National Conference on Artificial Intelligence. 1996 Aug 4-8; Portland, OR, USA. Vol. 1. Palo Alto, CA: AAAI Press;. 1996. 725–30.10.Breiman L. Bagging predictors. Mach Learn. 1996. 24:123–40.
Article11.Schapire RE. The strength of weak learnability. Mach Learn. 1990. 5:197–227.
Article12.Freund Y., Schapire RE. A short introduction to boosting. J Jpn Soc Artif Intell. 1999. 14:771–80.13.Friedman JH. Stochastic gradient boosting. Comput Stat Data Anal. 2002. 38:367–78.
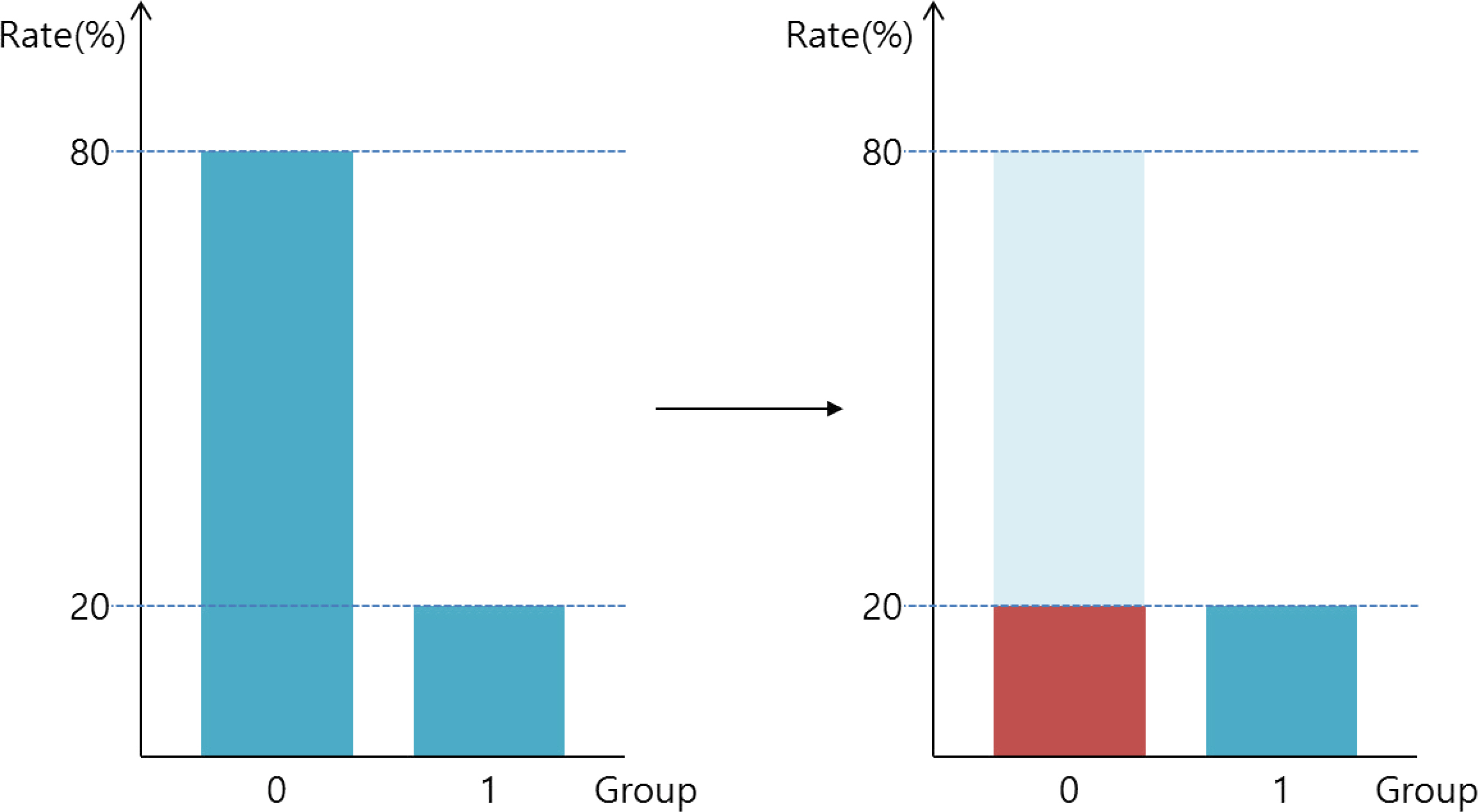
Article14.Wang R., Lee N., Wei Y. A case study: improve classification of rare events with SAS Enterprise Miner. In: Proceedings of the SAS Global Forum 2015 Conference. Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc.;2015.15.Rahman MM., Davis DN. Addressing the class imbalance problem in medical datasets. Int J Mach Learn Comput. 2013. 3:224–8.
Article16.Purps J., Siegert S., Willuweit S, et al. A global analysis of Y-chromosomal haplotype diversity for 23 STR loci. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2014. 12:12–23.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Data Mining for High Dimensional Data in Drug Discovery and Development
- Text Mining in Biomedical Domain with Emphasis on Document Clustering
- Identification of Ethnically Specific Genetic Variations in Pan-Asian Ethnos
- Data-Mining-Based Coronary Heart Disease Risk Prediction Model Using Fuzzy Logic and Decision Tree
- The Efficient Ways of Health Promotion Program on Public Health Center Using Data Mining