J Korean Med Sci.
2017 Jul;32(7):1207-1210. 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.7.1207.
A Case of Rheumatoid Vasculitis Involving Hepatic Artery in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. leejisoo@ewha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2379619
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2017.32.7.1207
Abstract
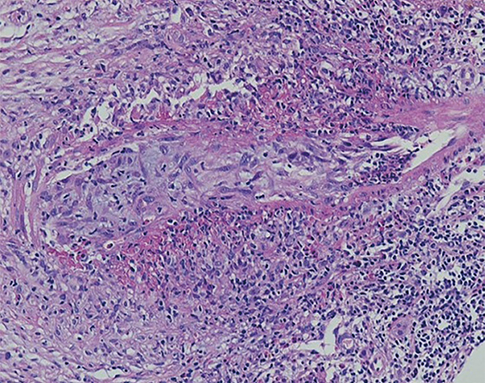
- Rheumatoid vasculitis is a rare, but most serious extra-articular complications of long-standing, seropositive rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Vasculitis of hepatic artery is an extremely rare but severe manifestation of rheumatoid vasculitis. A 72-year-old woman who presented with polyarthralgia for 2 months was diagnosed with early RA. Since she had manifestations of livedo reticularis, and liver dysfunction which was atypical for RA patients, a percutaneous needle liver biopsy was performed revealing arteritis of a medium-sized hepatic artery. Extensive investigations did not reveal evidences of other systemic causes such as malignancy or systemic vasculitis. The patient was diagnosed with rheumatoid vasculitis involving hepatic arteries based on Bacon and Scott criteria for rheumatoid vasculitis. With high dose corticosteroid and cyclophosphamide induction and methotrexate and tacrolimus maintenance treatment, she was successfully recovered. Association of rheumatoid vasculitis at very early stages of the disease may represent an early aggressive form of RA.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Voskuyl AE, Zwinderman AH, Westedt ML, Vandenbroucke JP, Breedveld FC, Hazes JM. Factors associated with the development of vasculitis in rheumatoid arthritis: results of a case-control study. Ann Rheum Dis. 1996; 55:190–192.2. Genta MS, Genta RM, Gabay C. Systemic rheumatoid vasculitis: a review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2006; 36:88–98.3. Makol A, Crowson CS, Wetter DA, Sokumbi O, Matteson EL, Warrington KJ. Vasculitis associated with rheumatoid arthritis: a case-control study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014; 53:890–899.4. Scott DG, Bacon PA. Systemic rheumatoid vasculitis: a clinical and laboratory study of 50 cases. Medicine (Baltimore). 1981; 60:288–297.5. Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO 3rd, Birnbaum NS, Burmester GR, Bykerk VP, Cohen MD, et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010; 69:1580–1588.6. Parker B, Chattopadhyay C. A case of rheumatoid vasculitis involving the gastrointestinal tract in early disease. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007; 46:1737–1738.7. Sandhu SK, Choy G. Vasculitis of the gallbladder in early rheumatoid arthritis. BMJ Case Rep. 2013; 2013:bcr2012008228.8. Voskuyl AE, van Duinen SG, Zwinderman AH, Breedveld FC, Hazes JM. The diagnostic value of perivascular infiltrates in muscle biopsy specimens for the assessment of rheumatoid vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1998; 57:114–117.9. Scott DG, Bacon PA, Tribe CR. Systemic rheumatoid vasculitis: a clinical and laboratory study of 50 cases. Medicine (Baltimore). 1981; 60:288–297.10. Matsumoto T, Kobayashi S, Shimizu H, Nakajima M, Watanabe S, Kitami N, Sato N, Abe H, Aoki Y, Hoshi T, et al. The liver in collagen diseases: pathologic study of 160 cases with particular reference to hepatic arteritis, primary biliary cirrhosis, autoimmune hepatitis and nodular regenerative hyperplasia of the liver. Liver. 2000; 20:366–373.11. Pagnoux C, Mahr A, Cohen P, Guillevin L. Presentation and outcome of gastrointestinal involvement in systemic necrotizing vasculitides: analysis of 62 patients with polyarteritis nodosa, microscopic polyangiitis, Wegener granulomatosis, Churg-Strauss syndrome, or rheumatoid arthritis-associated vasculitis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2005; 84:115–128.12. Scott DG, Bacon PA. Intravenous cyclophosphamide plus methylprednisolone in treatment of systemic rheumatoid vasculitis. Am J Med. 1984; 76:377–384.13. Ntatsaki E, Mooney J, Scott DG, Watts RA. Systemic rheumatoid vasculitis in the era of modern immunosuppressive therapy. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014; 53:145–152.14. Puéchal X, Gottenberg JE, Berthelot JM, Gossec L, Meyer O, Morel J, Wendling D, de Bandt M, Houvenagel E, Jamard B, et al. Rituximab therapy for systemic vasculitis associated with rheumatoid arthritis: results from the Autoimmunity and Rituximab Registry. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012; 64:331–339.15. Radić M, Martinović Kaliterna D, Radić J. Drug-induced vasculitis: a clinical and pathological review. Neth J Med. 2012; 70:12–17.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Acute Myocardial Infarction and Multiorgan Involvement Secondary to Rheumatoid Vasculitis
- A Case of Rheumatoid Vasculitis
- A Case of Rheumatoid Neutrophilic Dermatitis
- Clinical significance of rheumatoid factor in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
- Rheumatoid vasculitis manifesting as ischemic colitis