Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2017 May;21(2):67-75. 10.14701/ahbps.2017.21.2.67.
Mirizzi syndrome: a new insight provided by a novel classification
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Hospital Doctor Peset, Valencia, Spain. carmenpayallorente@gmail.com
- KMID: 2379103
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2017.21.2.67
Abstract
- BACKGROUNDS/AIMS
Mirizzi syndrome (MS) is an uncommon complication of cholelithiasis. The aim of this study is to evaluate our 15-year experience in this challenging entity and to propose a new classification for this disease.
METHODS
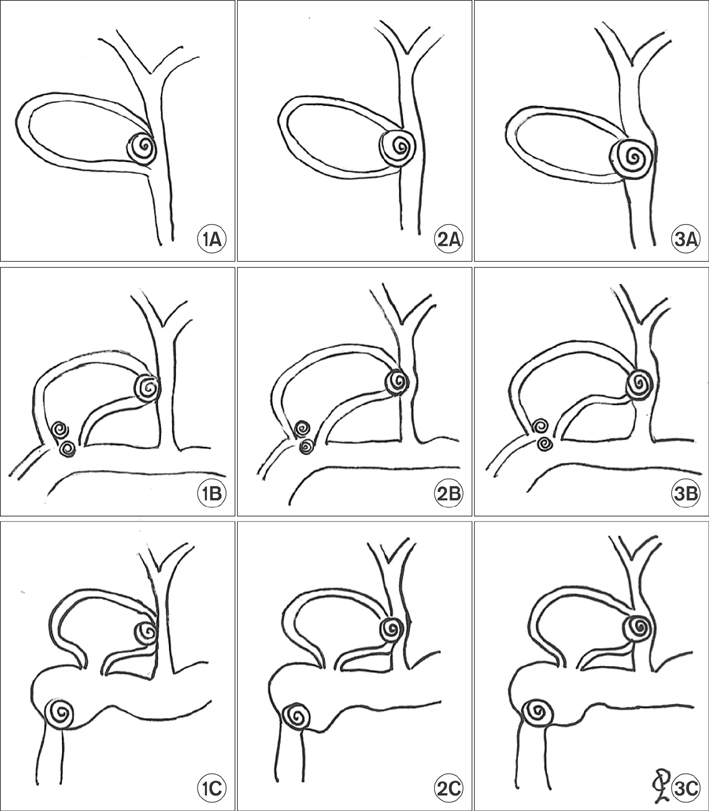
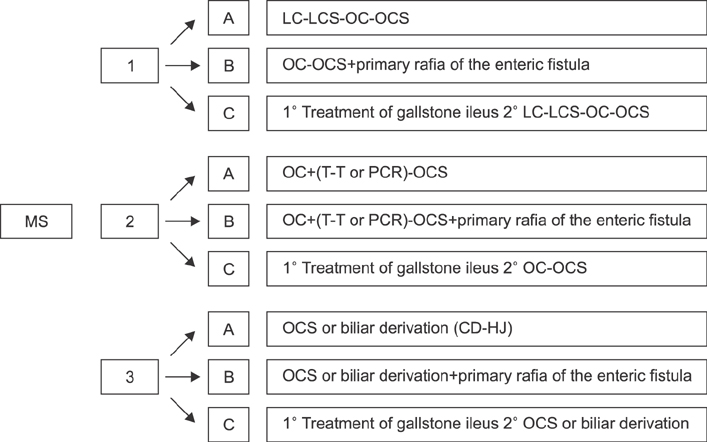
A retrospective study including patients diagnosed with Mirizzi syndrome and undergoing surgical procedures for Mirizzi syndrome between January 2000 and October 2015 was conducted. Data collected included clinical, surgical procedure, postoperative morbidity. Patients were evaluated according to the Csendes classification and the proposed system, in which patients were divided into three types and three subtypes.
RESULTS
28 patients were included for analysis. They accounted as the 0.5% of a total of 4853 cholecystectomies performed in the study period. There were 21 women and 7 men. Initial laparotomic approach was performed in 12 patients and in 16 patients laparoscopic procedures were attempted. The procedure was completed in only 6 patients, 5 presenting type I and 1 type II Mirizzi syndrome. Mean postoperative stay was 15±9 days. Postoperative morbidity rate was 28%. Postoperative mortality was none.
CONCLUSIONS
Laparoscopic surgery for Mirizzi syndrome has been shown succesful only in early stages. A novel classification is proposed, based on the types of common bile duct injuries and in the presence cholecystoenteric fistula.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kehr H. Die in neiner klinik geubte technik de gallenstein operationen, mit einen hinweis auf die indikationen und die dauerersolge. Munchen: JF Lehman;1905.2. Ruge E. Deitrage zur chirurgischen anatomie der grossen galenwege (Ductus hepaticus, choledochus, und pancreaticus). Arch Clin Chir. 1908; 78:47.3. Abou-Saif A, Al-Kawas FH. Complications of gallstone disease: Mirizzi syndrome, cholecystocholedochal fistula, and gallstone ileus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002; 97:249–254.4. Mirizzi PL. Physiologic sphincter of the hepatic bile duct. Arch Surg. 1940; 41:1325–1333.5. Mirizzi PL. Sindrome del conducto hepatico. J Int Chir. 1948; 8:731–777.6. Pemberton M, Wells AD. The Mirizzi syndrome. Postgrad Med J. 1997; 73:487–490.7. Dorrance HR, Lingam MK, Hair A, Oien K, O'Dwyer PJ. Acquired abnormalities of the biliary tract from chronic gallstone disease. J Am Coll Surg. 1999; 189:269–273.8. Beltran MA, Csendes A, Cruces KS. The relationship of Mirizzi syndrome and cholecystoenteric fistula: validation of a modified classification. World J Surg. 2008; 32:2237–2243.9. Zhong H, Gong JP. Mirizzi syndrome: experience in diagnosis and treatment of 25 cases. Am Surg. 2012; 78:61–65.10. McSherry CK, Ferstenberg H, Virshup M. The Mirizzi syndrome: suggested classification and surgical therapy. Surg Gastroenterol. 1982; 1:219–225.11. Csendes A, Díaz JC, Burdiles P, Maluenda F, Nava O. Mirizzi syndrome and cholecystobiliary fistula: a unifying classification. Br J Surg. 1989; 76:1139–1143.12. Beltran MA, Csendes A. Mirizzi syndrome and gallstone ileus: an unusual presentation of gallstone disease. J Gastrointest Surg. 2005; 9:686–689.13. Csendes A, Muñoz C, Albán M. Síndrome de Mirizzi-Fístula colecistobiliar, una nueva clasificación. Rev Chil Cir. 2007; 59:63–64.14. Beltrán MA. Mirizzi syndrome: history, current knowledge and proposal of a simplified classification. World J Gastroenterol. 2012; 18:4639–4650.15. Solis-Caxaj CA. Mirizzi syndrome: diagnosis, treatment and a plea for a simplified classification. World J Surg. 2009; 33:1783–1784.16. Lai EC, Lau WY. Mirizzi syndrome: history, present and future development. ANZ J Surg. 2006; 76:251–257.17. Baer HU, Matthews JB, Schweizer WP, Gertsch P, Blumgart LH. Management of the Mirizzi syndrome and the surgical implications of cholecystcholedochal fistula. Br J Surg. 1990; 77:743–745.18. Erben Y, Benavente-Chenhalls LA, Donohue JM, Que FG, Kendrick ML, Reid-Lombardo KM, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of Mirizzi syndrome: 23-year Mayo Clinic experience. J Am Coll Surg. 2011; 213:114–119.19. Antoniou SA, Antoniou GA, Makridis C. Laparoscopic treatment of Mirizzi syndrome: a systematic review. Surg Endosc. 2010; 24:33–39.20. Clavien PA, Sanabria JR, Strasberg SM. Proposed classification of complications of surgery with examples of utility in cholecystectomy. Surgery. 1992; 111:518–526.21. Zaliekas J, Munson JL. Complications of gallstones: the Mirizzi syndrome, gallstone ileus, gallstone pancreatitis, complications of “lost” gallstones. Surg Clin North Am. 2008; 88:1345–1368.22. Cui Y, Liu Y, Li Z, Zhao E, Zhang H, Cui N. Appraisal of diagnosis and surgical approach for Mirizzi syndrome. ANZ J Surg. 2012; 82:708–713.23. Cornud F, Grenier P, Belghiti J, Breil P, Nahum H. Mirizzi syndrome and biliobiliary fistulas: roentgenologic appearance. Gastrointest Radiol. 1981; 6:265–268.24. Choi BW, Kim MJ, Chung JJ, Chung JB, Yoo HS, Lee JT. Radiologic findings of Mirizzi syndrome with emphasis on MRI. Yonsei Med J. 2000; 41:144–146.25. Ravo B, Epstein H, La Mendola S, Ger R. The Mirizzi syndrome: preoperative diagnosis by sonography and transhepatic cholangiography. Am J Gastroenterol. 1986; 81:688–690.26. Cruz FO, Barriga P, Tocornal J, Burhenne HJ. Radiology of the Mirizzi syndrome: diagnostic importance of the transhepatic cholangiogram. Gastrointest Radiol. 1983; 8:249–253.27. Safioleas M, Stamatakos M, Safioleas P, Smyrnis A, Revenas C, Safioleas C. Mirizzi syndrome: an unexpected problem of cholelithiasis. Our experience with 27 cases. Int Semin Surg Oncol. 2008; 5:12.28. Yonetci N, Kutluana U, Yilmaz M, Sungurtekin U, Tekin K. The incidence of Mirizzi syndrome in patients undergoing endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2008; 7:520–524.29. Tan KY, Chng HC, Chen CY, Tan SM, Poh BK, Hoe MN. Mirizzi syndrome: noteworthy aspects of a retrospective study in one centre. ANZ J Surg. 2004; 74:833–837.30. Lledó JB, Barber SM, Ibañez JC, Torregrosa AG, Lopez-Andujar R. Update on the diagnosis and treatment of mirizzi syndrome in laparoscopic era: our experience in 7 years. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2014; 24:495–501.31. Shah OJ, Dar MA, Wani MA, Wani NA. Management of Mirizzi syndrome: a new surgical approach. ANZ J Surg. 2001; 71:423–427.32. Estellés Vidagany N, Domingo Del Pozo C, Peris Tomás N, Díez Ares JÁ, Vázquez Tarragón A, Blanes Masson F. Eleven years of primary closure of common bile duct after choledochotomy for choledocholithiasis. Surg Endosc. 2016; 30:1975–1982.33. Redaelli CA, Büchler MW, Schilling MK, Krähenbühl L, Ruchti C, Blumgart LH, et al. High coincidence of Mirizzi syndrome and gallbladder carcinoma. Surgery. 1997; 121:58–63.34. Aydin U, Yazici P, Ozsan I, Ersõz G, Ozütemiz O, Zeytunlu M, et al. Surgical management of Mirizzi syndrome. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2008; 19:258–263.35. Kwon AH, Inui H. Preoperative diagnosis and efficacy of laparoscopic procedures in the treatment of Mirizzi syndrome. J Am Coll Surg. 2007; 204:409–415.36. Kamalesh NP, Prakash K, Pramil K, George TD, Sylesh A, Shaji P. Laparoscopic approach is safe and effective in the management of Mirizzi syndrome. J Minim Access Surg. 2015; 11:246–250.37. Xu XQ, Hong T, Li BL, Liu W, He XD, Zheng CJ. Mirizzi syndrome: our experience with 27 cases in PUMC hospital. Chin Med Sci J. 2013; 28:172–177.38. Chowbey PK, Sharma A, Mann V, Khullar R, Baijal M, Vashistha A. The management of Mirizzi syndrome in the laparoscopic era. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2000; 10:11–14.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Mirizzi syndrome: one case report
- Laparoscopic management of Mirizzi syndrome with liver cirrhosis using indocyanine green mapping: A case report and review of the literature
- Mirizzi Syndrome-Diagnostic Dilemma for Surgeons
- Laparoscopic treatment for post-cholecystectomy Mirizzi syndrome
- Two Cases of the Endoscopic Treatment of Type I Mirizzi Syndrome