Korean J Adult Nurs.
2017 Apr;29(2):166-176. 10.7475/kjan.2017.29.2.166.
Differences between Nurses and Patients' Perception of Nurses' Communication Skills
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Nursing, Eulji University, Daejeon, Korea. sagaciouspark@naver.com
- KMID: 2378870
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7475/kjan.2017.29.2.166
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The study aimed to assess differences between nurses' and patients' perception of the communication skills to promote patients' health literacy in a hospital.
METHODS
The convenience sample consisted of 150 patients and 169 nurses in a university hospital. The data were collected from January to February 2014 using the Communication Skills Scale for Hospital nurses and patients. Descriptive statistics, independent t-test, ANOVA, Kruskal-Wallis test, and Lin's concordance were used to analyze the data.
RESULTS
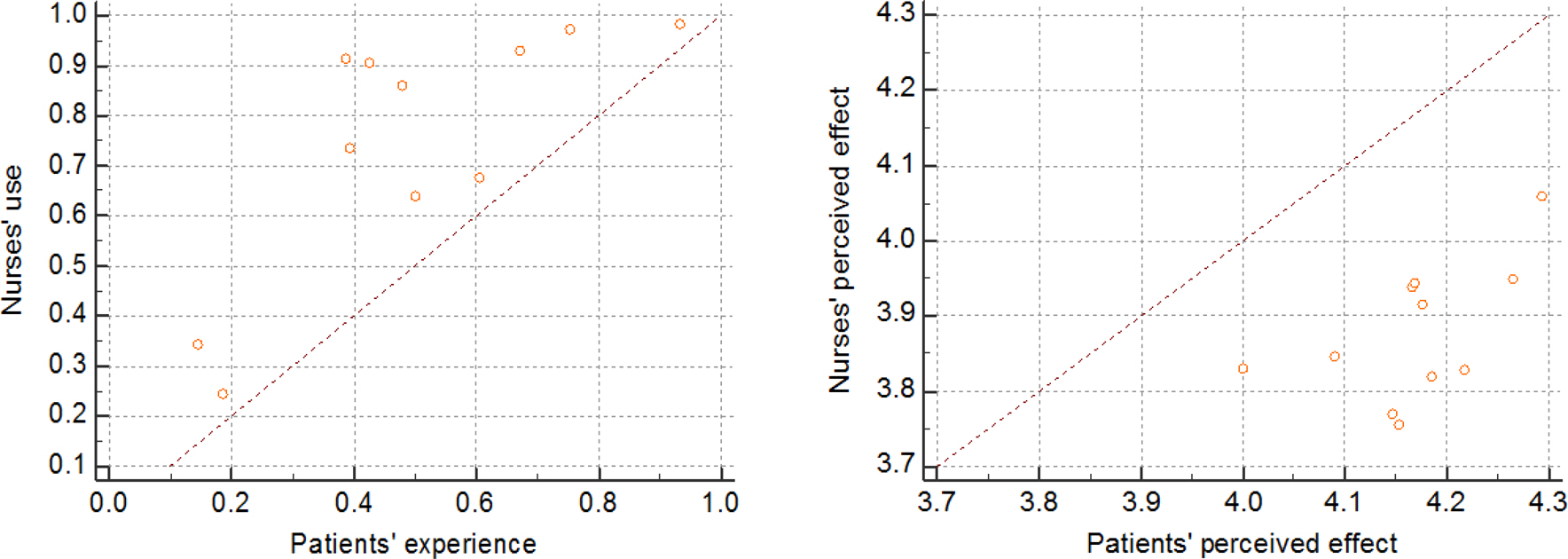
There were significant differences (t=9.44, p<.001) between the perception of nurses (8.18±2.00) and patients (5.49±2.95) on the communication skills used by nurses. Most nurses (3.87±0.39) perceived that the communication skills were effective, but more patients (4.13±0.62) reported significantly higher scores (t=−4.34, p<.001).
CONCLUSION
The results implied that nurses need to make sure that their communication skills are effective when they communicate with patients, and education programs for nurses to develop the advanced communication skills would be necessary.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Development of the Patient Caring Communication Scale
Myoung Lyun Heo, Sook Bin Im
J Korean Acad Nurs. 2019;49(1):80-91. doi: 10.4040/jkan.2019.49.1.80.
Reference
-
1. Kourkouta L, Papathanasiou IV. Communication in nursing practice. Materia Socio-Medica. 2014; 26(1):65–7. https://doi.org/10.5455/msm.2014.26.65-67.
Article2. McCabe C. Nurse-patient communication: an exploration of patients' experiences. Journal of Clinical Nursing. 2004; 13(1):41–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2702.2004.00817.x.
Article3. Bosworth HB. Challenges and strategies to improve patient health literacy and competencies. Patient Intelligence. 2010; 2:19–25. https://doi.org/10.2147/pi.s9491.
Article4. Webb L. Introduction to communication skills. Webb L, editor. Nursing: communication skills in practice. Oxford: Oxford University Press;2011. p. 3–19.5. Ahn JH. Communication and human relations. Cogito. 1989; 34:163–88.6. Macabasco-O'Connell A, Fry-Bowers EK. Knowledge and perceptions of health literacy among nursing professionals. Journal of Health Communication. 2011; 16(suppl 3):295–307. https://doi.org/10.1080/10810730.2011.604389.7. Schlichting JA, Quinn MT, Heuer LJ, Schaefer CT, Drum ML, Chin MH. Provider perceptions of limited health literacy in community health centers. Patient Education and Counseling. 2007; 69(1):114–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pec.2007.08.003.
Article8. Ahn S. Breast cancer patients' treatment decisions and communication experiences. Korean Journal of Health Communication. 2007; 2(2):146–54.9. Schwartzberg JG, Cowett A, VanGeest J, Wolf MS. Communication techniques for patients with low health literacy: a survey of physicians, nurses, and pharmacists. American Journal of Health Behavior. 2007; 31(Supplement 1):S96–S104. https://doi.org/10.5993/ajhb.31.s1.12.
Article10. Hong IH, Eun Y. Health literacy of inpatients at general hospital. Korean Journal of Adult Nursing. 2012; 24(5):477–88. https://doi.org/10.7475/kjan.2012.24.5.477.
Article11. Williams MV, Davis T, Parker RM, Weiss BD. The role of health literacy in patient-physician communication. Family Medicine. 2002; 34(5):383–9.12. Barrett SE, Puryear JS, Westpheling K. Health literacy practi-ces in primary care settings: examples from the field. New York: Commonwealth Fund;2008. p. 1–36.13. Jeong SY. Satisfaction of patients by nurse's communication styles. Korean Journal of Health Communication. 2013; 8(1):35–44.14. Park KI, Jeong YS. Nurse's communication skills as perceived by the parents of inpatients. Korean Parent Child Health Journal. 2011; 14(2):69–75.15. Yudkowsky R, Downing SM, Sandlow LJ. Developing an in-stitution-based assessment of resident communication and interpersonal skills. Academic Medicine. 2006; 81(12):1115–22. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.acm.0000246752.00689.bf.
Article16. Kim YJ, Lee GE. Evaluation of readability of health leaflets and health literacy of elderly inpatients in a medical center. Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing. 2014; 16(1):9–17. https://doi.org/10.17079/jkgn.2014.16.1.9.17. Jung EY, Hwang SK. Health literacy and health behavior compliance in patients with coronary artery disease. Korean Journal of Adult Nursing. 2015; 27(3):251–61. https://doi.org/10.7475/kjan.2015.27.3.251.
Article18. Son YJ, Song EK. Impact of health literacy on disease-related knowledge and adherence to self-care in patients with hyper-tension. Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing. 2012; 19(1):6–15. https://doi.org/10.7739/jkafn.2012.19.1.006.
Article19. Kim SH, Lee E. The influence of functional literacy on perceived health status in korean older adults. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2008; 38(2):195–203. https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.2.195.
Article20. Yang JR. The effect of health literacy and self-efficacy on medi-cation adherence among the elderly patients with chronic diseases. Nursing Science. 2014; 26(1):29–38.21. Safeer RS, Keenan J. Health literacy: the gap between physicians and patients. American Family Physician. 2005; 72(3):463–8.22. Dickens C, Lambert BL, Cromwell T, Piano MR. Nurse over-estimation of patients' health literacy. Journal of Health Communication. 2013; 18(sup1):62–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/10810730.2013.825670.
Article23. Cornett S. Assessing and addressing health literacy. Online Journal of Issues in Nursing. 2009; 14(3):Manuscript 2.
Article24. Lee EO, Lim NY, Park HA, Lee IS, Kim JI, Bae JE, et al. Nursing Research & Statistics. Seoul: SuMoonSa;2009. p. 203–5.25. Millis SR, Jain SS, Eyles M, Tulsky D, Nadler SF, Foye PM, et al. Assessing physicians' interpersonal skill: do patients and physicians see eye-to-eye? American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation. 2002; 81(12):946–51. https://doi.org/10.1097/00002060-200212000-00011.26. Turner T, Cull WL, Bayldon B, Klass P, Sanders LM, Frintner MP, et al. Pediatricians and health literacy: descriptive results from a national survey. Pediatrics. 2009; 124(Sup3):S299–S305. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2009-1162f.
Article27. Koo LW, Horowitz AM, Radice SD, Wang MQ, Kleinman DV. Nurse practitioners' use of communication techniques: results of a Maryland Oral Health Literacy Survey. PLoS One. 2016; 11(1):e0146545. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0146545.
Article28. Jager AJ, Wynia MK. Who gets a teach-back? Patient-reported incidence of experiencing a teach-back. Journal of Health Communication. 2012; 17(sup3):294–302. https://doi.org/10.1080/10810730.2012.712624.
Article29. Johnson A. Health literacy: how nurses can make a difference. Australian Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2015; 33(2):20–7.30. Sheridan S, Halpern D, Viera A, Berkman N, Donahue K, Crotty K. Interventions for individuals with low health literacy: a systematic review. Journal of Health Communication. 2011; 16:30–54. https://doi.org/10.1080/10810730.2011.604391.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current domestic research trends on nurses’ communication programs
- Effect of SBAR-Collaborative Communication Program on the Nurses' Communication skills and the Collaboration between Nurses and Doctors
- The Effects of Humanistic Knowledge and Emotional Intelligence on Communication Skills of Nurses
- Influence of Emergency Department Nurses' Grit, Self-Leadership, and Communication on Their Triage Competencies: A Descriptive Survey Study
- Effects of Emotional Intelligence on Job Satisfaction of Pediatric Nurses: The Mediating Effect of Communication Skills and Pediatric Nurse-Parent Partnership